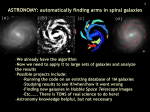
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adolescents with TBI: Commonly Observed Behaviors and Possible
James M. Honeycutt wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Relational aggression wikipedia , lookup
Unpopularity wikipedia , lookup
Social loafing wikipedia , lookup
Social facilitation wikipedia , lookup
Social dilemma wikipedia , lookup
Interpersonal relationship wikipedia , lookup
Communication in small groups wikipedia , lookup
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Adolescents with TBI: Commonly Observed Behaviors and Possible Strategies (Document provided courtesy of Courage Kenny Rehabilitation Institute) Behavior Impulsivity Definition -Acts on impulse instead of thoughts Difficult to filter immediate reactions -Little regard to consequences of the behavior Lack of Initiation -Difficulty starting and/or completing tasks -Getting stuck are starting a task Distractibility -Can appear to be disorganized or unmotivated -Short attention span -Difficulty sustaining attentiveness -Difficulty focusing on one item at a time -Inability to filter out external stimuli Difficulties with Relationships -Difficulty forming and maintaining peer relationships -Difficulty with social interactions, lack of self awareness Coping Skills -Difficulty managing and working through emotions -Reacting impulsively on feelings Independence & Responsibility Issues -Assisting an individual in being realistic of challenges -Working with an individual to learn basic steps towards being independent Examples of Behavior Strategies -Verbal and physical outbursts -Poor boundaries with others -Socially inappropriate reactions or comments to others -Difficulties with food /beverage limits -Difficulties following financial budget -Difficulties with tasks such as: personal care routines, ADL’s, homework, household tasks, etc. -Difficulties with social interactions / communication skills -Provide structure, modify environment -Planning ahead for events, role-play situations -Reviewing expectations -Supervision -Providing written or verbal cues -Limiting options -Setting short-term goals -Timeouts -Positive feedback for appropriate behavior -Stop and Think cue -Stopping conversation in mid-sentence -Modify environment to minimize sudden changes -Limit possible external distractions -Focusing on one task at a time -Setting short-term goals / Break things into small amounts of time -Provide positive feedback -Stop and Think cue -Focusing on background sounds -Focusing on a particular object/ item/person with difficulty redirecting -Establishing schedules, checklists, calendars,etc. -Break tasks into small steps -Establish and maintain consistent routine -Attainable reinforcement programs -Identifying and building off success -Positive feedback -Slowly increase accountability -Provide triggers/cues to begin tasks Personality traits and difficulty interacting with others who may have personality traits that are similar or completely opposite. -Poor social skills. -Poor personal space. -Difficulty knowing how to interact with others in a socially appropriate manner -Structured social group either within school or an agency working on peer interaction and basic social skills. -School working to set up activities -Involving young people in team athletics to increase teamwork. -Role playing general skills. -Modeling social skills during activities. -Anger/stress management -Time Management -Emotional expression -Understanding how to react in a way that is socially acceptable. -Teaching relaxation techniques. -Utilizing things around the individual’s space and environment that can assist with being overwhelmed or anxious. -General body awareness (i.e. Engine level) model. -Use of feeling cards/pictures/and individual’s cues. -Difficulty grasping a full -Working with parents and caregivers to support the understanding of the steps it takes to be independent. -Safety and vulnerability. -Setting personal priorities. -Slow progress is okay and typical of transitioning. individual however not do things for the individual. -Working on understanding basic skills for independent living. -Setting up checklists and daily routines. -Normalizing the struggle to be independent. -Modeling and role playing skills. -Clearly outline consequences that may accompany the lack of routine