* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tom Cameron`s presentation
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
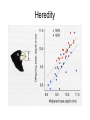
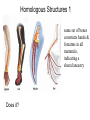
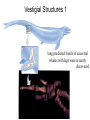
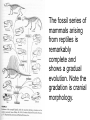
Evolution T412 The Modern Synthesis 1932-1953 Restated Darwin’s ideas: (1) Individuals in a population are variable for most traits, because in every generation, mutation creates new genes; further, sexual reproduction creates new gene combinations (2) Individuals pass some of their genes to their offspring Heredity The Modern Synthesis 1932-1953 Restated Darwin’s ideas: (1) Individuals in a population are variable for most traits, because in every generation, mutation creates new genes; further, sexual reproduction creates new gene combinations (2) Individuals pass some of their genes to their offspring (3) More offspring are produced than can survive (4) Individuals that survive, or reproduce the most, have gene combinations that best adapt them to their environment i.e. adaptive radiation Sexual Selection 1 male Peacocks Fiddler crabs Males have traits important in mating displays (color, tail, claws) whereas females lack such ornamentation - male energy goes into looking good, attracting mates - females invest energy in making large, healthy offspring Sexual Selection 2 male Peacocks Fiddler crabs Why do females chose fancy males? If a male can survive predation and look that good while harbouring parasites and resisting disease, he must have good GENES!! Females want the best genes to combine with their own to give their offspring the best chance of survival (i.e. natural selection). Have a variety of offspring as environment is unpredictable (bet-hedging) Natural selection 1 Darwin's finches 1977 - Drought Mean beak depth Drought favored deeper beaks that could crack the tough seeds that were available Directional selection – not random Natural selection 2 Peppered moths • Before Industrial revolution, all moths were light • As habitats became sooty, being light was dangerous! • Darker moths favoured, experimental and genetic proof • This did not happen in northern Scotland or other rural areas • Can still be seen today! • Lighter moths re-appearing as pollution reduced! Phenotypic plasticity Natural selection 3 Sickle Cell Anemia in humans • Single point mutation • SS, Ss, ss = genotypes • African & Mediterranean groups • Anopheles mosquito • 150 bites per year • 100% malaria infection rate in kids • 25% greater survivability from malaria = Ss Artificial selection Darwin used examples of pigeon fanciers to show how selection worked. Other than a useful technique • Experimental proof of natural and sexual selection • Used widely in farming, horticulture and medicine Summary • Evolution is selection of favourable inheritable genes that increase an individuals ability to survive. • Characteristics of the surviving individuals are concentrated in future generations causing changes in phenotype • Selection can be natural, sexual or artificial Break Evidence for Evolution Evidence supporting the theory of evolution is found in: (1) Similarities among related organisms (2) Redundant/Unused structures (3) Biogeography (4) Fossil record (intermediate forms in a given families) (5) Molecular evidence Homologous Structures 1 same set of bones constructs hands & forearms in all mammals, indicating a shared ancestry Does it? Homology in Embryological evidence Note that in the first row all of the embryos have a similar number of gill arches, which are later destroyed in all embryos after the salamander; note in the second row the similarity of the spinal column or all organisms. Why should human embryos develop gill arches if not a vestige of history? Vestigial Structures 1 long predicted fossils of ancestral whales with legs were recently discovered Vestigial Structures 2 Cavefish Eye Reduction Vestigial Structures 2 Snake Hind-limbs Biogeography 1 • The study of the global distribution of organisms • Why are the faunas of Europe & North America so similar, while those of Africa and South America so dis-similar? • Why is the fauna of Australia so different from all other continents? Biogeography 2 • Prediction: Groups that evolved after separation of modern continents should be confined to those continents, whereas lineages that evolved before separation should be found on all continents. • Reptile-like primitive mammals are broadly distributed over all continents (as fossils) • carnivores & hoofed mammals, which evolved later have never been found on Australia and South America because they split off earlier. The fossil series of mammals arising from reptiles is remarkably complete and shows a gradual evolution. Note the gradation is cranial morphology. Amphibious fish! Phylogeny of modern fish Reptiles to Birds The Fossil Record 1 • Why is the fossil record not continuous? – Fossilization is a rare event. – Evolution isn’t always gradual. – We do have quite a few complete and gradual fossil series, i.e. modern horses (Eohippus to Equus), mammals from reptiles, whales from ungulate ancestors. The Fossil Record 2 Where are all the intermediate forms? The Fossil Record 3 Where are all the intermediate forms? • They do exist! • Often rare • Limbs often lost • Living fossils The Fossil Record 4 Where are all the intermediate forms? Molecular Evidence • Genetic clocks • Genetic code similarities • Homology in biological processes, proteins, gene properties and possession • Similar disease profiles and history • Matches evidence from fossils and preserved remains Evidence for Evolution Evidence supporting the theory of evolution is found in: (1) Similarities among related organisms (2) Redundant/Unused structures (3) Biogeography (4) Fossil record (intermediate forms in a given families) (5) Molecular evidence Break Human evolution Human evolution • First change from other apes was bipedalism — Australopithecus anamensis • Much debate on why – Adaptation for cooling? – Run faster? – Carry things? Early Hominids • Australopithecines 4.2 -2.5 million years ago – 3’7”, brain 400cm3 • Homo habilis – 5’, brain 700cm3 • Homo erectus – large, brain 1000cm3 Homo sapiens • • • • Many ideas about human evolution All recognize multiple species of Homo All recognize origin in Africa Questions about interbreeding of different early groups • Questions about which were direct ancestors of modern humans Theistic evolution If we evolved where does God fit in? Either…… • God created us separately from other hominids but so that it would look like we had evolved, or • Our physical bodies evolved from animal matter like everything else on earth but the properties that make us human (i.e. the ability to control our instinct, morality, our soul) were given to us when God deemed us ready, i.e. the creation of humans, or • God was not involved Evidence against evolution 1 2nd law of thermodynamics: in a closed system, things will move from an ordered to unordered state (decay) – The Earth is not in a closed system. New energy from the sun is constantly flowing in. – Evolution doesn’t have to be a “progression.” (eg. intestinal parasites) Evidence against evolution 2 The Human Eye (and other complex structures) • Within each taxonomic group variation in eye structure occurs • Increasing complexity can be seen within and between families • Some invertebrates have very complex eyes, similar to mammals, i.e. squid, octopus Evidence against evolution 3 Living cells • Proteins and cells are easy • Self-replication cant be replicated • RNA + DNA not yet formed experimentally Consciousness • Very hard to define • Some evidence of animal consciousness • Speech + grammar can be genetically linked YEC claims • Why have the apes in WY stopped evolving? • RNA + DNA independently appeared? • Drosophila experiments irrelevant! • Cat + Dog don’t make “cog or dot”! • Peacock’s tail too pretty • Behaviour can’t evolve, i.e. Migration • Speciation happens but not evolution