* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 10 Grammar Notes
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Basque grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Grade 10 Grammar Notes
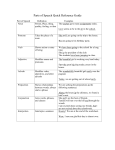
Eight Parts of Speech
Clause and simple sentence
AVHS English Department
The Eight Parts of Speech
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
PRONOUN
NOUN
ADJECTIVE
VERB
ADVERB
PREPOSITION
CONJUNCTION
INTERJECTION
PRONOUN
- a word which takes the place of a noun. Its antecedent is a noun.
EX.: The door broke. It should be fixed. ("door" is the antecedent of "it")
Types of pronouns:
– Personal: I/me, you, she/her, he/him, it, we/us, they/them (subj./obj)
– Demonstrative: this/that , these/those
– Relative: who which that (act as conjunctions)
– Intensive: I myself make mistakes occasionally
– Reflexive: He told himself to slow down
– Indefinite: either/any/anyone/someone/everybody/both/each/one etc,
– Interrogative: who/whom, whose which (when asking a question)
NOUN
1) a "thing", in its concrete or abstract sense
2) person, place, thing / idea, quality, emotion
3) always a "subject" or "object"
4) forms plurals (usually with -s or -es)
5) often preceded by adjectives (incl. "the" and "a")
ADJECTIVE
modifies (i.e. describes or limits) a noun.
Ex. The big cat is dangerous.
VERB
1)shows action (except the verb "to be")
2) always forms a tense (past-present-future)
3) always has a "subject"
ADVERB
a) modifies a verb by showing the manner time
or place of the verb's action. Asking howwhen-where? of the verb will lead you to
adverbs.
Ex. Yesterday, the birds sang sweetly here.
b) also, modifies another adverb or an
adjective. Such adverbs are sometimes called
intensifiers.
Ex. That very black cat screamed rather
loudly last night.
PREPOSITION
- a word which shows a relation between a) the noun (or pron.)
which always follows it and b) some other noun or verb in the
sentence.
Ex. The man in the street shouted at the sailor.
The combination of the preposition followed by a noun is called a
"prepositional phrase". Prepositional phrases always act like
oversized adjectives or adverbs.
Ex. a) in the street - prep. adj. phrase (modifies "man")
b) at the sailor - prep. adv. phrase (modifies "shouted") Some
common prepositions:
in/after/through/with/over/under/by/of/at/for/into
CONJUNCTION
There are two types:
1)COORDINATE - and / but / or / for
It always joins 2 parts of speech or 2 phrases or 2 clauses of the same
type (co = equal)
Ex. The girl and her cat stared and sighed through the evening and into the
night, but they seemed quite happy nonetheless.
2) SUBORDINATE - only joins clauses, making one sentence out of two.
The subordinate conj. (unlike the coord. conj.) makes the clause that it
starts subordinate to the one it attaches to.
Some common sub. conjunctions: because/when/
where/before/that/until/unless/except/than/as/if/although
Ex. The dog barked. It was hungry. (2 sentences) The dog barked
because it was hungry. (2 clauses,1 sentence) The clause beginning
with "because" is subordinate to the opening clause; it needs the
opening clause to make sense. The subordinate conjunction is
additional meaning and always forms the first word in a subordinate
clause.
INTERJECTION
-a word which is interjected (i.e. "thrown in") to
a sentence without any connection to the rest
of the words. It is often for emphasis and so
may be accompanied by an exclamation
mark.
Example: Hey! are you listening?
– Shucks, it warn't nothin'.
– Well, I'll think of something.
CLAUSE and SIMPLE
SENTENCE
A clause is a group of words centered
around a subject (noun or pronoun)+ Verb.
A single such group of words makes a
"simple" sentence.