* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle
Cappadocian Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Regions of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek warfare wikipedia , lookup
Greek mythology wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Greek Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek medicine wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
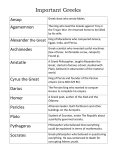
6th Grade UBD - Unit 5 - Greek Cultural Achievements How has classical Greek culture affected our modern lives? Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle- Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle each developed distinctive philosophies. They were similar to and different from other philosophies. Achievements of the Ancient Greeks- The ancient Greeks were responsible for many cultural achievements. These influenced societies around them as well as future civilizations. Alexander the Great- Alexander the Great conquered the Persian Empire. He spread Greek ideas and culture. The philosophies of Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle greatly influenced political and cultural life in ancient Greece. These philosophies were passed on through the ages. They influenced leaders throughout Western history. Philosophy, literature, architecture, and sculpture flourished. As a result, this period came to be known as the Golden Age of Greece. Philosophy, the search for wisdom, became an important part of life in Athens. Greeks built palaces and temples that still stand. The influence of their architecture and sculpture can be seen in many modern buildings and works of art. Socrates, the famous Greek philosopher and teacher, developed a method of teaching that involved asking questions and engaging people in debate. This approach came to be called the Socratic method. Key Term Socratic MethodA method of teaching by question and answer; used by Socrates. Over the years, Socrates attracted many followers. His teachings often opposed commonly held beliefs of Greek society and offended powerful Athenians. Eventually, Socrates was tried in court, convicted of treason, and executed. Socrates did not write down his own ideas, but many of his followers wrote about him and his teachings. His teachings influenced many thinkers throughout the ages. Plato was Socrates’ most important student. He established a school called the Academy that provided instruction in mathematics, science, and philosophy. He also wrote a series of dialogues, which often depicted Socrates debating moral and ethical issues. These works criticized popular views on concepts like justice, courage, and moderation. One of Plato’s most famous dialogues is a work called the Republic, which describes an ideal state. Plato also had a famous student, Aristotle, who analyzed the process of logical thinking and wrote books on many topics, including forms of government. Aristotle thought that monarchies, aristocracies, and democracies all had serious flaws. Because of this, he reasoned that a constitutional monarchy would work best. With this type of government, a constitution limits the power of the monarch. The ancient Greeks developed the first version of democracy. The ancient Greeks developed a complex mythology. It shaped Roman mythology. The Olympic Games began in ancient Greece. The Greek language forms the basis of many English words. Homer wrote the epic poems the Iliad and Odyssey. Greek drama included comedy and tragedy. Ancient Greek thinkers were not just philosophers. Greeks had traded with many civilizations. They traded with Egyptians, Mesopotamians. The Greeks adopted an alphabet. They made coins. They learned innovations. Pythagoras, a mathematician and philosopher. Developed the Pythagorean Theorem, an important and well-known mathematical equation. This famous equation, a2 + b2 = c2, shows the relationship between the sides of a right triangle. It is still used in geometry today. People use it to calculate everything from the heights of tall buildings to the diagonal on a TV screen. Hippocrates was a doctor who lived during the Classical period. He studied the causes of diseases and their possible cures. He also wrote about the roles and responsibilities of doctors to their patients. In one work, Hippocrates wrote an oath. Those who took the oath swore to protect patients from harm. They swore to live an ethical life. Today, doctors still make a similar pledge. It is called the Hippocratic Oath. They make this pledge before they are licensed to practice medicine. One of the best examples of Greek architecture is the Parthenon, a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena. Ancient Greek architecture has had a significant impact on Western architecture. During the classical period, the ancient Greeks also developed sculptures that were natural and lifelike. The ancient Greeks practiced polytheism, or the belief in many gods. They believed in 12 major gods and goddesses, known as the Olympians. The Greeks also believed that their gods and goddesses could speak through certain human priests and priestesses known as oracles. The Greeks consulted these oracles for advice in making decisions. The Greeks thought that their gods and goddesses were involved in their daily lives and sometimes controlled events. Ancient Greek religious beliefs also informed their myths, or stories about heroes and gods that explained the world around them and human behavior. The mythology of ancient Greece impacted other societies in its own time, and still influences world literature today. The ancient Greeks created the Olympics, an athletic competition that was part of a religious festival honoring the god Zeus. At first, the games only involved running a race. Later, other events were added, including longer races, javelin throwing, and jumping. After Rome conquered Greece, the Romans banned the games in 393 CE. However, they were revived in 1896 with the first modern Olympic games in Athens. Since then, the Games have become one of the most important international athletic events in the world. Literature was an important element of Greek culture. The ancient Greeks wrote many types of literature but were most well known for their poetry and drama. The poet Homer is believed to have written the Iliad and the Odyssey, two epic poems. The ancient Greeks also wrote plays, including tragedies and comedies. The Greek language has had a significant impact on English. Many English words are derived from Greek words. English also uses Greek word parts to create words that did not exist in ancient Greek, such as telephone and telescope (using the Greek prefix tele-, which means farseeing). In 336 BCE, Alexander the Great became king of Macedonia, a northern Greek state. Alexander had been a student of Aristotle. From his base in Greece, he conquered many lands and defeated the Persian Empire, creating a great empire. By 331 BCE, Alexander had conquered present-day Turkey, the east coast of the Mediterranean, and Egypt. Alexander went on to conquer Babylon, Susa, and Persepolis. During the fighting, Darius III of Persia was killed and Alexander became the undisputed king of Asia. However, Alexander failed to set up a stable government. After his sudden death in 323 BCE, at age 32, his empire broke apart into several states. But Alexander’s conquests had a lasting effect on the world, as Greek ideas, architecture, and culture spread throughout the Asian lands he conquered. In return, Asian ideas and culture influenced Greece. This intermingling of Greek and Asian cultures produced a unique civilization called the Hellenistic Civilization.