* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cm16_9
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Lagrangian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chaos wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Analytical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Mechanics of planar particle motion wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
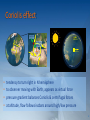
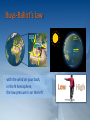
Classical Mechanics PHYS 2006 Tim Freegarde Classical Mechanics LINEAR MOTION OF SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES centre of mass Newton’s 2nd law for bodies (internal forces cancel) rocket motion rotations and infinitessimal rotations ANGULAR MOTION angular velocity vector, angular momentum, torque parallel and perpendicular axis theorems rigid body rotation, moment of inertia, precession conservative forces, law of universal gravitation GRAVITATION & KEPLER’S LAWS 2-body problem, reduced mass planetary orbits, Kepler’s laws energy, effective potential NON-INERTIAL REFERENCE FRAMES NORMAL MODES centrifugal and Coriolis terms Foucault’s pendulum, weather patterns coupled oscillators, normal modes boundary conditions, Eigenfrequencies 2 Rotating coordinate systems • local coordinates not an inertial frame • ‘ficticious’ forces: • centrifugal • Coriolis 3 Rotating coordinate systems 4 Rotating coordinate systems xkcd.com 5 Coriolis effect H Coriolis 300 m s-1 L • • • • pressure gradient L 460 m s-1 tendency to turn right in N hemisphere to observer moving with Earth, appears as virtual force pressure gradient balances Coriolis & centrifugal forces at altitude, flow follows isobars around high/low pressure 6 Buys-Ballot’s law H Coriolis 300 m s-1 L pressure gradient L • with the wind on your back, in the N hemisphere, the low pressure is on the left 460 m s-1 Low High 7 Geostrophic wind GEOSTROPHIC WIND • closer isobars → higher Coriolis force → stronger wind • isobars: pressure contours (4 hPa) • cold/warm fronts divide air masses 8