* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download upper limb - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
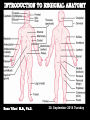
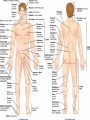
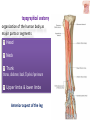
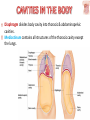
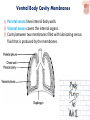
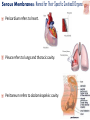
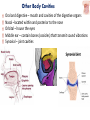
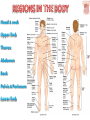
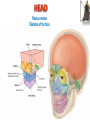
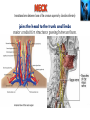
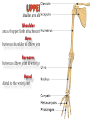
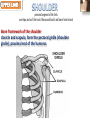
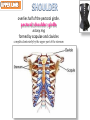
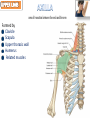
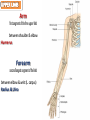
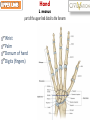
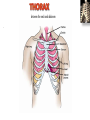
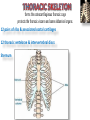
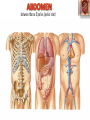
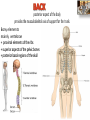
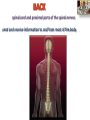
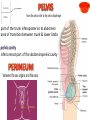
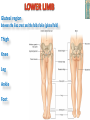
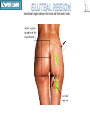
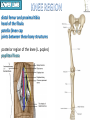
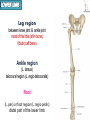
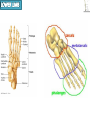
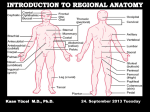
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs & lower limbs Anterior aspect of the leg Diaphragm divides body cavity into thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities. Mediastinum contains all structures of the thoracic cavity except the lungs. Ventral Body Cavity Membranes Parietal serosa lines internal body walls. Visceral serosa covers the internal organs. Cavity between two membranes filled with lubricating serous fluid that is produced by the membranes. Serous Membranes: Named for Their Specific Cavities& Organs Pericardium refers to heart. Pleura refers to lungs and thoracic cavity. Peritoneum refers to abdominopelvic cavity. Other Body Cavities Oral and digestive – mouth and cavities of the digestive organs Nasal –located within and posterior to the nose Orbital – house the eyes Middle ear – contain bones (ossicles) that transmit sound vibrations Synovial – joint cavities Head & neck Upper limb Thorax Abdomen Back Pelvis & Perineum Lower limb Neurocranium Skeleton of the face transitional area between base of the cranium superiorly clavicles inferiorly joins the head to the trunk and limbs major conduit for structures passing between them. several important organs with unique functions located here shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist, and hand Shoulder area of upper limb attachment to trunk Arm between shoulder & elbow joint Forearm between elbow joint & wrist joint Hand distal to the wrist joint proximal segment of the limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck Bone framework of the shoulder clavicle and scapula, form the pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle); proximal end of the humerus overlies half of the pectoral girdle. pectoral (shoulder) girdle a bony ring formed by scapulae and clavicles completed anteriorly by the upper part of the sternum area of transition between the neck and the arm Formed by Clavicle Scapula Upper thoracic wall Humerus Related muscles Arm first segment of the free upper limb between shoulder & elbow Humerus Forearm second longest segment of the limb between elbow & wrist (L. carpus) Radius & Ulna Hand L. manus part of the upper limb distal to the forearm Wrist Palm Dorsum of hand Digits (fingers) between the neck and abdomen . forms the osteocartilaginous thoracic cage protects the thoracic viscera and some abdominal organs. 12 pairs of ribs & associated costal cartilages 12 thoracic vertebrae & intervertebral discs Sternum between thorax & pelvis (pelvic inlet) organs of the alimentary system and part of the urogenital system Containment of the abdominal organs and their contents provided by musculoaponeurotic walls anterolaterally, diaphragm superiorly, muscles of the pelvis inferiorly posterior aspect of the body provides the musculoskeletal axis of support for the trunk. Bony elements mainly vertebrae + proximal elements of the ribs + superior aspects of the pelvic bones + posterior basal regions of the skull spinal cord and proximal parts of the spinal nerves send and receive information to and from most of the body. from the pelvic inlet to the pelvic diaphragm part of the trunk inferoposterior to abdomen area of transition between trunk & lower limbs pelvic cavity inferiormost part of the abdominopelvic cavity between the sex organs and the anus Pelvis surrounded by the pelvic girdle (bony pelvis) formed by three bones Right and left hip bones (coxal bones; pelvic bones) fusion of three bones, the ilium, ischium, and pubis Sacrum connects the vertebral column to the two femora Gluteal region between the iliac crest and the fold of skin (gluteal fold) Thigh Knee Leg Ankle Foot transitional region between the trunk and free lower limbs between gluteal, abdominal, and perineal regions proximally knee region distally most of the femur (thigh bone) distal femur and proximal tibia head of the fibula patella (knee cap joints between these bony structures posterior region of the knee (L. poples) popliteal fossa Leg region between knee joint & ankle joint most of the tibia (shin bone) fibula (calf bone) Ankle region (L. tarsus) talocrural region (L. regio talocruralis) Foot (L. pes) or foot region (L. regio pedis) distal part of the lower limb