* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Legal Forms of Organization
Survey
Document related concepts
Initial public offering wikipedia , lookup
Initial public offering of Facebook wikipedia , lookup
Dividend tax wikipedia , lookup
Stock exchange wikipedia , lookup
Tax consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Partnership taxation in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
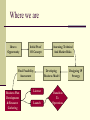
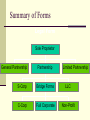
Moving from R&D to Operations Chapter 11 Where we are Idea to Opportunity Initial Proof Of Concept Final Feasibility Assessment Business Plan Development & Resource Gathering License Launch Assessing Technical And Market Risks Developing Business Model Transition To Operations Designing IP Strategy Transition Challenges Technical specifications that don’t fit Market expectations don’t match reality Determination of first application is hard First app versus killer app Technical and process uncertainty Initial assumptions about the market generally prove false What Makes a Successful Transition? People from the innovation team People from the operations team Transition management experts A mission Develop a Mission Statement Contributio n to Performanc e Component s of the Mission Statement Phrasing of the Mission Statement Communicati on to Stakeholder s Construct a Process Flow Chart Take a fantasy tour of the business to see how it works Track an order Note tasks, people, equipment Gather Resource Pieces Financial Capital Cash needs assessment Human Capital Process flow chart and Founding Team Assessment Physical Capital Process flow chart of business Resources have Significant Implications for Survival and Growth Bundles of resources create competitive advantages Resources that are unique, rare, and valuable create wealth Rapidly growing entrepreneurial firms require different resources at different times Choose an Organizational Model Engineering model: hire for technical skills Star model: hire for long-term potential Bureaucracy model: formal control procedures & employees hired for specific skills Autocracy model: employees motivated by financial rewards Commitment model: strong emotional bonds and informal peer-group control (best predictor of an IPO – Stanford Project on Emerging Companies Choose Legal Form of Organization Sole proprietorship Partnership Corporation Hybrid form How would you decide? Criteria for Choice Who will be the owners? Level of liability protection required Operating requirements and costs Effect on the tax strategy of the company & the founders When do you expect to earn a profit? How do you want to distribute earnings? Effect on financing plans Summary of Forms Legal Form Sole Proprietor General Partnership Partnership Limited Partnership S-Corp Bridge Forms LLC C-Corp Full Corporate Non-Profit Sole Proprietorship 76% of all businesses Flexible, easy, inexpensive Does not exist apart from the owner so pays no tax Salary or draw not deductible as expense Hobby rule (3 of 5 years) Sole Proprietorship Disadvantages Unlimited liability Difficult to raise debt capital Lacks advantage of team Survival dependent on owner Partnership Association of two or more persons as a business Doctrine of ostensible authority Specific property rights Share in profit/loss according to contribution Partnership Agreement Duties and responsibilities Profit/loss distribution Transfer of interest Duration and dissolution Arbitration and dispute resolution Type of partnership general v. limited secret, silent, dormant C-Corporation Legal entity Survival of death and separation Limited liability of shareholders Issue different classes of stock Raise capital by selling stock More status Benefit from retirement funds, profit sharing, stock options Owners can lease their assets to the corporation Disadvantages of Corporation Complex and costs more Stockholders do not have benefit of writing off losses Double taxation (earnings and dividends) Pay taxes on profits whether or not distributed as dividends Accountable to board of directors S-Corporation Not a tax-paying entity Owners taxed on corporate earnings Deduct losses on personal income tax up to amount invested No more than 75 stockholders, US citizens or legal residents One class of stock Disadvantages of S-Corp Difficult to get loans if distributes earnings No deductions based on medical reimbursements or health insurance plans If not a cash business, may not be able to pay taxes out of business. Must convert to C for IPO Limited Liability Company Limited liability of corporation with pass-through tax advantages of partnership Members and interests,Articles of organization Managers, officers, members not personally liable Most organize for tax purposes as partnership No limitation to membership, more than one class of stock Non-Profit Established for charitable, public benefit, religious or mutual benefit IRS 501(c)3 tax exempt Limited liability Owners give up proprietary interest Perpetual existence Apply for grants Take-Aways Add students’ comments here