* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ramesh M. Gowda, MD
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac arrest wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
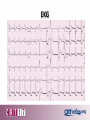
Ventricular Fibrillation Cardiac Arrest During Exercise Stress Testing: A Case Study in the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death Dr. Ramesh M. Gowda, M.D. The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai Beth Israel Ramesh M. Gowda, M.D. I have no relevant financial relationships Learning objectives 1. To elucidate the rare, yet significant, risk of sudden cardiac death during exercise stress testing. 2. To discuss the management of a case of ventricular fibrillation arrest during exercise stress testing. Clinical Presentation • 71 year old male, with a history of coronary artery disease with percutaneous coronary intervention 4 years prior, underwent a routine exercise stress test. – Completed 6 minutes – Developed significant dyspnea • 2 mm ST depressions in the inferolateral leads and ST elevation in aVR. • The exercise stress test was stopped • Upon sitting in a stretcher thereafter – ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest. EKG Clinical Presentation • He was successfully defibrillated and transferred to the nearest emergency room. • On arrival, he was awake and alert but having chest pain. EKG Clinical Presentation • The exercise stress test was stopped • Upon sitting in a stretcher thereafter – ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest. • He was successfully defibrillated and transferred to the nearest emergency room. • On arrival, he was awake and alert but having chest pain. Cath video • He underwent emergent invasive angiography, which revealed: – a distal left main 85% focal calcified stenosis involving the ostial LAD – patent stents in the proximal and mid LAD – an 80% ostial diagonal lesion – 100% ostial left circumflex (LCx) disease – 95% distal RCa lesion Cath video The presentation, including videos, was too large to attach (as stated in the emails to [email protected] and [email protected]) - however the complete presentation was emailed thank you for your consideration. Cath video The presentation, including videos, was too large to attach (as stated in the emails to [email protected] and [email protected]) - however the complete presentation was emailed thank you for your consideration. Cath video The presentation, including videos, was too large to attach (as stated in the emails to [email protected] and [email protected]) - however the complete presentation was emailed thank you for your consideration. Clinical Presentation • At this time, the decision was made to consult cardiac surgery. – However, the patient continued to have chest discomfort despite IV nitroglycerin, IV heparin and integrillin bolus. • Because of this unstable situation, urgent PCI of left main was done. Cath video The presentation, including videos, was too large to attach (as stated in the emails to [email protected] and [email protected]) - however the complete presentation was emailed thank you for your consideration. Clinical Presentation • The patient was chest pain free at the end of the procedure and transferred to the CCU in stable condition. • Because of the severity of the patient’s remaining coronary disease, a heart team discussion was had and coronary artery bypass graft surgery was scheduled for the next week. • Meanwhile, the patient was monitored in the CCU with an intraaortic balloon pump and on heparin and aggrastat infusion. He did well post surgery. Take Home Messages • Although the risk of cardiac arrest during exercise stress testing is small, it does exist. • Patients who have ischemic ECGs post resuscitation should be taken for invasive angiography as the likelihood of an ischemic cause is high. • Decisions regarding revascularization strategies should then be made with a heart team approach on a case by case basis.