* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MON-APR-4
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
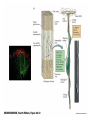
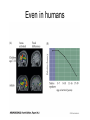
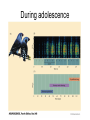
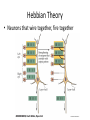
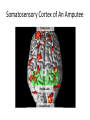
Modification of Neural Circuits with Experience Experience gained… • In utero • Development • Adulthood – By experience, we mean changes in the chemical and external environments – Really hot research area (epigenetics) Changes to Neuron Diversity in Utero • Cellular Interaction Model – Neuron diversity reliant on the extent and type of intracellular signaling – These signaling cascades are sensitive to changes in pH, calcium levels, and other molecular factors that could be modified by environmental stressors – This, in turn, can influence where these neurons migrate to in the cortex , for example Imprinting After Birth Even in humans During adolescence The Importance of Time During Development The Importance of Length During the Critical Period Whole System Changes During the Critical Period Complementary Changes in Neuronal Architecture Hebbian Theory • Neurons that wire together, fire together Somatosensory Cortex of An Amputee Genetic Changes Due to Environmental Stressors (Epigenetics) • affects DNA transcription and translation which can have a HUGE impact on neuron function • How? adding of DNA methyl groups, preventing or enabling unwinding of DNA around chromatin, to name a few • Hugely popular in psychiatric research Optional Reading • From my blog “Dormivigilia” – www.dormivigilia.com • Basic review of epigenetic factors and the effects of early-life stress on subsequent development and social relationships