* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 1: american geography
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
Children's geographies wikipedia , lookup
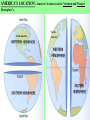
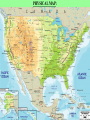
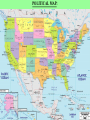
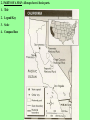
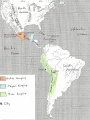
From Sea to Shining Sea GEOGRAPHY OF THE AMERICA’S: *Understanding geography is important to our understanding of the past and present. -Geography is linked to history. -To understand history, you must understand geography. -All of human history has taken place in the environment. Question: What do all 3 events have in common? Answer: ALL 3 took place in the environment. General George Washington at Valley Forge in 1777. Columbus landing in New World in 1492. Erie Canal in New York in the 1800’s. GEOGRAPHY: GEOGRAPHY: The study of the physical, biological, and cultural features of the Earth’s surface. ●Geography is the environment in which we live. ENVIRONMENT: The surroundings in which we live. ●Geography includes: 1. Physical/geographic features 2. Human, animal, and plant life 3. Weather 4. Climate 5. Natural resources Plants and animals are part of the geography. Rivers and mountains are physical or geographic features. Gold, trees, and cotton are examples of natural resources. PHYSICAL FEATURES: (LANDFORMS, GEOGRAPHICAL FEATURES) -Features on the Earth’s surface such as mountains, rivers, lakes, and deserts. NATURAL RESOURCES: Materials humans take from the environment to use to survive. Ex: Plants, Trees, Gold, Oil, Water, Sun WEATHER: The condition of the Earth’s atmosphere at a given time and place. CLIMATE: The average weather of a place over a period of 20-30 years. -Made up of temperature and precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, hail) 5 Themes of Geography: ●To understand geography, historians study the 5 Themes of Geography. 1. Location: Uses Latitude and Longitude lines on maps. 2. Place: 3. Interaction Between People and Their Environment: 4. Movement: 5. Region: 1. Location: Tells where a place is. A. Relative Location: Tells where a place is in relation to another place. Example: Gloversville is 1 hour northwest of Albany, New York. B. Exact (Absolute) Location: Tells where a place is by using Latitude and Longitude lines on maps. LATITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance north and south from the Equator. LONGITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance east and west from the Prime Meridian. Latitude: Lines that run north (above) and south (below) of the equator. They go left to right on the map. Longitude: Lines that run east (right) and west (left) of the Prime Meridian. They run up and down the map. Equator Prime Meridian When you combine the two sets of lines, you get a grid. This allows you to find exact or absolute locations on the Earth’s surface. UNDERSTANDING GEOGRAPHY: AMERICA’S LOCATION: ●The United States is part of North America. ●North America is one of the seven continents on the Earth. 3 1 5 4 6 2 7 AMERICA’S LOCATION: America’s location is in the Northern and Western Hemisphere’s. North North America America 2. Place: Describes an area’s physical and human features. A. Physical Features: (LANDFORMS, GEOGRAPHICAL FEATURES) B. Human Features: Houses, transportation, jobs, language, and religion. 3. Interaction Between People and Their Environment: A. People adapt to their environment by changing the way they live in order to survive. B. People change the environment by physically changing it. Vineyard ●As humans, we can either change our environment, or we have to change to fit into it. Sometimes, humans cannot change the environment. Therefore, humans need to change to fit into and survive in the environment. For example, we cannot change mountains or stop snow from falling. Therefore, we need to change to survive. 4. Movement: Movement of people, goods, and ideas. 5. Regions: An area with certain unifying characteristics. -Physical or human. This picture shows land that has been cleared by humans in order to plant and grow crops. Clearing land and planting crops is an example of humans changing the environment to suit our needs. POLITICAL/SOCIAL REGIONS OF THE UNITED STATES: The United States is broken down into 6 general sections. This breakdown is for political/social purposes. 1. Northeast 3. Midwest 5. Mountain States 2. Southeast 4. Southwest 6. West Mountain States Northeast Midwest West Southeast Southwest MAP: A representation of the features of the Earth or part of the Earth. 1. TYPES OF MAPS: There are 2 main types of maps; physical and political maps. PHYSICAL MAP: A map that shows the physical features, geographical features, or landforms on the surface of the Earth. POLITICAL MAP: A map that shows states, national boundaries, cities, capitals, roads, and other human features. PHYSICAL MAP: POLITICAL MAP: 2. PARTS OF A MAP: All maps have 4 basic parts. 1. Title 2. Legend/Key 3. Scale 4. Compass Rose