* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MIDTERM Study packet 2016
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
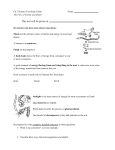
NAME _____________________ DATE _______________ GROUP _____________ To prepare for the Science midterm, complete the following packet with information you know from our class discussions, our Ecology textbook, your notes and your tests, so far, in science. A. There are 5 (sometimes 6) steps to complete the scientific method. What are they? (HINT: Queen Helen Eats Ice Cream) B. When conducting an experiment, there are many variables. If we conducted an experiment to see what kind of soil is best for a bean plant to grow, what would the variables be? a. Independent variable ______________________________ b. Dependent variable _______________________________ c. Constants _______________________________________ C. If I were to keep data on the plants as we conducted this experiment, what is an example of qualitative data that I might include? _________________________ What is an example of quantitative data I might include? ___________________ D. What would be an observation I could make about the plant experiment? __________________________________________________________________ E. What would be an inference I could make about the plant experiment? ___________________________________________________________________ What is the difference between an observation and an inference? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ECOLOGY F. Think about the “foldable” project we made. What is the difference between a population and a community? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ G. Food Web. What is a producer? How do they obtain energy? Give an example. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ A consumer cannot make their own energy rich molecules and must eat other organisms. Herbivores get energy from eating ____________________ . Examples; ________________ Carnivores get energy from eating _____________________. Examples; ________________ Omnivores get energy from eating _____________________. Examples; ________________ Decomposers get energy from eating ___________________. Examples; ________________ H. SYMBIOSIS. A symbiotic relationship is a close relationship between species other than for feeding. What are the three symbiotic relationships we learned and what is the difference between each? Relationship Organism A Organism B example Benefits Benefits Benefits I. Define predator and prey and give two examples of a predator/prey relationship. Predator- _______________________________________________________ Prey - __________________________________________________________ Two examples: __________________________________________________ J. Competition is _____________________________________________________ K. Structural Adaptations – _____________________________________________ a. Examples: i. Feeding__________________________________________________ ii. Movement ______________________________________________ iii. Protection________________________________________________ The NON-LIVING Environment Define biotic and abiotic. Include examples of each. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Climate___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ WATER CYCLE ____________________- process that takes place when a liquid changes to a gas. ____________________ - process that takes place when a gas changes to a liquid. ____________________ - process by which plants give off water vapor through their “pores”. ____________________ - process in which water falls to the earth in the form of rain, snow, hail or sleet. NITROGEN CYCLE Although nitrogen is the most plentiful gas in the atmosphere, most organisms cannot use nitrogen directly from the air. Plants need nitrogen that has been combined with other elements to form nitrogen compounds. This process is called ______________________________. CARBON CYCLE The carbon cycle is critical to life on earth. List some ways Carbon is recycled (added and removed) from the atmosphere. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ HOW ECOSYSTEMS CHANGE After a major event like a volcanic eruption or a forest fire, an ecosystem can build itself up again. Primary Succession – The process of succession that begins in a place without any _________________________. It starts with pioneer species such as lichens that do not need soil to survive. Secondary Succession – The process that occurs faster because it begins in a place that already has _________________. A community that has reached a stable stage of ecological succession is called a _______________________________. BIOMES The largest biome - __________________ The wettest biome -__________________ The most biologically diverse biome-____________________ The driest biome- ___________________________ The northernmost biome- ______________________ CONSERVING RESOURCES – Define and Give examples. NATURAL RESOURCES RENEWABLENON-RENEWABLE1. 2. 3. 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. Alternatives to Fossil Fuels – name four ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ POLLUTANTS How is Acid precipitation formed? What does it affect and how can we prevent it? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ What is the Greenhouse Effect? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ What changes might be caused by global warming? ___________________________________________________________________ What is ozone depletion? Why is it dangerous? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ The three R’s of Conservation are _____________, _____________ & __________ Food Web Producers (examples)– Carnivores(examples)– Herbivores(examples)– Decomposers – ( Are there any in this picture? What are some examples of decomposers?) Energy Pyramid Water Cycle