* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Windows Server 2012 Dynamic Access Control Deep Dive for Active
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Outlook.com wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Trusted Computing wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
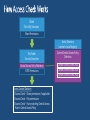
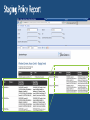
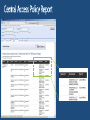
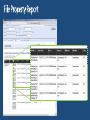
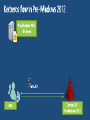
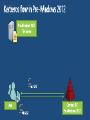
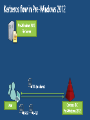
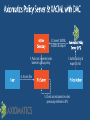
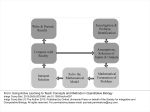
Expression-based access policy File Server AD DS User claims User.Department = Finance User.Clearance = High Device claims Device.Department = Finance Device.Managed = True Resource properties Resource.Department = Finance Resource.Impact = High ACCESS POLICY Applies to: @File.Impact = High Allow | Read, Write | if (@User.Department == @File.Department) AND (@Device.Managed == True) 4 User and Device Claims • User and computer attributes can be used in ACEs Expression-Based ACEs • ACEs with conditions, including Boolean logic and relative operators Classification Enhancements • File classifications can be used in authorization decisions • Continuous automatic classification • Automatic RMS encryption based on classification Central Access and Audit Policies • Central authorization/audit rules defined in AD and applied across multiple file servers Access Denied Assistance • Allow users to request access • Provide detailed troubleshooting info to admins Pre-2012: Security Principals Only • • • • • Restricted to making policy decisions based on the user’s group memberships Shadow groups are often created to reflect existing attributes as groups Groups have rules around who can be members of which types of groups No way to transform groups across AD trust boundaries No way to control access based on characteristics of user’s device Windows Server 2012: Security Principals, User Claims, Device Claims • • • • • Selected AD user/computer attributes are included in the security token Claims can be used directly in file server permissions Claims are consistently issued to all users in a forest Claims can be transformed across trust boundaries Enables newer types of policies that weren’t possible before: • Example: Allow Write if User.MemberOf(Finance) and User.EmployeeType=FullTime and Device.Managed=True Pre-2012: ’OR’ of groups only • Led to group bloat • Consider 500 projects, 100 countries, 10 divisions • 500,000 total groups to represent every combination: • ProjectZ UK Engineering Users • ProjectZ Canada Engineering Users [etc…] Windows Server 2012: ‘AND’ in expressions • ACE conditions allow multiple groups with Boolean logic • Example: Allow modify IF MemberOf(ProjectZ) AND MemberOf(UK) AND MemberOf(Engineering) • 610 groups instead of 500,000 Windows Server 2012: with Central Access Policies • 3 User Claims Resource Property Definitions 3rd party classification plugin In-box content classifier Resource Property Definitions See modified / created file Save classification FCI 3rd party classification plugin In-box content classifier Resource Property Definitions See modified / created file Save classification For Security FCI 3rd party classification plugin In-box content classifier Resource Property Definitions See modified / created file Save classification FCI For Security Match file to policy File Management Task 3rd party classification plugin In-box content classifier Resource Property Definitions See modified / created file Save classification FCI For Security Match file to policy File Management Task CA DataMinder integrates with Windows Server 2012 CA Technologies Content-Aware Identity & Access Management Control identity, control access and control information CA DataMinder discovers, classifies and controls information Controls Collaboration & File Sharing Environments SharePoint 2010 – March 2012 Windows Server 2012 Dynamic Access Control – July 2012 Delivers precise & fine-grained access control Copyright © 2012 CA. All rights reserved. No unauthorized copying or distribution permitted. Supercharge DAC with automated file classification A leader in automatic file classification Enables accurate automated file classification enterprise-wide with both attribute-based and content-based classification For more information visit us at Booth 230 (Orlando) / PP17 (Amsterdam) or at www.dynamic-access-control.com Deeply integrated with Windows Server 2012. dg classification can also be used to fuel powerful Governance, Compliance and Archiving solutions Share Permissions NTFS Permissions Access Control Decision Share Permissions NTFS Permissions Central Access Policy Access Control Decision Share Security Descriptor Share Permissions File/Folder Security Descriptor Central Access Policy Reference NTFS Permissions Access Control Decision: 1) Access Check – Share permissions if applicable 2) Access Check – File permissions 3) Access Check – Every matching Central Access Rule in Central Access Policy Active Directory (cached in local Registry) Cached Central Access Policy Definition Cached Central Access Rule Cached Central Access Rule Cached Central Access Rule Classifications on File Being Accessed Permission Type Department Engineering Sensitivity High Target Files Share Permissions Everyone:Full Engineering FTE Engineering Vendor Sales FTE Full Full Full Central Access Rule 1: Engineering Docs Dept=Engineering Engineering:Modify Everyone: Read Modify Modify Read Rule 2: Sensitive Data Sensitivity=High FTE:Modify Modify None Modify Rule 3: Sales Docs Dept=Sales Sales:Modify NTFS FTE:Modify Vendors:Read Effective Rights: [rule ignored – not processed] Modify Read Modify Modify None Read www.jijitechnologies.com [email protected] User claims Clearance = High | Med | Low Company = Contoso | Fabrikam Resource properties Department = Finance | HR | Engg Impact = High | Med | Low Current Central Access policy for high impact data Applies to: @File.Impact = High Allow | Full Control | if @User.Company == Contoso Staging policy Applies to: @File.Impact = High Allow | Full Control | if (@User.Company == Contoso) AND (@User.Clearance == High) Proposed Central Access Policy does not grant the same access permissions as the current Central Access Policy Subject: Object: Security ID: Account Name: Account Domain: Object Server: Object Type: Object Name: CONTOSODOM\alice alice CONTOSODOM Security File C:\FileShare\Finance\FinanceReports\FinanceReport.xls Current Central Access Policy results: Access Reasons: READ_CONTROL: Granted by Ownership ReadAttributes: Granted by D:(A;ID;FA;;;BA) Proposed Central Access Policy results that differ from the current Central Access Policy results: Access Reasons: READ_CONTROL: NOT Granted by CAR “HBI Rule” ReadAttributes: NOT Granted by CAR “HBI Rule” Enterprise-wide visibility into server and application health 2012 Token User Account User Pre-2012 Token User Account User Groups [other stuff] Groups Claims Device Groups Claims [other stuff] NT Access Token User Contoso\Alice Claim type Groups:…. Display Name Source Claims: Title=SDE Suggested values Value type Kerberos Ticket Contoso\Alice User Groups:…. Claims: Title=SDE First Claim User Claims Set Compound-ID Claims Sets 1 Boolean Claim 5 Claims: • 1 Boolean • 1 Integer • 2 String – Single Valued • Avg Len/value: 12 chars • 1 String – Multi Valued • Avg Len/value: 12 chars • Avg #Values: 6 values User - 5 Claims: • 1 Boolean • 1 Integer • 2 String – Single Valued • Avg Len/value: 12 chars • 1 String – Multi Valued • Avg Len/value: 12 chars • Avg #Values: 6 values Adds 242 Bytes Bytes Before Compression 120 user overhead 120 device overhead 114 per int/bool claim 8 per int/bool value 138 per string claim 2 per string character Adds 970 Bytes Worst-Case Analysis (assumes no compression): Gives us confidence that claims and compound-ID should not result in huge spikes of ticket sizes in most environments. Device - 2 Claims: • 1 Boolean • 1 String – Single Valued • Avg Len/value: 12 chars Adds 1374 Bytes of Claims Data + Computer Group’s AuthZ Data Windows Server 2012 Active Directory Access Policy Windows Server 2012 File Server End User Microsoft SharePoint 2010 2. Convert XACML to SDDL & import 3. Push out imported rules based on group policy 1. Author policy & export to AD 4. Access files 5. Check access based on rules previously defined in APS Current infrastructure Windows Server 2012 File Servers • Access and Audit Policies based on security groups and file tagging Windows Server 2012 DCs • Centrally defined access and audit policies • User claims can be used by access and audit policies Windows 8 clients • Add device claims to access and audit policies • Better access denied experience #TE(sessioncode) DOWNLOAD Windows Server 2012 Release Candidate Hands-On Labs microsoft.com/windowsserver DOWNLOAD Windows Azure Windowsazure.com/ teched http://northamerica.msteched.com www.microsoft.com/learning http://microsoft.com/technet http://microsoft.com/msdn
























































![Did You Know? SQL Server 2008 * [Feature]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002454547_1-127f1f83c4aa125339e9dfae02309208-150x150.png)



