* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Packet Optical Networking for LTE Cell Tower Backhaul
Optical sound wikipedia , lookup
PSTN network topology wikipedia , lookup
Windows Vista networking technologies wikipedia , lookup
History of network traffic models wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Dell PowerConnect wikipedia , lookup
Cellular network wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Long-tail traffic wikipedia , lookup
Dell M1000e wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
LTE (telecommunication) wikipedia , lookup
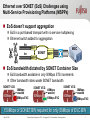
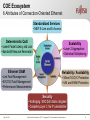
Packet Optical Networking for LTE Cell Tower Backhaul Ralph Santitoro Carrier Ethernet Market Development [email protected] Current landscape Many, if not most, backhaul deployments use SONET Using Multi-Service Provisioning Platforms (MSPP) SONET delivered via MSPPs well served cell tower backhaul providers for a long time May 18, 2011 Reliable Secure Provides guaranteed bandwidth Efficiently supports T1s (predominant circuit type requiring backhaul) Supports Ethernet, albeit inefficiently this is where the problem lies Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 2 Ethernet over SONET (EoS) for Backhaul Why use it ? Many different implementations of Ethernet Transport Switched (Connectionless) Ethernet Ethernet over MPLS Ethernet over SONET Connection-Oriented Ethernet Each implementation varies significantly in: QoS Performance (packet latency, loss) Network Availability (protected / unprotected transport) Bandwidth Assurances (statistical versus guaranteed) Network Security (number of vulnerabilities) EoS used because it is the safe choice… It just works ! May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 3 Mobile Backhaul Technology Migration 3G/4G Data Bandwidth Keep 2G traffic on TDM No traffic growth so T1 MRC is flat Voice + 2G Data High growth 3G and emerging LTE traffic Time High bandwidth cell site base stations upgrade to Ethernet Ethernet over SONET on MSPPs not efficient for packet-centric traffic • How do you evolve this to a more efficient technology? Backhaul Network 2G 3G LTE May 18, 2011 T1s T1s Ethernet Ethernet SONET Ethernet over SONET ?? Mobile Switching Center Connection-Oriented Ethernet for Efficient Cell Tower Backhaul. (c) Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications. 4 Packet Optical Networking Packet Optical Networking provides the integration of Packet: Connection-Oriented Ethernet Optical Transport: SONET, ROADM, WDM, OTN Packet Optical Networking: Reliable Secure Provides guaranteed bandwidth Efficiently supports T1s (predominant circuit type requiring backhaul) Efficiently supports Ethernet for high-growth packet centric data Packet Optical Networking Platforms (P-ONP) Enable 3G/LTE high growth data services to be efficiently backhauled over existing SONET infrastructure While facilitating migration to packet-centric infrastructure May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 5 Ethernet over SONET challenges and how Packet Optical Networking addresses them Ethernet over SONET (EoS) Challenges using Multi-Service Provisioning Platforms (MSPPs) EoS doesn’t support aggregation EoS is a port-based transport with no service multiplexing Ethernet switch added for aggregation Eth MSPP Eth MSPP MSC SONET MSPP EoS bandwidth dictated by SONET Container Size EoS bandwidth available in only 50Mbps STS increments Other bandwidth rates waste SONET bandwidth SONET VCG 50Mbps 30Mbps wasted 20Mbps EVC SONET VCG 50Mbps 40Mbps wasted 10Mbps EVC SONET VCG 50Mbps 30Mbps wasted 20Mbps EVC 150Mbps of SONET BW required for only 50Mbps of EVC BW May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 7 COE over SONET on Fujitsu’s Packet Optical Networking Platforms (P-ONP) COE supports aggregation Aggregates EVCs onto higher speed Ethernet port Eth P-ONP Eth P-ONP COE over SONET MSC P-ONP COE aggregates EVCs onto same SONET VCG Can achieve up to 100% bandwidth utilization 50Mbps 20Mbps EVC 10Mbps EVC 20Mbps EVC More Service Revenue and Higher Margins using Existing Assets May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 8 Cell Tower Backhaul Evolution From SONET to Ethernet using COE FMO Step 1: Add P-ONP with COE over SONET to increase BW efficiency PMO: Cell tower MSC SONET P-ONP at MSC MSPP at MSCEach Ethernet service SONET requires a separate SONET VCG SONET MSPP at Cell Site TDM T1s EoS Ethernet 2G/3G 3G/LTE FMO Step 2: Begin Migration to Ethernet over Fiber (EoF) network. Existing services unaffected P-ONP at MSC COE muxes Ethernet services onto same SONET SONET VCG P-ONP at Cell Site P-ONP at Cell Site TDM T1s COE EoF TDM Ethernet 2G/3G 3G/LTE T1s 2G/3G COE Ethernet 3G/LTE Fujitsu’s Packet Optical Networking Platforms facilitate CTBH network evolution while supporting multi-generation Connection-Oriented 2G/3G/LTE services Ethernet: A No-Nonsense Overview May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 9 Connection-Oriented Ethernet for Efficient, Packet-centric Cell Tower Backhaul Why COE for Cell Tower Backhaul ? Makes Ethernet more like SONET which dominates CTBH networks today Network operations procedures similar to SONET Smoother transition for SONET-trained operations personnel Highly scalable packet-centric technology Meets large scale CTBH connectivity and aggregation requirements COE is supported over any Layer 1 networking technology Key Attributes Guaranteed Bandwidth (CIR) Consistent QoS Performance (Bounded Packet Delay, Packet Loss) High Security May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 11 Connection-Oriented Ethernet (COE) FAQs What is COE ? Industry term defining a point-to-point implementation of Carrier Ethernet • Tracked by industry analysts for past few years COE technologies have been around for about 10 years What’s the difference between COE and Carrier Ethernet ? COE is a high performance implementation of Carrier Ethernet Are COE implementations based on industry standards ? Implementations utilize MEF, IEEE, IETF and ITU-T standards • Plus value added enhancements where standards are nascent What technologies can be used to implement COE? COE can be implemented using Ethernet or MPLS technologies May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 12 COE designed to mimic SONET Makes Ethernet point-to-point Just like SONET circuits Ethernet Virtual Connections (EVCs) are provisioned across the network Just like SONET circuits Eliminates Ethernet control plane and many layer 2 control protocols Provide 50ms EVC path protection / restoration Just like SONET linear path protection Provide EVC fault management at demarcation points Just like DS1 circuit loopbacks Provides guaranteed bandwidth throughout the network Just like SONET circuits May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 13 Different approaches to COE Technology selection depends on the problem you’re trying to solve Ethernet-centric COE MPLS-centric COE Static PW Eth PW MPLS-TP T-MPLS MPLS LSP PBB-TE PBT PW Eth Eth • Ethernet • MPLS Pseudowire (PW) • MPLS Label Switched Path (LSP) Optimized for Multi-Service Transport New standards being developed Augmenting MPLS standards BMAC/BVID or C/SVID Optimized for Ethernet Service Transport One OAM Layer Less optimal for multi-service transport Standardized Now Reuses existing Carrier Ethernet standards, e.g., Service OAM Ethernet-centric COE optimized for Ethernet Transport MPLS-centric COE optimized for Multi-service Transport May 18, 2011 Eth • Ethernet Three OAM Layers Less optimal for Ethernet service transport Standards Under Development Ethernet VLAN Tag Tag Switching 14 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications Connection-Oriented Ethernet: A No-Nonsense Overview COE Ecosystem 6 Attributes of Connection-Oriented Ethernet Standardized Services • MEF E-Line and E-Access Deterministic QoS •Lowest Packet Latency and Loss •Bandwidth Resource Reservation Ethernet OAM • Link Fault Management • EVC/OVC Fault Management • Performance Measurements Scalability • Layer 2 Aggregation • Statistical Multiplexing Reliability / Availability • 50ms EVC/OVC Protection • UNI and ENNI Protection Security • No Bridging: MAC DoS attacks mitigated • Completely Layer 2: No IP vulnerabilities May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 15 High Availability Ethernet for Cell Tower Backhaul Multi-level Fault Tolerance with Fujitsu Packet Optical Networking High Availability CTBH Service Service Ethernet Service OAM via 802.1ag and Y.1731 50ms Network Protection via G.8031 Network NE Software Management Network Element May 18, 2011 In-Service System Software Upgrades Working / Protect EMS/NMS Instances Protected Power, Switch Fabric, etc. Card Card protection (active/standby or active/active) Port Port protection via Link Aggregation Link Aggregation across cards Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 16 COE vs. Ethernet over SONET for LTE Backhaul Key differences summary Attribute COE on P-ONP EoS on MSPP High Security Bounded QoS (latency, loss) 50 ms protection/restoration Ethernet Service OAM No Guaranteed Bandwidth (CIR) through resource reservation (CIR in 1Mbps increments) (CIR in SONET 50Mbps increments) (EIR in 1Mbps increments) No Service Multiplexing and Aggregation No Efficient Bandwidth Utilization No MEF-compliant Services EPL, EVPL, Access EPL, Access EVPL EPL Ethernet Topologies P2P, P2MP (hub & spoke) P2P Oversubscribed Bandwidth (EIR) May 18, 2011 Packet Optical Transport for LTE. © Copyright 2011 Fujitsu Network Communications 17