* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy Review: The Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
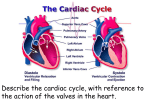
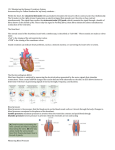
Extra Credit Assignment for Cardiovascular System This assignment is worth a maximum of two (2) points **See the gserianne.com Web site for due dates 1. Cardiopulmonary Circulation -- Draw a diagram or pathway showing how blood returns to the heart from the body, how it goes THROUGH the heart, how it gets to the lungs, and how it gets back to the heart again, and where it goes after it gets back from the lungs. You can draw this, if you like, or you can just do a pathway list, e.g., first place second place … **If you draw a diagram label all the vessels you draw, the heart chambers, the valves, and indicate the direction of blood flow. If you want to take a diagram from somewhere, be sure it’s blank and be sure to 1) label it yourself, and 2) cite where you got it from. You might want to use different colors in your diagram, but you don’t have to as long as you label everything. Continued on the next page.... Study Questions on Anatomy Review: The Heart and Cardiovascular System 1. What's the difference between the blood in the right side of the heart and the left side of the heart? 2. a. Where does the blood go that is pumped out of the right heart? b. What happens to the blood in the lungs? c. Where does the blood go that is pumped out of the left heart? 3. What is the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit? 4. What three structural features are found on histological (light microscope) images of cardiac muscle that help you identify it as cardiac muscle? 5. What are the names of the two types of cell junctions in cardiac muscle cells? 6. What is the function of desmosomes? 7. What is the function of gap junctions? Continued on next page.... Intrinsic Conduction System Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 8. Label the following graphic: Continued on next page... 9. Draw a diagram of an EKG (ECG) labeling all the waves, and indicate where the following normally occur: atrial depolarization, ventricular depolarization, ventricular repolarization, atrial repolarization Study Questions on the Intrinsic Conduction System: 1. What is the purpose of the intrinsic conduction system of the heart? 2. Are the cells of the intrinsic conduction system of the heart nerve cells? Explain your answer. 3. Match the six areas within the heart where autorhythmic cells are found to their location within the heart. Location Within the Heart: __ a. Interatrial septum to the interventricular septum. __ b. Lower interventricular septum to the myocardium of the ventricles. __ c. Inferior interatrial septum. __ d. Upper right atrium. __ e. Throughout the walls of the atria. __ f. Within the interventricular septum. Continued on Next page... Areas Where Autorhythmic Cells Are Found: 1. Internodal Pathway 2. AV Node 3. Bundle Branches 4. SA Node 5. Purkinje Fibers 6. AV Bundle 5. Match the six areas within the heart where autorhythmic cells are found to their function. Functions: __ a. Initiates the depolarization impulse that generates an action potential, setting the overall pace of the heartbeat. __ b. Convey the action potential to the contractile cells of the ventricle. __ c. Delays the action potential while the atria contract. __ d. Links the SA node to the AV node, distributing the action potential to the contractile cells of the atria. __ e. Electrically connects the atria and the ventricles, connecting the AV node to the Bundle Branches. __ f. Conveys the action potential down the interventricular septum. Areas Where Autorhythmic Cells Are Found: 1. Internodal Pathway 2. AV Node 3. Bundle Branches 4. SA Node 5. Purkinje Fibers 6. AV Bundle 6. Explain the difference between the electrical and mechanical events which occur within the heart, and explain the cell types that carry out each. Which occurs first, the electrical or mechanical events? 8. Why is it important for the contraction of the ventricle to begin at the apex and move superiorly. 9. a. What mechanical event follows the P wave? b. What mechanical event follows the QRS complex? c. What mechanical event follows the T wave ? The Cardiac Cycle Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Study Questions on the Cardiac Cycle: 1. What is a cardiac cycle? 2. What opens and closes the heart valves? 3. List the three phases of the Cardiac Cycle. 4. Match the stages of the cardiac cycle to their description. ___ 1a. Ventricular Filling: Passive v. Ventricles contract and intraventricular pressure rises, closing the AV valves. ___ 1b. Ventricular Filling: Atrial Contraction w. Ventricles relax and ventricular pressure drops. Blood backflows, closing semilunar valves. ___ 2a. Ventricular Systole: Isovolumetric Contraction x. Blood flows passively into the atria, through open AV valves, and into the ventricles. ___ 2b. Ventricular Systole: Ejection y. Rising ventricular pressure forces semilunar valves open. Blood is ejected from the heart. ___ 3. Isovolumetric Relaxation z. Atria contract, forcing the remaining blood into the ventricles. 5. True or false: Blood passes through the aortic semilunar valve at the same time blood is also passing through the pulmonary semilunar valve. 6. What closes the AV valves? 7. What opens the semilunar valves? 8. What closes the semilunar valves? 9. What opens the AV valves? 10. True or false: The right side of the heart contracts, then the left side of the heart contract. 11. Explain the relationship between the pressure in a heart chamber, the amount of fluid in the chamber, and the size of the chamber. 12. Blood always moves from ___________ pressure to ____________ pressure. 13. Predict if the AV and semilunar valves are open or closed during the following phases of the cardiac cycle by writing "Open" or "Closed" in the boxes on the chart. State of AV Valves Isovolumetric Contraction Isovolumetric Relaxation Ventricular Ejection Ventricular Filling Continued on next page... State of Semilunar Valves 14. Label the parts of the cardiac cycle diagram below by filling in as many boxes and circles as you can. Continued on next page... Cardiac Output Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Regulation of CO: HR • Think about the effect increased sympathetic or parasympathetic input might have on heart rate. • Fill out this chart, making note of the reasons for the increase or decrease: Effect on Heart Rate Increased sympathetic stimulation Increased parasympathetic stimulation Regulation of CO: SV • Think about the effect increased sympathetic or parasympathetic input or venous return might have on stroke volume. • Fill out this chart, making note of the reasons for the increase or decrease: Effect on Stroke Volume Increased sympathetic stimulation Increased parasympathetic stimulation Increased venous return Study Questions on Cardiac Output (be sure to include UNITS where appropriate) 1. Define cardiac output (CO). 2. What two factors does cardiac output depend on? 3. What is the mathematical relationship between cardiac output, heart rate, and stroke volume. 4. Define heart rate. 5. Why is the average heart rate in an adult at rest slower than the pacing rate of the SA node? 6. What is the term for the volume of blood that is pumped out of the heart with each beat? What is a normal average value for this volume for an adult at rest? 7. What is term for the amount of blood present in the ventricles just before they contract? What is a normal average value for this volume for an adult at rest? 8. Define end systolic volume. Is this volume directly or inversely proportional to CO? 9. What is the mathematical relationship (equation) that relates end diastolic volume, end systolic volume, and stroke volume? 10. If the ESV is 90 ml and the EDV is 120 ml, what is the stroke volume? normal? Is this 11. If the heart rate is 55 beats per minute and the stroke volume is 90 ml per beat, then what is the cardiac output? Would this be normal? Would you say this individual is healthy? Why? 12. What's the relationship between venous return and stroke volume? 13. List as many ways as you can think of to increase cardiac output. For each one you list, explain whether it affects heart rate, stroke volume, or both. 14. List as many ways as you can think of to decrease cardiac output. For each one you list, explain whether it affects heart rate, stroke volume, or both. 15. What is the effect of a sudden loss of blood, e.g., hemorrhage, on heart rate and stroke volume? Explain your answer.