* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Asia Tsumani Disaster
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Dec 26, 2004 Tsumani Disaster
What happened and why
The Source: A Great Earthquake
In order to understand
what happened and why it
happened, we must
understand the Earth, its
processes, and the nature
of waves: Physical
Geology
What happened
– A very large earthquake
(great earthquake) moved
the ocean floor
– The movement of the ocean
floor, displaced a large
amount of water
– The water wave generated
by the displacement
propagated throughout the
ocean
– The wave, similar to a very
fast tide, overcame many
low lying areas
Plate tectonics
Earth's outer shell made up of ~15 major rigid plates ~
100 km thick
Plates move relative to each other at speeds of a few cm/ yr
(about the speed at which fingernails grow)
Plates are rigid in the sense that little (ideally no)
deformation occurs within them,
Most (ideally all) deformation occurs at their boundaries,
giving rise to earthquakes, mountain building, volcanism,
and other spectacular phenomena.
Style of boundary and intraplate deformation depends on
direction & rate of motion, together with thermomechanical structure
Earth’s Tectonic Plates
At boundaries:
earthquakes,
volcanoes, mountains
Each drifting in
different directions
The Earthquake
India subducts beneath
Burma microplate
at about 50 mm/yr
Earthquakes occur at plate
interface along the
Sumatra arc (Sunda
trench)
These are spectacular &
destructive results of
many years of
accumulated motion
INTERSEISMIC:
India subducts beneath
Burma microplate
at about 50 mm/yr
Fault interface is locked
Displaces Water in Ocean
EARTHQUAKE
(COSEISMIC):
Fault interface slips,
overriding plate
rebounds, releasing
accumulated motion
HOW OFTEN:
Stein & Wysession, 2003
Fault slipped ~ 10 m = 10000 mm; 10000 mm / 50 mm/yr = 200 yr
Longer if some slip is aseismic
Faults aren’t exactly periodic for reasons we don’t understand
The Size: Magnitude 9
Earthquakes rupture a patch along
fault's surface (like a crack in a
mirror).
Generally speaking, the larger the
rupture patch, the larger the
earthquake magnitude.
Initial estimates from the aftershock
distribution show the M 9.0 SumatraAndaman Islands Earthquake
ruptured a patch of fault roughly the
size of California, and modeling
seismic waves show that most of the
slip occurred in the southern 400 km
of the patch.
For comparison, a magnitude 5
earthquake would rupture a patch
roughly the size of New York City's
Central Park
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE 9
Stein & Wysession after IRIS
One of the largest earthquakes since seismometer invented
~ 1900
TSUNAMI - water wave generated by earthquake
NY Times
Tsunami
generated
along fault,
where sea floor
displaced, and
spreads
outward
Reached Sri
Lanka in 2 hrs,
India in 2-3
QuickTime™ and a
Photo decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
NOAA
Movies
IN DEEP OCEAN tsunami has long wavelength, travels fast,
small amplitude - doesn’t affect ships
AS IT APPROACHES SHORE, it slows. Since energy is
conserved, amplitude builds up - very damaging
TSUNAMI WARNING
Deep ocean buoys can measure
wave heights, verify tsunami and
reduce false alarms
Because seismic waves travel much
faster (km/s) than tsunamis, rapid
analysis of seismograms can identify
earthquakes likely to cause major
tsunamis and predict when waves will
arrive
The Damage:
Banda Aceh,
North Shore
Before
After
Gleekbruk Village
IK Aceh
“CIVILIZATION EXISTS
BY GEOLOGICAL
CONSENT”
The same geologic processes
that make our planet
habitable also make it
dangerous
Can We Predict Earthquakes?
Because little is known about the fundamental
physics of faulting, many attempts to predict
earthquakes searched for precursors, observable
behavior that precedes earthquakes. To date,
search has proved generally unsuccessful
Best to develop hazard reduction
– United States Geological Survey
» National Earthquake Hazard Reduction Research Program
» Seismic Networks: Volcanic and Eartquake Warning Systems
– National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
(NOAA) National Warning Centers
» Pacific Tsunami Warning Center in Ewa Beach, Hawaii
» The Alaska Tsunami Warning Center ATWC) in Palmer,
Alaska
PLATE TECTONICS IS
DESTRUCTIVE TO HUMAN
SOCIETY
Mt Saint Helens
1980 eruption
USGS
1989
Loma Prieta
earthquake
BUT PLATE TECTONICS
IS ALSO CRUCIAL FOR
HUMAN LIFE
Plate boundary volcanism produces
atmospheric gases (carbon dioxide
CO2 ; water H2O) needed to support life
and keep planet warm enough for life
("greenhouse" )
May explain how life evolved on earth
(at midocean ridge hot springs)
Plate tectonics raises continents above
sea level
Plate tectonics produces mineral
resources including fossil fuels
Press & Siever
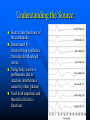
Understanding the Source
Source time functions of
the earthquake
Determined by
deconvolving synthetics
from data for Rayleigh
waves
Using body waves is
problematic due to
duration (interference
causes by other phases)
Used both empirical and
theoretical Green’s
functions
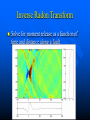
Inverse Radon Transform
Solve for moment release as a function of
time and distance along a fault