* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Asexual Reproduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
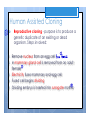
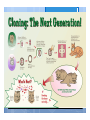
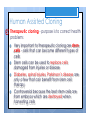
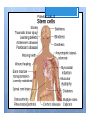
Types of Asexual Reproduction 2. BUDDING yeast When areas of some y multicellular organisms (ex. hydra, sponge) undergo repeated mitosis to form an identical organism. Buds sometimes detach to form a separate organism. Offspring y = . Bud Human 9 methods assisted Cutting Cut : a piece Condition 2 Grafting : scion is of of vegetable reproduction plant and it place in a . growing . removed and Attached to rootstock 83¥ gTI .se?swea e%St [ } roots stock scion • . graft DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 5 New Plants from Grafting CLASS: BLM 2-22 Copyright © 2007, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. Types of Asexual Reproduction 5. SPORE FORMATION Ex ) mushroom mold When some bacteria, micro-organisms and fungi can form spores - single cells that can grow into a whole new organism. through mitosis . Advantages & Disadvantages = Fast to = form a large family Big family can Compete for food better 2 To save genetic information from endangered species Human Assisted Cloning µ ! purpose : D To mass produce Organism wl desirable traits . . Humans use all the asexual cloning methods in order to produce desired results with organisms. This is done in several ways. Human Assisted Cloning 1 ! Reproductive cloning - purpose is to produce a genetic duplicate of an existing or dead organism. Steps involved: 1 1. 2. Remove nucleus from an egg cell from female A mammary gland cell is removed from an adult female Electricity fuses mammary and egg cell Fused cell begins dividing Dividing embryo is inserted into surrogate mother 2 3. 4. 5. 3 Human Assisted Cloning 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Remove nucleus from an egg cell A mammary gland cell is removed from an adult female Electricity fuses mammary and egg cell Fused cell begins dividing Dividing embryo is inserted into surrogate mother embryo Once is insert Fuse large to Frutos 's enough surrogate mother . eg ) Dolly World the Cat , sheep Human Assisted Cloning ! 2 Therapeutic cloning - purpose is to correct health problems ! ! ! ! Very important to therapeutic cloning are stem cells - cells that can become different types of cells Stem cells can be used to replace cells damaged from injuries or disease Diabetes, spinal injuries, Parkinson’s disease are only a few that can benefit from stem cell therapy Controversial because the best stem cells are from embryos which are destroyed when harvesting cells Human Assisted Cloning k Fused Give birth the to offspring |^ Embryo 1 Organ Embryonic 2 STEM CELL µ transplant to the patient DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 5 CLASS: Comparing Reproductive and Therapeutic Cloning BLM 2-23 Goal • Use this page to compare the similarities and differences between reproductive and therapeutic cloning. What to Do After reading pages 176–178 in the student book, construct a Venn diagram to compare reproductive and therapeutic cloning. • DNA is an make TO Offspring extracted Fused cell w/ cell - embryo an . Embryo into a Is . inserted surrogate mother . . an No Fused grows egg nucleus a an before inserted a • a patent Is becomes cell stem cell grown desired Organ is to . embryonic which into body extracted from Fused • cell problem is DNA fused and . becomes is extracted from mammary Gland cell of female • DNA . health fix To the into Organ . transplanted patient . Copyright © 2007, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. ,