* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Cardiac Ultrasound
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
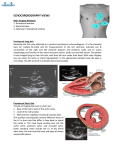
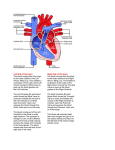
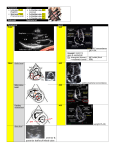
Intro to Bedside Ultrasound Cardiac Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina Trevor Plescia Jack Silva [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Aorta Pulmonary trunk Left ventricle Pericardium Right ventricle The 4 Views of Cardiac Ultrasound PARASTERNAL LONG PARASTERNAL SHORT APICAL 4-CHAMBER SUBXIPHOID (SUBCOSTAL) Parasternal Short Parasternal Long Apical 4-Chamber Right Subxiphoid CARDIAC ULTRASOUND TRANSDUCERS Phased Array (P21) Convex (C60) • The best transducer for viewing the heart is the phased array P21 • The convex C60 can also be used PARASTERNAL LONG - - Start with the probe just to the left of the sternum (parasternal), in the 2 nd intercostal space The indicator should be pointed to the patient’s left hip This will give a view of the heart along its long axis What is the arrow pointing to? Left Ventricle What is the arrow pointing to? Right Ventricle What is the arrow pointing to? Interventricular septum What is the arrow pointing to? Pericardium What is the arrow pointing to? Aortic Outflow Tract What is the arrow pointing to? Mitral Valve Left Atrium 17 Mitral Valve (Anterior Leaflet) Mitral Valve (Anterior Leaflet) LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION - In parasternal long axis, observe movement of mitral valve - Anterior leaflet should slap interventricular septum - Observe left ventricular contraction during systole - Deficiencies indicate poor left ventricular function - Avoid fluid overload HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY - Normal septum thickness: 0.8 – 1.2 cm - >1.2 cm – HCM - Each tick mark = 1 cm - Useful for estimation - Use calipers to make exact measurement ATHLETE’S HEART VS HCM Athlete’s Heart (Benign Enlargement) HCM Septum Thickness <15 mm >15 mm Symmetry Yes (for septum and LV wall) No (septum much thicker) Deconditioning Reduction within 3 months None PARASTERNAL SHORT - Start in the parasternal long axis (indicator pointed to patient ’s left hip) - Then rotate the probe 90° clockwise so that the indicator is pointed to the patient’s right hip PARASTERNAL SHORT - Once positioned, use the fanning technique to view different structures: Initially you will see the mitral valve, which resembles a “fish mouth” Fan inferiorly to see the papillary muscles and the apex - - - You may also see the chordae tendineae Fan superiorly, to see the aortic valve, which resembles the “Mercedes-Benz” logo Mitral Valve: “Fish Mouth” Fan inferiorly to see papillary muscles Fan superiorly to see the aortic valve Aortic Valve: “Mercedes-Benz” QUESTION From the parasternal short view, how would you manipulate the transducer to visualize the aortic valve? Fan superiorly APICAL 4-CHAMBER - - Start with the transducer over the patient’s Point of Maximal Impulse or PMI (4 th or 5 th intercostal space, midclavicular or anterior axillary) Point the indicator to the patient’s right APICAL 4-CHAMBER - Fan the probe superiorly toward the base of the heart Assess the size of the ventricles. The right ventricle should be approximately 2/3 the size of the left ventricle. The apical 4-chamber view can be hard to find on patients in a supine position - - Try the left lateral decubitus position, as it brings the heart closer to the thoracic cage APICAL 4-CHAMBER Tricuspid valve RV RA LV LA Mitral valve SUBXIPHOID - Indicator pointed to patient’s right SUBXIPHOID VIEW The subxiphoid view is useful clinically for: • Diagnosing pericardial effusion • The pericardium is a high attenuating structure, and will appear hyperechoic. Fluid will be hypoechoic. • Diagnosing cardiac arrest • FAST scan SUBXIPHOID TRICK Start at liver edge and follow subcostal margin until heart is seen Aim beam at chin Subxiphoid Tricuspid Valve RV Pericardium LV RA LA Mitral Valve PERICARDIAL EFFUSION - Fluid in the pericardial sac Increased intrapericardial pressure can disrupt cardiac rhythm and efficiency Cardiac tamponade SUMMARY Cardiac ultrasound utilizes 4 different views: 1) Parasternal long 2) Parasternal short 3) Apical 4-chamber 4) Subxiphoid The indicator is pointed to the patient ’s right in all views except for parasternal long, where it is pointed to the patient ’s left hip SUMMARY Structures visible in each view Parasternal long: interventricular septum, left ventricle, mitral valve, aortic valve, aortic outflow tract, and right ventricle In a normal heart, the mitral valve’s anterior leaflet will make contact with the interventricular septum Parasternal short: aortic valve, mitral valve, and papillary muscles Apical 4-chamber: all 4 chambers of the heart Subxiphoid is good for assessing pericardial effusion REFERENCES Atlas of Anatomy, Second Edition, By Gilroy, MacPherson, Ross, Schuenke, Schulte, Schumacher. Thieme Medical Publishers, 2012. Select images from the UCISOM Ultrasound in Education Department