* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Land Plants
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
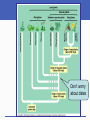
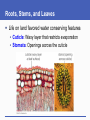
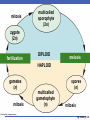
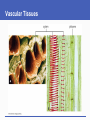
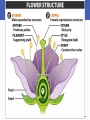
The Land Plants Chapter 12 Impacts, Issues Beginnings and Endings Don’t worry about dates Roots, Stems, and Leaves Life on land favored water conserving features • Cuticle: Waxy layer that restricts evaporation • Stomata: Openings across the cuticle From Haploid to Diploid Dominance • Gametophyte: Haploid stage that forms gametes by mitosis • Sporophyte: Diploid stage that forms spores by meiosis; a sporangium helps protect and disperse spores mitosis multicelled sporophyte (2n) zygote (2n) fertilization DIPLOID meiosis HAPLOID gametes (n) mitosis multicelled gametophyte (n) spores (n) mitosis Fig. 23-5a, p. 372 zygote is only diploid phase green algae bryophytes ferns gymnosperms angiosperms Fig. 23-5b, p. 372 Bryophytes The Bryophytes Importance of Mosses Seedless Vascular PlantsEX: Ferns Vascular Tissues Ferns – No Seeds, Much Diversity Ferns • The most diverse seedless vascular plants • Spores are dispersed from clusters of sporangia (sori) on lower surfaces of frond leaves • Many live as epiphytes attached to another plant spores Fern Diversity Human Use of Seed Plants Humans depend heavily on : • • • • Food crops Lumber and wood product Drugs and medicines Fabrics and dyes Two Lineages of Seed-Bearing Vascular Plants Gymnosperms • Cycads, conifers, ginkgos, and gnetophytes Angiosperms (flowering plants) • Most modern plants • Seeds form inside floral tissue that later develops into a fruit Vascular PlantsGymnosperms Some Gymnosperms Vascular PlantsAngiosperms Keys to Angiosperm Success Short life cycles and rapid growth Specialized reproductive structures (flowers) Specialized pollination and dispersal structures • Wind and animal pollinators • Fruits that float or stick • Seeds that survive animal digestive tracts Specialized Angiosperm Structures A flower is a specialized reproductive shoot Seeds develop inside the ovaries (chambers that enclose ovules) of flowers After fertilization, an ovary becomes a fruit Pollination and Coevolution Pollinators • Animals move pollen grains from male parts of one flower to female parts of another Coevolution • Over time, plants and their animal pollinators jointly evolved; changes in one exerts selection pressure on the other Focus on a Flowering Plant Life Cycle Flowering plants form eggs in ovaries and pollen in stamens Flowering plants make fruits containing seeds which supply their embryo sporophytes with endosperm, a nutritive tissue Life Cycle: Lilium Summary: Plant Evolutionary Trends