* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint 演示文稿
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
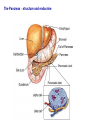
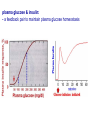
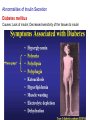
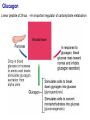
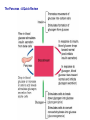
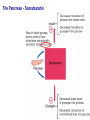
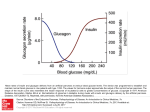
The Pancreas – structure and endocrine Pancreatic Islet Types of cells – β cells: 60% • Insulin – α cells: 25% • Glucagon – δ cells: 10% • Somatostatin – F cells • Pancreatic polypeptide Insulin A small protein – molecular weight 5808 – 2 amino acid chains, connected by S-S bonds A chain - 21 aa B chain - 30 aa Major Targets of Insulin - liver, muscle, adipose tissue Glucose – stimulates glucose oxidation and glycolysis – increases glucose storage (glycogenesis ↑, glycogenolysis ↓) – inhibits gluconeogenesis (uptake of aa in liver ↓) brain utilization of glucose is independent of insulin ! →Plasma glucose↓ Lipid – promotes deposition of circulating lipid in the adipose tissue – inhibits lipolysis via suppressing hormone-sensitive lipase Protein – promotes protein formation – inhibits proteolysis – contributes to body growth Major response of target cells to insulin – Negative feed-back by glucose – Amino acids (proteins), Free fatty acids, Hormones (GH, cortisol, adrenaline, glucagon) – Neural control: parasympathetic (stimulates), sympathetic (inhibits) plasma glucose & insulin: - a feedback pair to maintain plasma glucose homeostasis Abnormalities of Insulin Secretion Diabetes mellitus Causes: Lack of insulin; Decreased sensitivity of the tissues to insulin Type II Diabetes Mellitus A Quick Review Glucagon Linear peptide of 29 aa. - An important regulator of carbohydrate metabolism Action of Glucagon The major site of action is liver – glycogenolysis↑ – gluconeogenesis ↑ – ketogenesis ↑ – proteolysis and urea production ↑ Lipolytic effect in adipose tissue (activates lipase) Glucagon has minimal effect on skeletal muscle in the presence of insulin Regulation of glucagon secretion Negative feed-back (glucose suppresses) Amino-acids (gluconeogenesis, e.g. after protein rich meals – prevent hypoglycaemia) Exercise Insulin and glucagon are critical participants in glucose homeostasis and serve as acute regulators of blood glucose concentration Glucose is the primary fuel source for the brain, retina, and some cells in the gonads The Pancreas - A Quick Review The Pancreas - Somatostatin Qs: Terms: Thyroid Hormones, Glucocorticoid, Stress, Insulin List the main physiological actions of thyroid hormones Describe the mechanisms that regulate secretion of glucocorticoids Summarize the homeostatic mechanisms that combat hypoglycemia What are the endocrinologic causes of dwarfism and cretinism? how does each lead to short stature? What are the advantages and disadvantages of long-term, high dose treatment with glucocorticoids in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and asthma? What problems occur when steroid treatment is stopped suddenly?