* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Micro1-4th(part One) Lec- Pharm D
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Phage therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Bacteriophage wikipedia , lookup
Unique properties of hyperthermophilic archaea wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
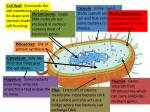
PharmD : Arwa Bdair Subject: Structures of bacteria Doctor: Randa Haddadin PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD Sheet: 4(part1) University of Jordan – Faculty of Pharmacy –Pharmaceutical Microbiology (1) – 1202341- Dr. Randa Haddadin– PharmD- 2nd Semester 2013 University Of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Microbiology for PharmD students 13th Of Feb 2013 Dr.Randa Haddadin Arwa Bdair Structures of bacteria Structures of bacteria : 4th lecture - Human body contains 70 S ribosome in mitochondria … that is why some drugs which target bacterial ribosomes may be toxic to human. 1. Cytoplasm of bacteria 2. Nuclear Region - semi- fluid substance - contains DNA , some RNA and proteins - 80% is water , the rest 20% (proteins , lipids ..) - In cytoplasm , anabolic & catabolic reactions take place. - ribosomes in the cytoplasm, are composed of RNA with proteins in a spherical shape. - Usually bacteria contain one circular ... some bacteria contain plasmid , which is an extra chromosomal DNA , circular and outside the original chromosome. Plasmid enables bacteria to resist antibiotics. 3. Inclusions -ribosomes usually present in the cytoplasm in the form of chains (polyribosomes) - each ribosome is composed of two subunits (small subunit and large subunit) - ribosomes are measured according to their sedimentation rate , which is done by centrifugation - Rate of sedimentation is measured by the unit Svedberg (S) - 70 S means the sedimentation rate equals 70 Svedberg. - Human ribosome (Eukaryotes) ATS 80 S (60 S large subunit, 40 S small subunit) - small bodies, they may be granules or vesicles in the cytoplasm - the contain compacted materials such as glycogen , polyphosphate (granules) - gas filled vacuole (vesicle) , membrane enclosed , this air vacuole present in bacteria which live in water , used for movement and changing depth depending on the amount of air in the vesicles. - some vesicles contain lipids to be used in metabolism 4. Endospores - Endospores present inside the bacteria , but exospores are produced by Fungi - prokaryotes 70S (30 S small , 50 S large) - Fungi can spread exospores everywhere there is a difference in the sedimentation rate between eukaryotic ribosome and prokaryotic ribosome , so by using this difference a certain drug is used to target bacterial ribosome only. - Bacteria may be at vegetative form (metabolically active, alive , can do reproduction), or at resting stage as endospores. 1 Microbiology for PharmD students 13th Of Feb 2013 Dr.Randa Haddadin Arwa Bdair Structures of bacteria 4th lecture →Bacillus and Clostridium can form endospores (they are Gram +ve) - Ca2+ deposit in endospores also elevate resistancy. → Examples of Gram +ve bacteria ( Bacillus, Clostridium , streptococcus and staphylococcus) - Spores may live for thousands of years. - The goal of spores formation is to survive during harsh conditions , not for reproduction. - If the surrounding conditions become good enough for the bacteria, it will convert to the vegetative form the process is called Germination. - form within the cell * Germination = spore living bacteria. -they have high resistance since they have low amounts of water - highly resistant to heat, alkaline and acidic media , and it’s very hard to get rid of them -they may be also resistant to radiations, but Gama radiations can kill them * Sporulation = living bacteria spore. ------------------------------------------ * External structures of bacteria:Flagellum: used for movement. - once the bacteria detect depletion of nutrients , sporulation starts. Sporulation : conversion from vegetative form to endospore formation Naming according to the number of flagella: Monotrichous = one flagellum. Amphitrichous = two flagella, one on each side. -Endospore is composed of *core (contains DNA) Lophotrichous = two or more flagella from one side. *cortex Peritrichous = many, from all sides. *coat Atrichous = No Flagellum. *some spores contain a layer called “exosporium” * The type of bacteria who has flagella is usually rod-shaped. - Endospores contain dipicolonic acid , which is not present in the vegetative form of bacteria. This substance contributes to the high resistance of endospores * Flagellum is made out of the protein " Flagelline", extends beyond the cell wall, and the base of the flagellum is fixed to the cell membrane. 2 Microbiology for PharmD students 13th Of Feb 2013 Dr.Randa Haddadin Arwa Bdair Structures of bacteria *** Chemotaxis: Movement of the cell either toward something or away from something depending on chemical detection ( according to concentration). 4th lecture 2- Attachment Pili ( Fimbiae) , it helps the bacteria to attach to surfaces which making it more pathogenic. - The attachment of bacteria to the tissues makes it hard to get rid of it. * It may be positive chemotaxis toward nutrient. *Glycocalyx : * Or negative chemotaxis away from toxic substance "Repeler" . - a polysaccharide-containing substance fount external to the cell wall * Bacteria contain receptors to detect concentration gradient to decide where to go. - two types: *** Phototaxis: * Positive toward light. * Negative away from light. - Axial filaments or Endoflagella: - Present in the spiral bacteria, such as spirochete; which moves around an axis. * Pili: -(Pilus: singular), composed of the protein piline ; tiny hollow projections present on the bacteria and it comes in two types: 1- D conjugation Pili ,( sex pili or also called F pili), it connects two similar or different bacteria types to transfer DNA , a weak bacteria may be transferred to a resistant bacteria by transferring certain plasmid types. A) capsule: polysaccharide molecules present in a loose gel -function : protection - example: Bacillus anthrax, some cells of this type of bacteria have a capsule and other cells don’t … then they concluded that when this bacteria is present inside the human body it has a capsule, and when its outside no capsule present. (capsule protect the bacterial cell from immunity detection) B) Slim layer (Biofilm) : -causes 60% of the infections - thinner than capsule and less tightly bound to the cell wall. - when a certain type of bacteria exist in a large number, they start to secrete polysaccharides as a signal for the other bacterial cells to stick to a surface. 3 Microbiology for PharmD students 13th Of Feb 2013 Dr.Randa Haddadin Arwa Bdair Structures of bacteria 4th lecture - During the surgery of introducing a prosthetic device (ex: pace maker), some bacterial cells may inter the body through the wound and form Biofilm , infection produced is very hard to treat. -biofilm protects bacteria from drying, increases its resistance against chemicals and helps it to capture nutrients. (To be cont. in the next part) Good luck in your Quiz 4