* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Ocean floor Foldable Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
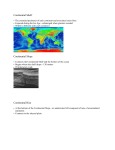
The Ocean Floor Continental slope Continental Shelf Volcanic island Seamount Continental Abyssal plain rise mid-ocean ridge Continental slope Rift valley Continental shelf trench The Ocean Floor Oceanography: The study of Earth’s oceans. 1. Continental Margin 6. Abyssal Plain 2. Deep-Ocean Basin 7. Rift Valley 3. Continental Shelf 8. Mid-Ocean Ridges 4. Continental Slope 9. Ocean Trench 5. Continental Rise 10. Seamount 1. Continental Margin Made of continental crust and consists of the continental shelf, the continental slope, and the continental rise. Deep-Ocean Basin The deep-ocean basin is made of oceanic crust and consists of the abyssal plain, mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, and ocean trenches. 3. Continental Shelf • The gently sloping section of the continental margin located between the shoreline and the continental slope. • The depth of continental shelf can reach 200m. 3. Continental Shelf • Some shelves stretch farther out into the ocean than others. • The topography of a shelf is very flat and the width varies. • The Atlantic shelf is much wider than the Pacific • NOT PART OF THE OCEAN FLOOR 4. Continental Slope • The steeply inclined section of the continental margin located between the continental rise and the continental shelf. 4. Continental Slope • The continental slope begins at the shelf edge. • The steep gradient that leads to the deep ocean floor and marks the seaward edge of the continental shelf. • slopes steeply from the continental shelf • Depth ranges from about 200m to about 4000m. 5. Continental Rise H • The gently sloping section of the continental margin located between the continental slope and the abyssal plain. 5. Continental Rise • The continental rise is the base of the continental slope, and is made of large piles of sediment. • Marks the boundary between the continental margin and the deep-ocean basin. • The deep-ocean basin lies underneath the continental rise. 6. Abyssal Plain • The abyssal plain is the broad flat part of the deep ocean basin. • Covered by mud and the remains of tiny marine organisms. • Average depth is about 4,000m • Flattest places on Earth. 7. Rift Valleys • A rift valley is a long narrow valley that forms as tectonic plates separate. 8. The Mid-Ocean Ridge System • A long chain of undersea mountains that form along the floor of the major oceans. • Form where tectonic plates pull apart. • The heat from rising magma that fills the rift valley causes the crust on either side of the rift valley to expand which forms the ridges. 9. Ocean Trenches • Ocean trenches are cracks in the deepocean basin. • Form where one oceanic plate is pushed beneath a continental plate or another oceanic plate • Usually near a continental margin or volcanic island chain 10. Seamounts • Seamounts are individual mountains of volcanic material. • They form where magma pushes itself through or between tectonic plates. • If a seamount builds up above sea level it becomes a volcanic island. 10. Seamount and Island Chains • A submerged mountain on the ocean floor that is at least 1000m high and made of volcanic material. • Hawaiian Islands are the best example.