* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology - msfoltzbio
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Cultural ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
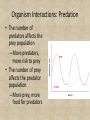
Ecology 2a- Ecology & Living Relationships Principles of Ecology • Ecology – study of relationships between living and nonliving parts of the world • Ernst Haeckel (1866) – first to use the word to name the study of how organisms fit into their environment Interdependence • All organisms interact with… 1. The other organisms around them 2. The nonliving parts of their environment • Survival depends on these interactions. Interdependence White-tailed deer Acorns Humans Deer mouse Deer tick Parts of the Environment • Abiotic factors – non-living parts of an organism’s environment – Air currents, temperature, moisture, light, soil • Biotic factors – all the living things that inhabit the environment Ecological Levels of Organization Organism Population Community Ecosystem Biome Biosphere Niche vs. Habitat vs. Ecosystem • Ecosystem – all the organisms in a given area and the abiotic factors that affect them • Habitat – the place an organism lives out its life • Niche – role and position a species has in its environment – Includes all biotic and abiotic interactions as an organism meets its needs for survival – If two species are competing for the same niche, one will most likely drive the other out and take control of the niche. Niche vs. Habitat vs. Ecosystem An egret lives around Jones Pond which is part of the Smith River Estuary. The egret and its mate eat fish, frogs, salamanders, snakes, crayfish, mice, aquatic insects, crickets, grasshoppers, and a variety of other insects in Jones Pond and build a nest in a tree along side the pond. • What is the egret’s habitat? • What is the egret’s niche? • What is the egret’s ecosystem? Organism Interactions: Predation • The number of predators affects the prey population – More predators, more risk to prey • The number of prey affects the predator population – More prey, more food for predators Organism Interactions: Competition • Competition – Organisms within a population must compete for resources – When populations grow, resources are in higher demand – If demand is greater than supply……population must decrease • Fight and kill each other • Reproduce less Relationships • All living things form relationships with other living things • Symbiotic Relationship – a relationship between organisms of two different species that live together in direct contact Commensalism • One organism benefits – The other is not affected – Examples: • Spanish moss on a tree • Barnacles on a whale • Burdock seeds on a passing animal Mutualism • Both organisms benefit – Acacia tree and ants – tree provides food for the ants and the ants protect the tree from animals that would eat the leaves – Lichens: algae and fungus living together. Algae provides food (photosynthesis) and the fungus provides protection and attaches the lichen to the rock or wood where it lives. - Bacteria living in human intestines: break down nutrients and have a safe environment Parasitism • One organism benefits, the other is harmed – Some live within the host • Tapeworms • Heartworms • Bacteria – Some feed on the external surface of the host • Ticks • Fleas • Mistletoe – Most do not kill their host (at least not quickly) What is this? • Commensalism, Mutualism, or Parasitism? Tube Worms and Hydrothermal Vents Hydrothermal Vent Communities • Symbiotic Relationship: Bacteria live in Tube worms. • Worm has no digestive tract, so it relies on bacteria for nutrition. • Bacteria oxidize hydrogen sulfide that the tube worms supplies to them. • Both need each other to survive so what type of relationship? – Mutualism Hydrothermal Vents are Pretty Rad. Hydrothermal Vents • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BXGF3XS -yAI