* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.4 Particle interactions
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Feynman diagram wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
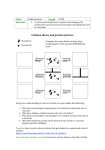
2.4Particleinteractions Particlesinteractthroughthefourfundamentalforces–theelectrostaticforce, thestrongnuclearforce,theweaknuclearforceandgravitationalforce. • Allparticleswithchargefeeltheelectromagneticforce. • Allparticleswithmassfeelthegravitationalforce. • Onlyparticlescontainingquarksexperiencethestrongnuclearforce. • Bothhadronsandleptonsfeeltheweaknuclearforce. AfamousAmericanphysicist,RichardFeynmansuggestedthattheinteractionis achievedbytheparticlesexchanging‘virtualparticles’.Inthecaseofcharged particles(e.g.proton-proton),theelectrostaticforceexperiencedbytheparticles comesfromaninteractionachievedbytheexchangeof‘virtualphotons’. Feynmancameupwithavisualwayofdescribingtheseinteractions.Theyare calledFeynmandiagrams. BelowisaFeynmandiagramshowingtheelectrostaticinteractionbetweentwo protons. p p time γ p p space Thesediagramsshouldbereadfrombottomtotop.Thisshowstheeventsas timeprogresses.Wecanseefromtheexampleabovethattwoprotonsmove towardseachother,exchangeavirtualgamma(γ)photonandthenmoveapart. (theyrepeleachother).Thewavylinerepresentstheexchangeofavirtual gammaphoton. Amodelforexchange Belowisamodeltopicturehowexchangeofvirtualparticlesresultsinaforceon twointeractingparticles. SkaterAthrowsaheavyball toskaterB.SkaterA experiencesaforcetotheleft. Oncatching,skaterB experiencesaforcetothe right. B A ©2016flippedaroundphysics.com (1)!UsingNewton’sthirdlaw,explainwhyAmovestotheleftonthrowingthe ball. (2)!UsingNewton’sthirdlaw,explainwhyBmovestotherightoncatchingthe ball. (3)!Explainhowthemomentumofthesystem(containingtwoskaters)is conserved. Theseconddiagrammodelstheeffectofattractionbetweenparticles(e.g. electrostaticinteractionbetweentheelectronandproton).PersonAthrowsa boomerangtotheleft,whichpushesthemtotheright.PersonBcatchesthe boomerang,whichmovesthemtotheleft.Theoveralleffectisattractive. B A Thestrongnuclearforce Thestrongnuclearforceactsbetweenallparticlescontainingquarks,whichare constituentsofparticles(neutronsandprotons)inthenucleus.Itactsovera veryshortrange.Theexchangeparticleforthestrongnuclearforceisthepion. (4)!Overwhatrangeisthestrongnuclearforceattractive? Gravitationalforce Theexchangeparticleforthegravitationalforceisthegraviton.Thesehaven’t beendetectedyet. Theweaknuclearforce ©2016flippedaroundphysics.com Theweaknuclearforceisresponsibleforinteractionswhichresultinchangesto theparticlesinvolved.Wbosonsaretheexchangeparticlesfortheweaknuclear force. Consideraninteractionbetweenanelectronneutrino(𝜐" )andaneutron(n). (Suchinteractionsareextremelyrare.) 𝑛 + 𝜈" 𝑝 + 𝛽 ( Wecanseethattheelectronneutrinointeractswiththeneutrontoproducea proton(p)andabetaminusparticle(𝛽 ( ).TheFeynmandiagramforthis interactionisshownbelow: Note:Itisagoodidea todrawanarrowto 𝛽( p showthedirectionthe exchangeparticle moves.Inthiscase,we couldsubstitutea𝑊 * ( 𝑊 bosonmovinginthe 𝜐" oppositedirection. n WecanseetheWminusexchangeparticle(𝑊 ( )isinvolvedinchanginga neutronintoaproton.Notethatthechargeisconserved–theoverallchargeis zerobeforeandaftertheinteraction. (5)!Ananti-electronneutrino(𝜐" )canalso(rarely)interactwithaproton, producinganeutronandabetaplus(𝛽 * )particle.A𝑊 * bosonistheexchange particle.DrawaFeynmandiagramforthisinteraction. ©2016flippedaroundphysics.com Theweaknuclearforceisresponsibleforchangeswhichoccurtonucleons duringbetadecay.Forexample,inbetaminusdecayaneutrondecaystoa protonandemitsabetaminusparticleandananti-electronneutrino: 𝑛 𝑝 + 𝛽 ( + 𝜐" Wecanshowthis‘weakinteraction’usingaFeynmandiagram: Inthiscasetheexchange 𝛽( particleisa𝑊 ( boson. p 𝜐̅" Youcanseethatchargeis ( conservedasthe𝑊 ( 𝑊 bosoncarriesanegative n chargeawayfromthe neutrontothe𝛽 ( (an electron). Inbetaplusdecay,aprotonchangestoaneutron andemitsabetaplusparticleandanelectronneutrino. (6)!Writeasymbolequationforbetaplusdecay. (7)!DrawaFeynmandiagramforbetaplusdecay. Electroncapture Insomecases,whereanucleusisprotonrich,aprotonwillcaptureaninner shellelectronandtransformtoaneutron. (8)!Whatotherparticleisproducedbyelectroncapture? (9)!DrawaFeynmandiagramforelectroncapture. ©2016flippedaroundphysics.com Electron-protoncollision Inacollisionbetweenanelectronandaproton,aneutroncanbeproducedand anotherparticle. (10)!Whatotherparticleisproducedbyelectron-protoncollision? (11)!DrawaFeynmandiagramforelectron-protoncollision. ©2016flippedaroundphysics.com