* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 Plant Characteristics Booklet Student Name
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
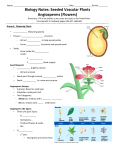
Plant Characteristics Booklet Student Name __________________________ 1 When scientists find an unknown plant, they first look and see if it has a vascular system. This helps them classify the plant. After looking for a vascular system, scientists look to see if the plant reproduces by spores or seeds. Vascular or Non-vascular? Reproduce with spores or seeds? Characteristics of plants that make spores: Smaller than seed-producing plants Usually have no flowers Reproduce with spores Examples include mosses and ferns!! Characteristics of plants that make seeds: Plants make flowers because seeds grow inside of flower Flower will turn into a fruit, which encloses the completely grown seeds Examples include trees, shrubs, flowers, fruits, vegetables 2 Examples include mosses and ferns!! Scavenger Hunt! Find an example of a plant that reproduces with spores and glue it in the box below. Find an example of a plant that reproduces with seeds and glue it in the box below. PLANT WITH SPORES PLANT WITH SEEDS What are the characteristics of spore-bearing plants? 1. 2. 3. What are the characteristics of seed-bearing plants? 1. 2. ******Plant Riddles ******** * I am a plant with beautiful white flowers. Tucked inside my flowers are tiny reproductive structures. Are these structures seeds or spores? 3 I am a Boston fern. Do I reproduce with seeds or spores? I am a rose bush. Do I reproduce with seeds or spores? I am a lovely green plant. I have reproductive structures on the undersides of my fronds. Sadly, I do not have any flowering structures. Will I reproduce with seeds or spores? We have already talked about the first two ways that plants are classified: Vascular or Non-vascular? Reproduce with spores or seeds? Third way scientists classify plants is by asking if seeds are made in cones or flowers Seeds are made in cones or flowers? Characteristics of cone plants Sometimes they’re called conifers or evergreens Have needle-like leaves Never have flowers Produce the seeds in cones Some cones are female, some are male Examples include pine trees, spruce, redwoods, junipers, and cedar trees 4 Match it up! Match up the plant with its characteristics. Draw a line from the plant to the correct characteristics. Has seeds created in flowers Produces seeds in cones; sometimes called a conifer Reproduces with spores What are the characteristics of cone plants? Vascular or Non-vascular? Reproduce with spores or seeds? Seeds are made in cones or flowers? Fourth way scientists classify plants is by opening the seed and counting the “seed leaves” Number of seed leaves (1 or 2)? 5 Seed Leaves The seed leaves are located inside of the seeds. They’re not leaves at all! These seed leaves have another name as well. Sometimes they’re called cotyledons. The purpose of the seed leaf (cotyledon) is to provide nourishment for the baby plant. It is the stored food for that growing baby plant. A baby plant is called the embryo. Why do you think they’re called seed leaves if they’re not really leaves? There’s no right or wrong answer. What do you think? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _________________ If a plant has one seed leaf or cotyledon, then it’s called a monocot. Mono = one, cot = short for cotyledon If a plant has two seed leaves or cotyledons, then it’s called a dicot. Di = 2, cot = short for cotyledon Parts of a seed: Seed coat Cotyledon or seed leaf Embryo Notice how the stored food is pointing to the same area as the cotyledon. That’s because they are the same thing! SEED COAT Protective covering for embryo and the food; keeps seed from drying out & protects embryo COTYLEDON Also called seed leaf; provides food for growing embryo EMBRYO Baby plant 6 Hey, what’s the deal with these monocots, anyway? A monocot has one seed leaf. It has one piece of stored food for its little embryo. All monocots share the same characteristics. Check it out! Increase your plant-itude! Hey, what’s the deal with these dicots, anyway? Look at the illustration above. All dicots share the same characteristics. Look above at these characteristics! Wow! Is it a monocot or a dicot? Write your answer next to the clue below. Vascular tissue neatly bundled Flower with 10 petals Flower with 3 petals Grass Flower with 20 petals Flower with 6 petals Vascular tissue is scattered Flower with 9 petals Flower with 16 petals 7 Seeds need to leave the parent plant so that they won’t compete for water & sunlight with other plants. They leave the parent plant in 3 main ways: 1. Wind (winged seeds) 2. Animals 3. Water Once a seed leaves the parent plant, it can either lay dormant OR germinate. If a seed lays dormant, that means it will wait until growing conditions are just right for it to grow. If a seed germinates, then it begins to grow. The roots grow down and stem & leaves grow up. This is called the process of germination. 8 Thorns for keeping animals from eating it Poisons to keep animals from eating Ability to close leaves when touched (thigmotropism) Sleeping Grass Mimosa Puddica Plant Processes Photosynthesis Process of a plant making food (glucose) from radiant energy; uses carbon dioxide & releases oxygen Gas exchange Take in carbon dioxide & release oxygen through stomata Respiration Changing food into energy by using oxygen Transpiration Loss of water vapor through the stomata on leaves 9 Cross section of a leaf Stomata (little doorways on leaf that open and close, allowing water vapor & oxygen to escape). The stomata open and close by means of the guard cells. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and carry on photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process in which plants use energy from light to produce ____. a. new cells c. Food b. organelles d. none of the above Respiration is the process in which organisms break down food to release ____. a. energy c. Sugar b. nutrients d. Oxygen Transpiration is part of the water cycle, too! Remember?? It is when _______ ________ is lost through leaves. Leaves are the site of photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration. 10 Stems hold up leaves to the sunlight so that food can be produced. Stems give support to the plants. They can also store food! Roots are used to anchor the plant and absorb water & nutrients from the soil. The greater surface area of the root, the better it absorbs water & nutrients. Fibrous Roots Tap Roots Small structures called root hairs help increase that surface area on roots to make absorption better! Flowers are the reproductive part of the plant and have female and male structures. In order for seeds to develop, the male “pollen” must travel to the female parts of the flower. This is quite a feat for an organism that can’t move! Pollination is when the pollen successfully travels to the female part of the flower and begins traveling through the flower to make the seed. It can occur by insects, animals, wind – even you! 11 Below are the parts of the flower: Male Female Stamen = “men” – boy part of the flower where pollen is located anther filament Pistil = girl part of the flower where pollen needs to go in order for a seed to be made stigma style ovary THE NEW SEED IS FORMED IN THE OVARY, AND THE OVARY BECOMES THE FRUIT! 12 Fill in the flower parts. Color the female parts pink & the boy parts should be colored blue. Draw a stork by the ovary! 13