* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide set 2 File
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Trading room wikipedia , lookup
Syndicated loan wikipedia , lookup
Algorithmic trading wikipedia , lookup
Stock selection criterion wikipedia , lookup
Stock trader wikipedia , lookup
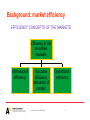
Legal Aspects of Finance Slide Set 2 The Role of Regulation on the Markets Matti Rudanko Why Regulate the Markets? • Mere policing purposes – investor protection – market functioning (efficiency): fair trading, codes of conduct, transparency, confidence • guidance intervention – scope and breadth of the markets – cannot be justified (Zufferey) Legal Aspects of Finance 2 2 Indications for regulation? • Financialisation (over-developed financial markets): financial bubbles, “bancocracy” ? – No link to the underlying economy: too abstract for attempts to determine the proper size (guidance function) • Increased volatility (no clear trend recently) – no regulation can control price fluctuations – markets include inherent risks – volatility may be advantageous for investors Legal Aspects of Finance 2 3 Episodic volatility • Hypervolatility and disorder of the markets undermine conditions of reasoned decisions • Target for policing intervention aiming at normal volatility limited to market risks – domino effects – investor reliance, market psychology – impact on the underlying economy Legal Aspects of Finance 2 4 Episodic volatility, cont´d • Policing intervention – – – – market stability through investor protection price formation mechanism trading halts in the event of a crisis efficiency of clearing systems • Target for guidance intervention? – Slowing down the market, increasing transaction costs (e.g. margin deposits imposed on investors on credit) Legal Aspects of Finance 2 5 Investor Protection • Direct protection: eg. ensuring transparency – sanctioned disclosure duties – anonymity of the market prevents investors from “contractual” information seeking • Indirect protection – protection of the weaker (cf. institutional investors)? – Often a by-product of other (e.g. insider) rules Legal Aspects of Finance 2 6 No Investor Protection? • E.g. disclosure regulation: – capacity of investors to evaluate information is unequal and limited (cf. also the role of psychological “irrational” factors) – market forces take care of sufficient information by affecting prices (risk averse) investors are willing to pay – on efficient markets, prices reflect all information Legal Aspects of Finance 2 7 Investor protection / market functions? • Market efficiency may require – minimum quality standards of operators having access to the markets – codes of conduct for all participants to avoid malpractice – quality standards of traded products – the quality of market support systems (marketplaces, information and clearing systems etc.) Legal Aspects of Finance 2 8 Insider offences: damages to whom ? • • • • • • Concealing information? Trading? These aspects together? Disclose or abstain rule Existence of damage? Would have purchased anyway? Consider the hypothetic impact of – insider abstaining / disclosure Legal Aspects of Finance 2 9 (De)regulation? • Pros and cons: • Reliance on the market – fair play -rules – cf. (bad) luck -argument (random / regular gains) • efficiency • ethical aspects • investor protection: damages? • the position of the issuer and its management Legal Aspects of Finance 2 10 Background: market efficiency EFFICIENCY CONCEPTS OF THE MARKETS Efficiency of the securities markets Informational efficiency Allocative efficiency (allocation of capital) Legal Aspects of Finance 2 Operational efficiency 11 Informational efficiency • Efficient Capital Markets Hypothesis (ECMH) • making use of inside information - disclose or abstain - duty to disclose ? – – – – Efficiency of information production incentive effects accuracy and speed of information production protective measures within companies: costs of insider trading / costs of disclosure (procedure costs / secrets) – self regulation / public regulation Legal Aspects of Finance 2 12 Issuer company and management • Part of remuneration and incentive systems of management – moral hazard? • Increased capital costs ? – Increased spread because of management activity and outsider reactions • monitoring costs (agency costs) • internal efficiency – information flows – misuse of management position e.g. in thwarting a takeover Legal Aspects of Finance 2 13 Ethical aspects • The unfairness of the possibility to make use of one’s position • ethics / efficiency • distributive aspects – impact on distribution of wealth – not based on productive work – cf. Labor and capital as factors of production (Marx) Legal Aspects of Finance 2 14 Protection of the Market Function • Technical efficiency – computerization: support by legal measures ensuring system reliability (responsibility of sponsors) • Information efficiency (ECMH) • Institutional efficiency – investor confidence leads to – liquidity and resistance to fluctuations – trading halts and suspensions Legal Aspects of Finance 2 15 Protection of the Market Function, cont’d • competition of systems, intermediaries and products • pricing mechanisms, operator access and listed issuers • self regulation based on general compulsory principles in law – avoidance of unfair competition – globalization of trading systems – moreover governed by competition rules Legal Aspects of Finance 2 16 Conclusions • Regulation should not eliminate market risk – cf. the Finnish investor compensation fund safeguarding the cash and claims of clients in case of insolvency or other nonperformance of an investment firm • important to seek optimal level of protection costs • risk of “moral hazard” should be eliminated • imperative of minimal intervention based on economic analysis Legal Aspects of Finance 2 17 Increased competition • Globalization increases competition between marketplaces (exchanges) – computerization leads to global dissemination of information – from “public service” exchanges to “enterprise” exchanges: diversification of products offered, campaigns • increased competition of intermediaries – cf. e.g. online brokerage: customers’self service Legal Aspects of Finance 2 18 Competition and Regulation • International imperative: non-intervention – only self-regulation can support the really needed technical improvements – state regulation for increased competitiveness is economically inefficient – liquidity cannot be reached by regulation – regulation to increase international competitiveness would lead to a “race to the bottom” in e.g. investor protection Legal Aspects of Finance 2 19 National competitiveness • National imperative: intervention increasing competitiveness of domestic marketplaces – e.g. France, Germany, Austria, Switzerland • guaranteeing a competitive level of competition is a legitimate cause for intervention – must be limited to the needs of investor protection and market function Legal Aspects of Finance 2 20 Concentration • Acceptable target for policy regulation when affecting market functions (the price formation ability) – e.g., concentration of intermediaries increases the risk of conflict of interests – codes of conduct • no need for guidance intervention – e.g. growth, survival of the national branch – cf. competition law Legal Aspects of Finance 2 21