* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I. What is a clone? - Manhasset Public Schools
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
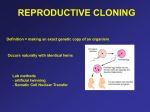
Name: Aim 33: What is cloning and how is it performed? I. Date: What is a clone? When you hear the word clone, you usually think of a copy of something. When scientists use the term clone, they are referring to an organism (or part of an organism) that is the exact genetic match of another organism. Identical twins are, in fact, clones of each other because they are an exact genetic match. This is how clones can occur naturally. a) Define clone: b) Why are identical twins clones? II. What do you need to create a clone? The first thing that a scientist needs to produce a clone is a somatic cell. A somatic cell is any cell in an organism other than a sperm cell or an egg cell. In other words, it is a body cell, such as a skin, liver or heart cell, not a reproductive cell. All somatic cells in an organism have the same exact DNA, and this DNA exists as a complete set of instructions to make an organism. In a reproductive cell, there is only half a set of chromosomes to make an organism. a) What do scientists need to produce a clone? ______________________________________________ b) Define Somatic Cell: c) Give an example of a Somatic Cell: ______________________________________________________ d) What are the two examples of a reproductive cell? _________________________________________ e) Why do scientists want to use a somatic cell instead of a reproductive cell for producing a clone? III. Cloning humans is unethical. But how do we use cloning as a type of therapy for humans? When scientists use cloning to produce certain cells or tissues of an organism, it is called therapeutic cloning. This involves taking the cloned embryo that is growing and dividing and removing the stem cells from inside the ball of cells. These cells are given specific signals to make them grow into different types of cells that will be a genetic match to the donor of the somatic cell. Scientists want to use this type of cloning to create stem cells that could be used to grow new cells and tissues for people with a diseased organ, such as a damaged heart or damaged cells in the pancreas that produces insulin. Making tissue that is a genetic match to a patient would mean that there would be no possibility of rejection by the immune system. a) Define therapeutic cloning: b) Define stem cell: c) Give two examples that therapeutic cloning can be used for: d) What is an advantage of therapeutically cloning an organ rather than receiving an organ from someone else? IV. Cloned Organisms The first time cloning was used to produce an animal from an adult somatic cell was done in 1996 when a sheep named Dolly was produced. Since then, many other organisms have been cloned, such as dogs, cats, rabbits, mice, goats, pigs, cows plants monkeys. One benefit of using reproductive cloning is to clone endangered species or even extinct animals. Animals on the verge of extinction could get a population boost if some cloned animals were produced. If a scientist has a tissue sample from an extinct animal with undamaged DNA, they might be able to clone them if they have a closely related species to use for the egg cell and as the surrogate mother. a) What year was the 1st organism cloned? ______________. What type of organism was it? ________________ b) Describe two benefits of reproductive cloning: V. Cloning Steps Take a __________________________ (body cell) from sheep A and Step 1 ONLY use the _________________ (DNA). Take an ____________ from sheep B and ONLY use the ______________________, discard nucleus. Step 2 Insert the _________________ from sheep A into the _____________________________ of sheep B Step 3 Egg cell (from sheep B) with donor DNA from sheep A will ________________ _and form an _________________, which is a ball of cells Step 4 The embryo is ________________________ into the womb of Sheep C (___________________ mother). Step 5 Surrogate mother will give ______________ to the cloned sheep Indicate whether the following statements are True or False. Correct the bolded term if the statement is false 1. Organisms made through cloning have the same number of chromosomes but different types of genes compared to the organism it was cloned from True or False: ____________ Correct bolded word if False: 2. DNA of offspring is identical to the original organism True or False: ____________ Correct bolded word if False: 3. Cloning produces results that are different from asexual reproduction True or False: ____________ Correct bolded word if False: 4. It is considered ethical to clone humans True or False: ____________ Correct bolded word if False: 5. The DNA of the cloned organism is identical to the organism that contributed the egg cell True or False: ____________ Correct bolded word if False: 6. Cloning results in the inheritance of new characteristics True or False: ____________ Correct bolded word if False: 7. Cloning does not add variation to a population of organism True or False: ____________ Correct bolded word if False: 8. Cloning is often used to produce large amounts of offspring that are genetically different True or False: ____________ Correct bolded word if False: Answer the following: 1. If one of YOUR somatic cells was removed from your body and underwent the process of cloning, what would be the age of your clone? Explain: 2. A scientist would like to make a clone of a white cat. They take a somatic cell from that cat, transfer the nucleus into an empty egg cell from a black cat. The embryo that is formed is then placed into a surrogate mother, who is a brown cat. a. What will be the color of the cloned cat? b. Explain why: 3. Why doesn’t the clone look like the surrogate mother if that is the organism that gave birth to the clone?