* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Winter 2004 Final Exam
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
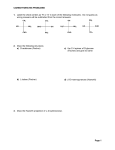
Memorial University of Newfoundland Chemistry 2440 Final Exam April 2004 S. V. Pansare Name:__________________ Time: 2 ½ hours Student Number:__________________ [Marks] 1. Give a brief description and provide a suitable example of each of the following: a) Markovnikov’s rule b) An aromatic substitution reaction c) Acetal formation d) A polyamide (a condensation polymer) e) Diastereomers f) An irreversible enzyme inhibitor [12] 2. Give IUPAC names for the following compounds [8] OH Cl b) a) Br H3CH2CO OCH3 F b) a) c) CH2CH3 O O CH3 c) O d) HO CH3 d) 3. Draw molecules with the formula C5H10 (one for each part) which match the following a) an alkene which is a trans compound c) an alkene which does NOT have cis/trans forms d) a cis compound which is not an alkene [6] 4. Provide structures for the following compounds: [8] a) Ser-Lys-Pro b) 2-Deoxy-D-ribose (Draw the open chain form as a Fischer projection) c) Glutamine d) Cytosine 5) a) Draw the linear form of D-glucose as a Fischer projection and circle the carbon which is inspected to determine that the configuration is ‘D’. b) Draw the two cyclic forms of D-glucose in Haworth type drawings and label ‘α’ and ‘β’ c) Which from of D-glucose is normally the most stable in an aqueous solution; linear, ‘α’, or ‘β’? d) Draw the structure of propyl-β-D-glucoside. [5] 5. Complete the following reactions. Show stereochemistry where applicable. a) [12] AlCl3 + Cl H2SO4 b) heat OH c) + major + minor-1 minor-2 solvent Br2 HBr d) e) + Ph O H2O, H+ O + warm OH f) g) + H2O NaOH H N + aqueous HCl O + heat 6. A) Aspartame, an artificial sweetener which is marketed as NutraSweet®, has the structure given below. Answer the following questions about Aspartame. [7] O HO H N H2N O O Aspartame a) Locate and name the functional groups in aspartame b) Name the amino acids in aspartame O B) Ibuprofen, a popular non-prescription anti-inflammatory drug, has the structure given below. Answer the following questions about ibuprofen. [3] OH O Ibuprofen a) Circle the chiral carbon or carbons in ibuprofen, if any. b) How would you convert ibuprofen to its methyl ester?(show the reaction, reagents, conditions) 7. A) What is the substrate for each of the following enzymes: a) Maltase b) fructose oxidase c) sucrase d) phenolase [4] 8. B) What is an enzyme active site? What types of forces hold a substrate at an enzyme active site? [4] 9. [6] a) Provide the base sequence in the complementary RNA strand if a portion of one strand of DNA has the following base sequence: 5’-AGTCCAGGT- 3’ b) Explain why the base sequence ATC could not be a codon c) In terms of hydrogen bonding, a G-C base pair is more stable than an A-T base pair. Explain. 10. The following questions are based on your laboratory work a) What is the bromine test used for? Write a reaction to explain how the test works. [5] b) List three detection methods used for visualizing colourless organic compounds on TLC plates 11. In the space provided, place the letter corresponding to a structure below which best fits the description or name. [10] Answer Description or name _____ Serotonin _____ A neurotransmitter _____ A triose _____ A sugar found in RNA _____ The most abundant steroid in humans _____ Adenine _____ progesterone _____ Histidine _____ A base found in DNA _____ D-mannose NH2 OH HO N NH2 N N H HO HO HO H H N (B) (A) CHO H H OH OH CH2OH O HO HO (C) CHO O H H HO OH (E) (D) O O OH NH2 HO O NH NH2 N H O (F) OH (G) N H HO (H) (I) O N H (J) 12. Write short notes on any two of the following topics: a) Chlorofluorocarbons and the ozone layer b) Diabetes, aldehyde oxidation and glucose testing c) Aspirin d) Enzymatic browning: Discolouration of fruits and vegetables [10]