* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solar System Vocabulary
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
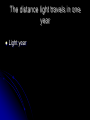
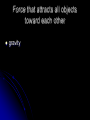
Solar System Vocabulary Composed of dust, rock and frozen gases; has a coma, nucleus, and tail comet Large ball of burning gas; fueled by nuclear fusion star Red planet; would take astronauts 3 years to get here and back. Mars The sun and all the objects orbiting it. Solar system Orbits another celestial body in space satellite Why do stars that are larger and brighter than the sun not appear this way from Earth? They are farther away Orbits a planet moon Sentenced to house arrest for his beliefs about the solar system Galileo Gas giant; large, blue-green; similar to Uranus Neptune Greenhouse effect; hottest planet Venus Large group of stars, gas and dust held together by gravity galaxy The distance light travels in one year Light year Closest planet to the sun; heavily cratered Mercury Every object exerts gravity on every other object in the universe. Universal Law of Gravitation Pluto; does not meet all criteria to be a planet Dwarf planet A meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere meteor A meteoroid that strikes Earth’s surface Meteorite Small pieces of rock moving in space Meteoroid Developed the sun centered model of the solar system Copernicus The distance from the Sun to Earth Astronomical unit Planet known for many rings Saturn Force that attracts all objects toward each other gravity Between Mars and Jupiter Asteroid belt Water exists in all three states on the surface; suitable for life Earth Planets beyond the asteroid belt; large and gaseous Outer planets Rocky/terrestrial planets with thin atmospheres Inner planets Largest planet Jupiter