* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Double Outlet Right Ventricle
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
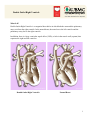
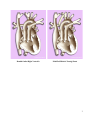
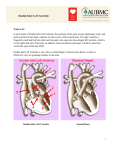
Double Outlet Right Ventricle What Is It? Double Outlet Right Ventricle is a congenital heart defect in which both the aorta and the pulmonary artery exit from the right ventricle. In the normal heart, the aorta leaves the left ventricle and the pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle. In addition, there is a large ventricular septal defect (VSD), or hole in the muscle wall (septum) that separates the right and left ventricles. Double Outlet Right Ventricle Normal Heart 1 What Are Its Effects? The symptoms associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle depend on the position of the Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) and the degree of pulmonary valve stenosis. Oxygen-rich blood enters the right ventricle through the VSD. If an insufficient amount of blood is pumped to the lungs (because of significant pulmonary stenosis), the infant will have difficulty adding weight and may show blueness (cyanosis). On the other hand, if too much blood is pumped to the lungs, heart failure may result. 1) Both the Aorta and Pulmonary Artery exit from the right ventricle 2) Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) How Is It Treated? If too much blood is pumped to the lungs with Double Outlet Right Ventricle, medications may be used to reduce the risk of heart failure. In cases where not enough blood is pumped to the lungs, a Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt (Gore-Tex® tube) may be surgically inserted between the aorta or one of its branches and the pulmonary artery (indicated by the red arrow in illustration below). This increases blood flow to the lungs and decreases the infant's blueness. In some case, open heart surgery will be performed to close the VSD (see Ventricular Septal Defect) and separate the heart to lungs and heart to body circulation. 2 Double Outlet Right Ventricle Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt 3