* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sea-Floor Spreading - Zion Central Middle School
Survey
Document related concepts
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
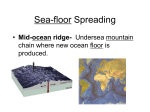
Review from yesterday! http://wrgis.wr.usgs.gov/docs/parks/animate/A08.gif What is the theory of continental drift? the idea that the continents were once all joined together in one super-continent called Pangaea and slowly moved to their current positions Key concepts Evidence of “continental drift”— . •Physical fit of continents •Fossil evidence •Measurements of movement •Rock layer sequences •Glacial evidence Alfred Wegener Sea-Floor Spreading Sea-Floor Spreading Sonar - a device that bounces sound waves off under-water objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. The time it takes for the echo to arrive indicates the distance to the object. Sea-Floor Spreading 1. Mid-Ocean Ridge – the longest chain of mountains in the world---these are divergent plate boundaries. Sea-Floor Spreading 3. Sea-Floor Spreading – Harry Hess in the 1960’s; the process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor while pushing older rocks away from the ridge Sea-Floor Spreading Ocean floor moves like a conveyor belt carrying continents with it. New ocean floor forms along cracks in the ocean crust as molten material erupts from the mantle spreading out and pushing older rocks to the sides of the crack. New ocean floor is continually added by the process of sea-floor spreading. Sea-Floor Spreading 1. Evidence from Molten Material – Rocks shaped like pillows(rock pillows) show that molten material has erupted again and again from cracks along the mid-ocean ridge Sea-Floor Spreading 2. Evidence from Magnetic Stripes – Rocks that make up the ocean floor lie in a pattern of magnetized stripes which hold a record of the reversals in Earth’s magnetic field Sea-Floor Spreading Sea-Floor Spreading Sea-Floor Spreading 3. Evidence from Drilling Samples – Core samples from the ocean floor show that older rocks are found farther from the ridge; youngest rocks are in the center of the ridge Sea-Floor Spreading 8. Subduction – Process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle; allows part of the ocean floor to sink back into the mantle Sea-Floor Spreading: Subduction zone Deep-Ocean Trench – Occurs at subduction zones. Deep underwater canyons form where oceanic crust bends Sea-Floor Spreading get from “blue” oceans to Magnetic Wiggles!!! such great detail? Earth’s Magnetic Field BUT…..Magnetic North is NOT at the North Pole AND…the Magnetic Field Reverses • Field reverses ~1 time every 200,000 years on average. • 400 times in last 330 million years. • Last reversal was 780,000 years ago. NORMAL REVERSE