* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces And Motion
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
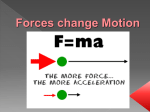
Motion • A change in the position of an object • Caused by force (a push or pull) Force • • • • Anything that is pushing or pulling on an object Measured in units called Newtons (N) Measured with a spring scale Forces act in pairs Forces & Motion Types of Force: – Gravity- pulls objects towards each other and pulls toward the center of Earth – Friction- when two surfaces rub against each other opposes motion Increasing friction will slow an object down Decreasing friction allows an object to move more freely – Magnetism – iron and steel are attracted to magnets opposite poles of a magnet attract and like poles repel – Electricity – these forces are produced when an object gains or looses electrons. Charged objects can exert a push or pull force on each other. Study Jams - Force Video Inertia Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist change to its state of motion. Newton’s 1st Law of Motion • An object at rest will remain at rest until acted upon by another force. • An object in motion will remain in motion until acted upon by another force. Balanced Forces • When all the forces acting on an object are equal (net force is zero) • Balanced forces do not cause a change in motion. How Can Balanced Forces Affect Objects? • Cause an object at rest to stay at rest or an object in motion to stay in motion (inertia) • Cause an object moving at a constant speed to continue at a constant speed • In your notes, describe an example of a balanced force affecting an object. Study Jams - 1st Law of Motion Video Newton’s Second Law of Motion • The greater the force on an object, the greater the acceleration on an object. The smaller the mass of an object, the greater the acceleration will be in comparison to an object with a larger mass. • Force= mass x acceleration Unbalanced Forces • When all the forces acting on an object are not equal • The forces can be in the same direction or in opposite directions. • Unbalanced forces cause a change in motion. How Can Unbalanced Forces Affect Objects? • Acceleration is caused by unbalanced forces: – – – – – slow down speed up stop start change direction • In your notes, describe an example of an unbalanced force affecting an object. Study Jams 2nd Law of Motion Video Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion • For every action or force, there is an equal and opposite reaction or force. Study Jams 3rd Law of Motion Video Mass and Weight • Mass is the amount of stuff (matter) in an object. – The mass of an object will remain the same anywhere in the universe. – Mass is measured in grams or kilograms. • Weight is the mass (kg) of an object multiplied by the acceleration of gravity (9.8 m/s2). – The weight of an object depends on the gravitational pull of the location in the universe. – The gravitational pull on the Moon is only 1/6 of Earth’s gravitational pull. – Weight is measured in newtons (N). Net Force • The total of all forces acting on an object: – Forces in the same direction are added. • The object will move in the direction of the force. – Forces in opposite directions are subtracted. • An object will move in the direction of the greater force. Calculating Net Force 10 N 30 N http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Jack-in-the-box.jpg A child was playing with a jack in the box. The lid pushed down with 10 N of force, while the spring pushed up with 30 N of force. What is the net force applied by the spring? In your notebook, calculate the net force and show all of your work. Check Your Answer 10 N 30 N http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Jack-in-the-box.jpg A child was playing with a jack in the box. The lid pushed down with 10 N of force, while the spring pushed up with 30 N of force. What is the net force applied by the spring? 30 N up - 10 N down = 20 N up Calculating Net Force 30 N Tug of War Game 50 N Two competitors are playing tug of war. What is the net force? Which direction will the rope move? In your notebook, calculate the net force and show all of your work. Check Your Answer Tug of War Game 30 N 50 N Two competitors are playing tug of war. What is the net force? Which direction will the rope move? 50 N to the right – 30 N to the left = 20 N to the right