* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecologists study . Ecology is the study of is an individual living thing
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
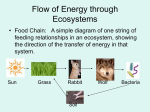
______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Ecologists study _____________________________________________. Ecology is the study of _____________________________________________________________ ___________________ is an individual living thing, such as an alligator ___________________ a group of the same species that lives in one area ___________________ a group of different species that live together in one area. _________________________ includes all of the organisms as well as the climate, soil, water, rocks and other nonliving things in a given area. ________________________ is a major regional or global community of organisms characterized by the__________________________________ and plant communities that thrive there. ______________________________ ______________________________ Section 2 An ecosystem includes _______________ and _______________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _______________________factors are living things. Ex. _______________________ factors are nonliving things. Ex. ______________________________________ species is a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem. Section 3 What is the main source of energy for all Ecosystems? _________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Some other organisms can make their own food from inorganic compounds (chemicals not containing carbon) using ____________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ __________________provide energy for other organisms in an ecosystem. Producers get their energy from ____________________________ resources. Producers are also called ___________________________________ because they make their own food. Types of Autotrophs ____________________________________- capture energy from sunlight and convert it to carbohydrates Ex. ____________________________________- capture energy from heat and inorganic compounds and convert it to carbohydrates Ex. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Section 4 A ________________________________ is a model that shows a sequence of ________________________________. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ A food chain links species by their _________________________________. It follows the connection between one producer and a _______________________of consumers within an ecosystem. ___________________________________ are consumers that primarily eat one specific organism or a very small number of organisms. _____________________________are consumers that have a varying diet ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ___________________Organisms that eat OR absorb food to obtain energy _________________________ Eat only plant life Ex. _________________________Feed on other consumers Ex. Omnivores- ___________________________________________________ Ex. Detritivores and Scavengers: _____________________________________________________________ Ex. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _______________________________________Break down organic matter and return it to the earth as inorganic matter Ex: Detritivore vs. Decomposer ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ __________________________ are the nourishment levels in a food chain. _________________________________ are herbivores that eat producers. _________________________________ are carnivores that eat herbivores. ________________________ are carnivores that eat secondary consumers. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _________________________________________, such as humans that eat both plants and animals, may be listed at different trophic levels in different food chains. ___________________ shows a complex network of feeding relationships. ______________________________ ______________________________ A food web emphasizes complicated feeding relationships and energy flow in an ecosystem. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _____________________________ Purpose of food webs and chains: Show how_______________________ flows in an ecosystemDirection of the arrow is the direction of ________________________________________- do NOT mix this up! Energy Flows in one direction through an ecosystem: ______________________________ ______________________________ Along the way, some energy is _____________________ (thermal energy) Law of Conservation of Energy: energy cannot be created or destroyed, ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Energy is converted from one form to another _________________________ is converted _______________________ stored in food (during photosynthesis). The plant USES some of it to grow, to reproduce, to help make food, etc. Energy is released as_________________ Hence through a food chain, much of the energy is lost to the environment as heat. ____________________ of energy goes to the next level. Section 5 Biogeochemical Cycles While energy is transferred in one direction in an ecosystem, _____________________ is cycled through the ecosystem in the biogeochemical cycles ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _____________________________ ________________________________ how water moves through the air, land, and organisms _______________________________- water to vapor from surface of bodies of water _______________________________- water to vapor from plants _______________________________- vapor to water in clouds _______________________________- clouds become too full and rain, snow, etc. fall to the earth ________________________________- water collects into bodies of water ________________________________- water from the surface sinks into ground water storage _________________________is the building block of life. The carbon cycle moves carbon from the atmosphere, through the food web, and back to the atmosphere. Carbon is emitted during the burning of ________________________. Some carbon is stored for long periods of time in areas called __________________________. The _______________________________ mostly takes place underground. Some bacteria convert gaseous nitrogen into ammonia through a process called ______________________________________. Some nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in nodules on the roots of plants; others live freely in soil. ______________________________ released into the soil is transformed into ammonium. Nitrifying bacteria change the ammonium into nitrate. Nitrogen moves through the food web and returns to the soil during decomposition. ____________________________________- bacteria take nitrogen (N2) from the atmosphere and change it into a form that plants can take up from the soil called ammonium (NH4). ______________________________- ammonium not taken up by plants are converted to nitrates and nitrites by bacteria which other plants can take up ______________________________ _______________________________- bacteria can turn the ammonium ______________________________ back to atmospheric nitrogen ______________________________ ______________________________ takes place at and below ground level. _______________________ is released by the weathering of rocks. Phosphorus moves through the food web and returns to the soil during ____________________. Phosphorus leaches into groundwater from the soil and is locked in sediments. Both mining and agriculture add phosphorus into the environment ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Nutrient Limitations An ecosystem needs a particular amount of each nutrient to thrive. A single nutrient can limit its success. An excess of a particular nutrient can cause over production of algae and plant growth Human Effects on Biogeochemical Cycles ________________________________ overgrowth of photosynthetic organisms in a body of water due to an excess of nitrates and phosphates from urban or agricultural runoff Section 6 Ecological Pyramids ______________________________________________ shows the distribution of energy among trophic levels. Energy pyramids compare energy used by producers and other organisms on trophic levels. Between each tier of an energy pyramid, up to ______________________ of the energy is lost into the atmosphere as________________. Only ____________________ of the energy at each tier is transferred from one trophic level to the next. ______________________________ ______________________________ ___________________________________ is a measure of the total dry mass of organisms in a given area. ______________________________ ______________________________ A pyramid of numbers shows the numbers of individual organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Notes: Ecosystems and Communities Pre-AP _____________ is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives. An ____________________________ includes all of the factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy, and reproduce. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _____________________________ _______________________ competing for resources, shelter, space, mates, etc. ____________________________ between members of different species -_____________________________: between members of the same species Competitive exclusion keeps two species from occupying the same niche. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Competitive exclusion One species is better suited to the niche and the other will either be pushed out or become extinct. o The niche will be divided. o The two species will further diverge. Ecological equivalents are species that occupy similar niches but live in different geographical regions. Predation- ______________________________________________ Ex: lion eats a deer Mutualism- ______________________________________________ Ex. ant live on an acacia tree, ant protects tree from harmful plants, tree gives ant a home Parasitism- _____________________________________________ Ex. Fleas or ticks on a dog; flea gets a home, sucks the dog’s blood and is bothered by it ______________________________ Commensalism- _________________________________________ Ex. moss growing on trees ______________________________ Symbiosis- ______________________________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Symbiotic Relationship Mutualism Parasitism Commensalism +: benefit -: harm Species A Species B 0: neutral ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Factors Affecting Populations Four things affect population size: ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Types of Growth ________________________- if a population has abundant space and food, no disease or predators; it will grow at an exponential rate. It is a J-shaped curve resembling y = ax2 + b ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _____________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ _________________________- population growth slows then stops (stays stable) after a period of exponential growth once resources become less available. The number at which the environment can support this population is known as the carrying capacity. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Limiting factor- factor that causes a population to decrease in size Density dependent_______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ Density independent_______________________________________________________ __. Unusual weather, natural disasters, seasonal cycles, and certain human activities Succession_______________________________________________________ After such disasters, a community can start anew by a process called ecological succession (series of predictable changes that occurs in a community over time); there are two types Primary succession_______________________________________________________ (after a volcanic eruption/ glacier retreats) ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Secondary succession____________________________________________________ (after a fire, disease, natural disaster Marine Succession Stage 1 – Begins when a large whale dies and sinks to the ocean floor – Attracts scavengers and decomposers (hagfish, sharks, crabs, shrimp), which eat the soft tissue ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ Stage 2 – After 1 year, most of the soft tissue has been eaten – Decomposition of the body enriches the sediment with nutrients, which attracts fish, crabs, and many marine snails and worms ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _____________________________ Stage 3 – Begins only when the skeleton remains – Bacteria decompose the oils inside the bones – The bacteria support a community of mussels, marine snails, marine worms, crabs, and clams