* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell transport in yeast cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
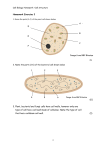
Osmosis and Active Transport in Cells NAME: _______________________________DATE: ________PERIOD: _____ OBJECTIVE: To observe various methods of transport across the membrane of elodea and yeast cells and to differentiate between the types of transport taking place. MATERIALS: elodea leaves yeast suspension salt water solution fresh water solution methyl blue stain Congo Red stain hot plate hot water bath two test tubes two medicine droppers two microscope slides two cover slips digital microscope Motic Images Software PROCEDURE: Part 1 1. Put approximately 20 drops of yeast suspension into each of 2 test tubes. 2. Add four drops of Congo Red Stain to each tube of yeast and mix by swirling the test tube. 3. Place one of the tubes containing yeast and Congo Red in the hot water bath and boil for 10 minutes. 4. Make one wet mount slide of the boiled yeast and one of the unboiled yeast. MAKE SURE THAT YOU DO NOT MIX UP THESE TWO SLIDES! 5. Observe and compare the boiled and unboiled yeast cells under low and then high power of the microscope. (Yeast cells appear as very tiny circles. Large circles with dark outlines are air bubbles!) 6. REMEMBER, USE ONLY THE FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB (THE LITTLE KNOB) TO FOCUS WHEN ON HIGH POWER! 7. Record the color of the yeast cells in Table 1 on the next page. Part 2 1. Prepare a wet mount slide of the elodea leaf stained with methyl blue. 2. Capture an image of the cells on this slide under the highest power possible and save it as a .jpg image called ElodeaStart. 3. Introduce the salt solution under the cover slip while drawing the solution out the other end of the cover slip with a tissue or paper towel. 4. Wait 2 min. and Capture an image of the cells. 5. Save image as a .jpg image called ElodeaSalt. 6. Introduce the freshwater solution under the cover slip while drawing the solution out the other end of the cover slip with a tissue or paper towel. Be sure to use plenty of water in order to wash out the salt solution. 7. Wait 5 min. and Capture an image of the cells. 8. Save image as a .jpg image called ElodeaFresh. NOTE: This lab concerns the transport of materials across a cell membrane. The lab has nothing to do with the movement of the yeast or elodea cells. Yeast and elodea cells have no means of movement. They appear to be moving only because the water molecules are moving. In the boiling water, the water molecules and therefore the yeast cells are moving faster due to the heating. This movement has nothing to do with this lab! FOCUS ON THE COLOR OF THE YEAST CELLS IN THE TWO TUBES and the shape of the elodea cell membranes! TABLE 1 Sample Observations Yeast Boiled Yeast QUESTIONS: 1. What does boiling do to the live yeast cells? (What would boiling do to most living organisms?) 2. How do the boiled yeast appear different from the unboiled yeast cells? 3. Are the cell membranes of the yeast permeable to Congo Red? _______ How do you know? 4. What are the unboiled cells able to do that the boiled cells could not do? 5. Was this lab an example of active or passive transport? Think carefully about this question and explain your answer. 6. What process is at work in the elodea cells? 7. Describe how the elodea cells change shape during the different phases of the experiment. 8. Why don’t the elodea cells burst when they are exposed to the fresh water?