* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Continental Drift - Frost Middle School
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
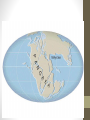
Continental Drift • Hypothesis proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1915 • The idea that Earth’s continents were once joined in a single landmass and gradually drifted apart. • This was not believed until the mid-1900’s • Wegener found many things that he claimed proved his hypothesis Evidence for Continental Drift • Fossils • Ancient reptile found in both South America and Western Africa - Mesosaurus Evidence for Continental Drift Evidence for Continental Drift • Geology • Rocks in Brazil matched perfectly to rocks in Africa • Limestone in Appalachian Mts. (N.A.) same as Scottish Highlands Evidence for Continental Drift • Climate • The same glacial till of the same age is found in southern Africa, South America, India and Australia • Large coal deposits were formed from tropical swamps in both N. America and Europe at the same time Super Continent • Wegener named his super continent • Pangaea • From the Greek word meaning “all lands” • Was a continent that reached from pole to pole • Began to split apart 200 million years ago New Evidence • In the 1960’s scientists really started studying the sea floor • Found underwater mountain ranges • Called mid-ocean ridges • Found in every ocean • Seemed to circle the Earth like the seams of a baseball • Sea-floor Spreading • Where the ridges form • Cracks in the crust where molten rock rises, cools, and forms new crust New Evidence • Age of the Sea Floor • Rock near the cracks are younger then rocks further away • Ocean Trenches • Where the oceanic crust sinks back into the Asthenosphere • Scientists put this new evidence together with Wegener's hypotheses to create the Theory of Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics • States that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into huge plates that move over the surface of the Earth • Driving force of this movement is the convection current in the Asthenosphere • Most major earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain ranges are where two plates meet. What causes Plate Movement • Convection Current • Motion that transfers heat energy in a material • As molten rock heats up it becomes less dense, as it rises it starts to cool becoming more dense and sinking again Convection Currents Create • Ridge Push • Happens at mid-ocean ridges • Pushes plates apart • Creates new sea floor • Slab Pull • Happens at Ocean Trenches • The denser plate sinks • Melts back into the Asthenosphere Hot Spots • Area where hot molten rock rises to the surface in plumes (columns) from the mantle • Usually found in the middle of tectonic plates but can be near boundaries • Hawaiian Islands • Can tell the direction and speed of plate movement • Yellowstone National Park • Sometimes found at divergent boundaries • Iceland • Azores • Galapagos Islands Magnetic Reversal • Recorded in the sea floor • Magnetic minerals in igneous rock lines up according to the direction of the poles • Last one was about 760,000 yrs ago • Flipped 170 times over the last 100 million years • The prediction for it happening again is 1,500 – 2,000 yrs from now