* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regents Review - Ancient Greece
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Acropolis of Athens wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
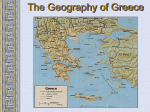
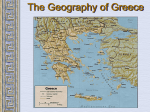
By: Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley H.S. Chappaqua, NY EDITED: Mr. Stonehill - THHS The Geography of Greece Questions • What seems to be the main “areas” of the Classical Greek world? • Where might potential enemies/rivals of Greece arise from? Bronze Age Greece Crete: Minoan Civilization (Palace at Knossos) Knossos: Minoan Civilization Minoan Civilization The Mycenaean Civilization Homer: The “Heroic Age” The Mask of Agamemnon Questions • What features of Archaic Greek culture do we associate with Western culture? ATHENS: Yesterday & Today Piraeus: Athens’ Port City Questions • Why is a port city necessary for Athens? Early Athenian Lawgivers $ Draco – initial dictator “draconian” $ Solon “law giver” $ Cleisthenes created the first democracy! Persian Wars: 499 BCE – 480 BCE Persian Wars: Famous Battles $ Marathon (490 BCE) 26 miles from Athens – Greeks defeat Persians $ Thermopylae (480 BCE) 300 Spartans at the Mountain pass – eventually Xerxes conquers Athens, burns it and leaves $ Salamis (480 BCE) Athenian navy victorious over Persians leading to “stalemate” Athens - Golden “Age of Pericles”: 460 BCE – 429 BCE Great Athenian Philosophers $ Socrates Know thyself! question everything only the pursuit of goodness brings happiness. $ Plato The Academy The world of the FORMS The Republic philosopher-king Great Athenian Philosophers $ Aristotle The Lyceum “Golden Mean” [everything in moderation]. Logic. Scientific method. Athens: The Arts & Sciences $ DRAMA (tragedians): Aeschylus Sophocles Euripides $ THE SCIENCES: Pythagoras - mathematician Democritus all matter made up of small atoms. Hippocrates “Father of Medicine” Architecture - Phidias’ Acropolis The Acropolis Today The Parthenon The Agora The Classical Greek “Ideal” – emphasis on human body – accuracy in art as well Olympia – human sport and the emphasis of what the human body can achieve The Ancient Olympics: Athletes & Trainers Olympia: Temple to Hera The 2004 Olympics Questions • What aspects of Athenian culture would you consider Western Culture? • Define art (how does it work, its materials, its subject matter, how does it look, etc.) in the Golden Age of Athens. SPARTA SPARTA Helots Messenians enslaved by the Spartans. Peloponnesian Wars Macedonia Under Philip II Questions • How was Sparta and its allies able to defeat Athens and the Delian League? • How was Macedonia able to conquer the rest of Classical Greece? Alexander the Great Alexander the Great’s Empire Alexander the Great in Persia The Hellenization of Asia Pergamum: A Hellenistic City The Economy of the Hellenistic World Hellenistic Philosophers $ Cynics Diogenes ignore social conventions & avoid luxuries. citizens of the world. live a humble, simple life. $ Epicurians Epicurus avoid pain & seek pleasure. all excess leads to pain! politics should be avoided. Hellenistic Philosophers $ Stoics Zeno nature is the expansion of divine will. concept of natural law. get involved in politics, not for personal gain, but to perform virtuous acts for the good of all. true happiness is found in great achievements. Hellenism: The Arts & Sciences $ Scientists / Mathematicians: Aristarchus heliocentric theory. Euclid geometry Archimedes pulley $ Hellenistic Art: More realistic; less ideal than Hellenic art. Showed individual emotions, wrinkles, and age! The Breakup of Alexander’s Empire