Hand-book on STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS for
... 4.3 Characteristic Function . . . . . . 4.4 Moments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5 Probability Content . . . . . . . . 4.6 Random Number Generation . . . 5 Binomial Distribution 5.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.2 Moments . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.3 Probability Generating Function 5.4 Cu ...
... 4.3 Characteristic Function . . . . . . 4.4 Moments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5 Probability Content . . . . . . . . 4.6 Random Number Generation . . . 5 Binomial Distribution 5.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.2 Moments . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.3 Probability Generating Function 5.4 Cu ...
Probability with Engineering Applications
... model. This structure encourages a modeler to have a consistent, if not completely accurate, model. It also offers a commonly used mathematical language for sharing models and calculations. Part of the process of learning to use the language of probability theory is learning classifications of probl ...
... model. This structure encourages a modeler to have a consistent, if not completely accurate, model. It also offers a commonly used mathematical language for sharing models and calculations. Part of the process of learning to use the language of probability theory is learning classifications of probl ...
Access Control Lists Lecture 1
... Distribution of routing updates can be controlled Security can be added at the network boundary Specific types of traffic can be permitted or blocked An administrator controls what areas a client can access Screen certain hosts to either allow or deny access to part of a network ...
... Distribution of routing updates can be controlled Security can be added at the network boundary Specific types of traffic can be permitted or blocked An administrator controls what areas a client can access Screen certain hosts to either allow or deny access to part of a network ...
On the Shortest Queue Policy for the tandem
... in states with queue lengths which are equal and not small. This counterexample explains why the SQBNP is not an optimal policy in the FI case when the traffic is light. It turns out that the states of node 2 for which delaying customers in the first node pays off, have a low probability of occurrin ...
... in states with queue lengths which are equal and not small. This counterexample explains why the SQBNP is not an optimal policy in the FI case when the traffic is light. It turns out that the states of node 2 for which delaying customers in the first node pays off, have a low probability of occurrin ...
2532524-queuing v1
... First developed to analyze statistical behavior of phone switches. Queueing Systems used to model processes in which customers arrive, wait their turn for service, are serviced and then leave. Eg: supermarket checkouts stands, world series ticket booths, doctors waiting rooms etc.. Five components o ...
... First developed to analyze statistical behavior of phone switches. Queueing Systems used to model processes in which customers arrive, wait their turn for service, are serviced and then leave. Eg: supermarket checkouts stands, world series ticket booths, doctors waiting rooms etc.. Five components o ...
Metrics for Packet Reordering – A Comparative Analysis Nischal M. Piratla
... • Load splitting: To balance the load among the multiple paths, different packets of the same stream take different routes leading to different delays causing reordering. Problems caused by reordering are handled at different levels in TCP/IP suite. TCP allows adjustment of ‘dupthresh’ parameter, i. ...
... • Load splitting: To balance the load among the multiple paths, different packets of the same stream take different routes leading to different delays causing reordering. Problems caused by reordering are handled at different levels in TCP/IP suite. TCP allows adjustment of ‘dupthresh’ parameter, i. ...
Chapter 3: Basic Monte Carlo Methods
... an accurate measure of time, or the amount of background cosmic radiation as the basis for such a generator, but these suffer from a number of disadvantages. They may well be “random” in some more general sense than are the pseudo-random number generators that are presently used but their properties ...
... an accurate measure of time, or the amount of background cosmic radiation as the basis for such a generator, but these suffer from a number of disadvantages. They may well be “random” in some more general sense than are the pseudo-random number generators that are presently used but their properties ...
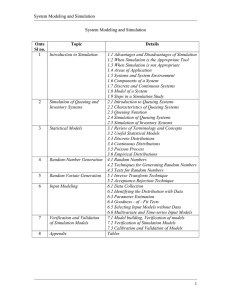
unit-3 statistical models in simulation
... Modeling of systems in which the state variable changes only at a discrete set of points in time. The simulation models are analyzed by numerical rather than by analytical methods. Analytical methods employ the deductive reasoning of mathematics to solve the model. Eg: Differential calculus can be u ...
... Modeling of systems in which the state variable changes only at a discrete set of points in time. The simulation models are analyzed by numerical rather than by analytical methods. Analytical methods employ the deductive reasoning of mathematics to solve the model. Eg: Differential calculus can be u ...
8.2 Interim Agreements on Key Issue #2: QoS
... It is proposed to use both inband signalling and no signalling to indicate reflective QoS. How to indicate reflective QoS to the UE is decided by the network during the PDU session establishment procedure. For example, when the UE is attached through 3GPP access the network may use inband signalling ...
... It is proposed to use both inband signalling and no signalling to indicate reflective QoS. How to indicate reflective QoS to the UE is decided by the network during the PDU session establishment procedure. For example, when the UE is attached through 3GPP access the network may use inband signalling ...
Complex architecture of primes and natural numbers
... Prime numbers have fascinated and puzzled philosophers, mathematicians, physicists, and computer scientists alike for the past two and a half thousand years. A prime is a natural number that has no divisors other than 1 and itself; every natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime is called a ...
... Prime numbers have fascinated and puzzled philosophers, mathematicians, physicists, and computer scientists alike for the past two and a half thousand years. A prime is a natural number that has no divisors other than 1 and itself; every natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime is called a ...
Invariants of random knots and links,
... method in topology. This methodology begins by defining a probability distribution on the objects of study. Parameters and invariants of interest then become random variables on this probability space. Tools of probability theory are then applied to investigate the distribution of these random varia ...
... method in topology. This methodology begins by defining a probability distribution on the objects of study. Parameters and invariants of interest then become random variables on this probability space. Tools of probability theory are then applied to investigate the distribution of these random varia ...
Networks and Operating Systems Chapter 6: Reliable data transfer
... – unfortunately, not possible in the Internet (on the contratrary, need to split into smaller packets) ...
... – unfortunately, not possible in the Internet (on the contratrary, need to split into smaller packets) ...
Temporal evolution of social networks
... By a “bow-tie” structure, and usually have a giant connected component(GCC) which involves a significantly large fraction of nodes ...
... By a “bow-tie” structure, and usually have a giant connected component(GCC) which involves a significantly large fraction of nodes ...
Part III: Monte Carlo Methods
... The binomial distribution describes the results of repeated experiments which has only two possible outcomes. Suppose a radioactive source is monitored for a time interval T . There is a probability p that one or more disintegrations would be detected in that time interval. If a total of m intervals ...
... The binomial distribution describes the results of repeated experiments which has only two possible outcomes. Suppose a radioactive source is monitored for a time interval T . There is a probability p that one or more disintegrations would be detected in that time interval. If a total of m intervals ...
Random geometric complexes in the thermodynamic regime
... When the points of Φ are those of a stationary Poisson process on Rd , this union is a special case of a ‘Boolean model’, and its integral geometric properties – such as volume, surface area, Minkowski functionals – have been studied in the setting of stochastic geometry since the earliest days of t ...
... When the points of Φ are those of a stationary Poisson process on Rd , this union is a special case of a ‘Boolean model’, and its integral geometric properties – such as volume, surface area, Minkowski functionals – have been studied in the setting of stochastic geometry since the earliest days of t ...
The complex architecture of primes and natural numbers
... 3. If number n does not√connect to any existing prime smaller or equal to n, it is declared as a prime and a new number n + 1 is added to the system. The intuition behind the second step in our model is as follows. In the case of the real primes, a composite number√n must have at least a prime facto ...
... 3. If number n does not√connect to any existing prime smaller or equal to n, it is declared as a prime and a new number n + 1 is added to the system. The intuition behind the second step in our model is as follows. In the case of the real primes, a composite number√n must have at least a prime facto ...
Packet Optical Networking for LTE Cell Tower Backhaul
... Each implementation varies significantly in: ...
... Each implementation varies significantly in: ...
Bernoulli trial
... · underlying causes of phenomena are unknown, but small effects are added into an observable score ...
... · underlying causes of phenomena are unknown, but small effects are added into an observable score ...
Close connection
... • Interface: send message to “specific process” at given destination; local process receives messages sent to it – How are they named? ...
... • Interface: send message to “specific process” at given destination; local process receives messages sent to it – How are they named? ...
Generating Random Variables from the Inverse Gaussian and First
... cycle length. The initial value or seed, x0 , is also an integer. The uniform random numbers are then calculated as ui = xi /m. The specific generator used for this simulation is the one described by Park and Miller [8] as the “minimal standard”. It has m = 231 − 1 and a = 16807. This generator has ...
... cycle length. The initial value or seed, x0 , is also an integer. The uniform random numbers are then calculated as ui = xi /m. The specific generator used for this simulation is the one described by Park and Miller [8] as the “minimal standard”. It has m = 231 − 1 and a = 16807. This generator has ...
X - Physics
... Caution: The above derivation is only approximate since we used Stirlings Approximation which is only valid for large m. Another subtle point is that strictly speaking m can only take on integer values while is not restricted to be an integer. ...
... Caution: The above derivation is only approximate since we used Stirlings Approximation which is only valid for large m. Another subtle point is that strictly speaking m can only take on integer values while is not restricted to be an integer. ...
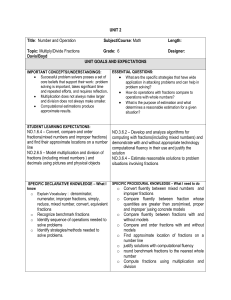
UNIT 2
... • Successful problem solvers posses a set of • What are the specific strategies that have wide core beliefs that support their work: problem application in attacking problems and can help in solving is important, takes significant time problem solving? and repeated efforts, and requires reflection. ...
... • Successful problem solvers posses a set of • What are the specific strategies that have wide core beliefs that support their work: problem application in attacking problems and can help in solving is important, takes significant time problem solving? and repeated efforts, and requires reflection. ...
幻灯片 1
... • The friction is the basic parameter that limits vehicle speed, stability and effects traffic safety and driver comfort. • In many countries standards, there are the minimum f value for new and maintained road. ...
... • The friction is the basic parameter that limits vehicle speed, stability and effects traffic safety and driver comfort. • In many countries standards, there are the minimum f value for new and maintained road. ...
Notes of SMS
... Static Mathematical Model gives the relationship between the system attributes when the system is in equilibrium. For example in market model there is balance between supply and demand for commodity and both factors depend upon price. Dynamic Mathematical Model allows the change of system attributes ...
... Static Mathematical Model gives the relationship between the system attributes when the system is in equilibrium. For example in market model there is balance between supply and demand for commodity and both factors depend upon price. Dynamic Mathematical Model allows the change of system attributes ...