* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arrhythmias in ECGs - Auckland Heart Group
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
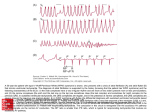
ECG Workshop Arrhythmia ECGs David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group DJH ECG Rhythm Analysis First principles 5 Questions • Heart rate – brady, normal or tachy ? • Regular or irregular ? • Narrow or wide QRS complexes • Can I see P (or flutter) waves • What is the relationship of P to QRS DJH • A 36 year old man comes to your rooms • He is a keen athlete • He has slow pulse but no significant symptoms • You do an ECG The patient A) Can go home, no problem, no referral required B) Needs to see an Cardiologist C) Should go to Hospital, but can go in a car D) Needs an ambulance The patient A) Can go home, no problem, no referral required B) Needs to see an Cardiologist C) Should go to Hospital, but can go in a car D) Needs an ambulance A 79 year old man comes to your rooms for routine review • Asymptomatic • Previously well • He has a slow pulse so you do an ECG This shows A) Sinus bradycardia B) Complete heart block C) Mobitz type 2 AV block D) Atrial fibrillation. This shows A) Sinus bradycardia B) Complete heart block C) Mobitz type 2 AV block D) Atrial fibrillation. The patient A) Can go home, no problem, no referral required B) Needs to see an Cardiologist C) Should go to Hospital, but can go in a car D) Needs an ambulance The patient A) Can go home, no problem, no referral required B) Needs to see an Cardiologist C) Should go to Hospital, but can go in a car D) Needs an ambulance •A 30 year old woman with a history of palpitations presents acutely to your rooms with a racing heart beat. • Your practice nurse to gets an ECG • She calls you into the room The most likely diagnosis is A) AV node re-entry tachycardia B) Atrial fibrillation C) Atrial tachycardia D) Ventricular tachycardia The most likely diagnosis is A) AV node re-entry tachycardia B) Atrial fibrillation C) Atrial tachycardia D) Ventricular tachycardia •A 65 year old woman with a history of palpitations presents acutely to your rooms with a racing heart beat. • Your practice nurse obtains an ECG • The tachycardia then spontaneously stops • A further ECG is normal • She has a history of hypertension and recently had a TIA with a normal Carotid Doppler The rhythm is: A) Atrial fibrillation B) Atrial tachycardia C) Atrial flutter D) Sinus tachycardia The rhythm is: A) Atrial fibrillation B) Atrial tachycardia C) Atrial flutter D) Sinus tachycardia •A 65 year old woman with a history of palpitations presents acutely to your rooms with a racing heart beat. • Your practice nurse obtains an ECG • The tachycardia then spontaneously stops • A further ECG is normal • She has a history of hypertension and recently had a TIA with a normal Carotid Doppler Her CHA2DS2VASc score is: A) 3 B) 5 C) 4 D) 1 E) 0 A) 3 B) 5 C) 4 D) 1 E) 0 • She had palpitations once before, and was racing to catch a bus • She suddenly had very rapid regular palpitations, and nearly passed out with this –the likely arrhythmia is A) Tachy-brady syndrome with a sinus pause B) Atrial fibrillation C) Ventricular tachycardia D) Atrial flutter with 1:1 conduction • She had palpitations once before, and was racing to catch a bus • She suddenly had very rapid regular palpitations, and nearly passed out with this –the likely arrhythmia is A) Tachy-brady syndrome with a sinus pause B) Atrial fibrillation C) Ventricular tachycardia D) Atrial flutter with 1:1 conduction • A 16 year old boy has minor palpitations • He is fit and healthy • You do an ECG The most common arrhythmia that can happen with this ECG is: A) SVT (orthodromic AV reciprocating tachycardia) B) Atrial fibrillation C) Ventricular fibrillation D) Sinus rhythm The most common arrhythmia that can happen with this ECG is: A) SVT (orthodromic AV reciprocating tachycardia) B) Atrial fibrillation C) Ventricular fibrillation D) Sinus rhythm The worst arrhythmia that can happen with this ECG is: A) SVT (orthodromic AV reciprocating tachycardia) B) Atrial fibrillation C) Ventricular fibrillation D) Sinus rhythm The worst arrhythmia that can happen with this ECG is: A) SVT (orthodromic AV reciprocating tachycardia) B) Atrial fibrillation C) Ventricular fibrillation D) Sinus rhythm DJH Midwinter Christmas Quiz – Spot Prize ?????????????