* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Air pollution impacts Agriculture
Survey
Document related concepts
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
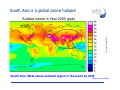
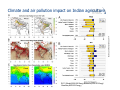
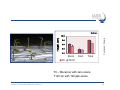
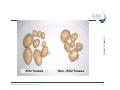
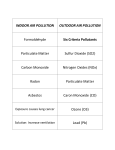
Air pollution impacts Agriculture Maheswar Rupakheti Group Leader Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) Potsdam, Germany Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies e.V. Media regional Training, 18 Nov 2015, ICIMOD, Kathmandu 1 Introduction Agriculture in South Asia in the global context Source: USDA, Nov 2015 Examples (year 2013/14): • South Asia contributes significantly to world crop production (rice, wheat, soybean, cotton, sorghum, oil seeds etc.) • South Asia, particularly vast Indo-Gangetic Plains (highly populated and heavily cultivated region), is one of the heavily polluted regions of the world 2 Introduction Sunlight Air (Carbon dioxide, oxygen, others*) Climatic Conditions (Temperature, humidity, rain) Key air pollutants that affect crops (Soil, water, nutrients) • Ground level ozone (O3) • Particulate matter (PM) • Acidic compounds • Ammonia • Nitrogen and Phosphorous (Nutrients) Medium 3 How does air pollution affect crops/agriculture? Direct effects Indirect effects • Reduction of incoming solar radiation (photosynthetically active radiation, PAR) • Change in climatic conditions (Temperature, humidity, clouds, extreme events) • Deposition of pollutants on plants (aerosols/gases) • Change in hydrological cycle and water availability • Acidification/acid rain • Damage due to ozone 4 How does air pollution affects crops? • Reduction of incoming solar radiation • Change in climatic conditions (temperature, humidity, clouds, extreme events) • Change in hydrological cycle and water availability • Deposition of pollutants on plants • Damage due to ozone 5 Direct effects Monsoon rain Glacier melting Indirect effects Ozone is the main pollutant that affects crops Foliar injury Accelerate senescence (aging) Decrease plant growth Alter plant metabolism Reduce ability to sequester carbon Reduce crop yield KHG-11 Bel-W3 Bel-W3 Courtesy: L. Ainsworth • • • • • • Effects of different levels of ozone on soybean 6 Ozone injury on tobacco plant (Lahore) South Asia is a global ozone hotspot The Royal Society 2008 Surface ozone in Year 2000 (ppb) South Asia: Most ozone polluted region in the world by 2030 (Dentener et al 2006) 7 Source: USDA, www.fas.usda.gov, Courtesy: K. Mahata Ozone seasonal variation and crops cycle in Asia AOT40: accumulated exposure to ozone above 40 ppb = hourly conc.x hours (ppm.h) 8 Ozone impact on crops: Global/Regional 9 CCAC, 2014 Agriculture benefits of ozone mitigation Largest benefits China: 12.7 mil. MT India: 9.8 MMT USA: 6.3 MMT Pakistan:2.1 MMT Brazil:1.6 MMT 10 CCAC, 2014 Aufhammer et al, 2007 Impacts of ABCs & GHGs reductions in rice in India Predicted increases in wet-season rice harvest in Indian in response to reductions in ABCs (PM, O3) and GHGs 11 Burney and Ramanathan, 2014 Climate and air pollution impact on Indian agriculture 12 RYC: [Model(2006-2010avg)-Baseline(2006-2010avg)/ Baseline(2006-2010avg)] Summary • Ground level ozone is the main air pollutant responsible for crop losses [Globally wheat: 7-12%, Soybean: 6-16%, Rice: 3-4%, Corn: 3-5%] Harmens, 2011, • Particulate air pollutant also affects crops in several ways (deposition on leaves, cut down solar radiation, change in clouds and precipitation pattern). • Combined effects/impacts of climate change and air pollution, in particular extreme climate events are yet to be fully understood (further research needed) • Agriculture sector is double-hit by air pollution and climate change. Any efforts to mitigate impacts of air pollution and/or climate change should go simultaneously. • There is urgent need to sensitize through media that reductions in key air pollutants could avoid a substantial amount of crop loses in South Asia. [email protected] Key References: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ramanathan et al,. Atmospheric Brown Clouds: Regional Assessment with Focus on Asia,, UNEP, 2008 UNEP/WMO. integrated assessment of black carbon and tropospheric ozone, UNEP, 2011 CCAC. Time to Act, CCAC/UNEP, 2014 Burney, J. and Ramanathan, V. Recent climate and air pollution impacts on Indian agriculture, PNAS, 2014 Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies e.V. 14 Some remarkable changes in S. Asia N-S Shift in Asian rainfall Weakening Indian monsoon Sahelian drought Observed rainfall during 1950-2002 - Weakened Asian Monsoon (~7%) - 20% decrease in rainfall in Indo-Gangatic plain since 1980s. - Accelerated melting of Hindu Kush-Himalayan-Tibetan glaciers due to BC deposition on snow/ice and atmospheric solar heating. 15 Soybean 9.0 6.0 3.0 0.0 T0 Shoot T120 Root Total Courtesy: U. Chopra Height (cm) 12.0 T0 – filtered air with zero ozone T120: air with 120 ppb ozone Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies e.V. 16 Mung Bean Plant without ozone protection EDU Treated Courtesy: M. Agrawal Mung Bean Plant protected for ozone Non - EDU Treated EDU: Ethylene diurea Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies e.V. 17 Courtesy: M. Agrawal EDU Treated Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies e.V. Non - EDU Treated 18 Effect of 400 ppm EDU treatment on yield parameters of mungbean plants Parameter Non – EDU EDU Seed wt. (g plant-1) 3.30 6.26 Pod wt. ( g plant-1) 5.38 6.90 No. of seeds (plant-1) 85 148 No. of pods (plant-1) 16 31 Yield (g m-2) 223.12 432.65 (Singh et al., 2009, IJEWM, in press) 19 Shindell et al, Science, 2012 Agriculture benefits of O3 & BC mitigation 20