* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrostatics Review
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aristotelian physics wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear drip line wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
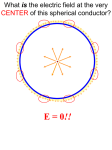
Electrostatics Review 1. When a neutral metal sphere is charged by contact with a positively charged glass rod, the sphere A) loses electrons C) loses protons Base your answers to questions 9 and 10 on the information and diagram below. B) gains electrons D) gains protons Two small metallic spheres, A and B, are separated by a distance of 4.0 × 10–1 meter, as shown. The charge on each sphere is +1.0 × 10–6 coulomb. Point P is located near the spheres. 2. A glass rod is given a positive charge by rubbing it with silk. The rod has become positive by A) gaining electrons C) losing electrons B) gaining protons D) losing protons Base your answers to questions 3 and 4 on the diagram below which represents a system consisting of two charged metal spheres with equal radii. 9. What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force between the two charged spheres? 3. If spheres A and B, as represented in the diagram, were touched together and then separated, the net charge on the two spheres would A) decrease C) remain the same B) increase 4. If the two spheres were touched together and then separated, the charge on sphere A would be A) C) B) D) A) 2.2 × 10–2 N C) 2.2 × 104 N B) 5.6 × 10–2 N D) 5.6 × 104 N 10.Which arrow best represents the direction of the resultant electric field at point P due to the charges on spheres A and B? A) B) C) D) 5. A particle could have a charge of A) C) B) D) 6. A positively charged glass rod attracts object X. The net charge of object X. A) B) C) D) 11. An electron is located 1.0 meter from a +2.0-coulomb charge, as shown in the diagram below. may be zero or negative may be zero or positive must be negative must be positive 7. Which procedure will give an electroscope a positive charge? A) B) C) D) touching the electroscope with a neutral object bringing a positively charged object near the electroscope touching the electroscope with a negatively charged object touching the electroscope with a positively charged object 8. An electric force F exists between two charged spheres. If the quantity of charge on each sphere is doubled, the electric-force between the two spheres will be equal to A) B) 2F C) 3F D) 4F The electrostatic force acting on the electron is directed toward point A) A B) B C) C D) D Electrostatics Review 12. The diagram below shows two metal spheres charged to +1.0 × 10-6 coulomb and +3.0 × 10-6 coulomb, respectively, on insulating stands separated by a distance of 0.10 meter. 15. Two isolated charges, +q and +2q are 4 centimeters apart. If F is the force acting on the charge +q, what is the magnitude and direction of the force on the charge +2q? A) B) C) D) E) F toward charge +2q F away from charge +2q 2F toward charge +2q F away from charge +q 2F away from charge +q Base your answers to questions 16 through 18 on the following: The spheres are touched together and then returned to their original positions. As a result, the magnitude of the electrostatic force between the spheres changes from 2.7 N to A) 1.4 N B) 1.8 N C) 3.6 N D) 14 N 13. Two point charges attract each other with a force of Newton. If the distance between the charges is doubled, the force will become A) C) B) D) 14. The distance between an electron and a proton is varied. Which pair of graphs best represents the relationship between gravitational force, Fg, and distance, r, and the relationship between electrostatic force, Fe, and distance, r, for these particles? A) A neutron, a proton, and an electron are initially at the same distance from a relatively large stationary nucleus moving at a constant velocity. Assume the masses of the proton and neutron are equal. 16. Which particle experiences the greatest acceleration? A) B) C) D) the neutron the proton the electron the electron and the proton experience the same acceleration E) the neutron and the proton experience the same acceleration 17. Which particle experiences the greatest force? A) B) C) D) E) the neutron the proton the electron the electron and the proton feel the same force the proton and the neutron feel the same force 18. Which is the first particle to reach the nucleus? B) C) A) B) C) D) E) the neutron the proton the electron both the neutron and the proton reach it simultaneously all three reach at the same time 19. An electron placed between oppositely charged parallel plates A and B moves toward plate A, as represented in the diagram below D) What is the direction of the electric field between the plates? A) toward plate A C) into the page B) toward plate B D) out of the page Electrostatics Review 26. Which diagram represents the electric field lines between two small electrically charged spheres? A) 20. In the diagram above, what is the force a small negative test charge of magnitude z would feel at point P? B) A) 12kqz 25r2 B) –396kqz 25r2 C) 4kqz 3r2 D) –4kqz 3r2 E) 0 C) Base your answers to questions 21 through 24 on the diagram below which shows two parallel metal plates A and B connected to a voltage source. D) 27. What is the magnitude of the electric field intensity at a point where a proton experiences an electrostatic force of magnitude 2.30 × 10–25 newton? A) 3.68 × 10–44 N/C C) 3.68 × 106 N/C 21. As a charged object moves from plate A to plate B, the electric force on the charged object A) decreases C) remains the same B) increases B) 1.44 × 10–6 N/C D) 1.44 × 1044 N/C Base your answers to questions 28 and 29 on the accompanying diagram which represents two large parallel plates which are oppositely charged. A, B, and C are reference points. 22. What is the electric field intensity between the two plates? A) 400. N/C C) 625 N/C B) 500. N/C D) 4,000 N/C 23. If only the original source voltage is increased, the electric field intensity between the plates will A) decrease C) remain the same B) increase 24. If only the distance between the plates is increased, the electric field intensity between the plates will A) decrease C) remain the same B) increase 25. Gravitational field strength is to Newtons per kilogram as electric field strength is to A) coulombs per joule C) joules per coulomb B) coulombs per newton D) newtons per coulomb 28. If an electron is moved from point A to point C, the potential energy of the electron will A) decrease C) remain the same B) increase 29. If an electron moves from point A to point B, the electron's electric potential energy will A) decrease C) remain the same B) increase Electrostatics Review 30. What is the total amount of work required to move a proton through a potential difference of 100. volts? A) 1.60 × 10–21 J C) 1.00 × 102 J B) 1.60 × 10 –17 J D) 6.25 × 1020 J 33. The graph below shows the relationship between the work done on a charged body in an electric field and the net charge on the body. 31. If 1.0 joule of work is required to move 1.0 coulomb of charge between two points in an electric field, the potential difference between the two points is A) 1.0 × 100 V C) 6.3 × 1018 V B) 9.0 × 109 V D) 1.6 × 10–19 V 32. The diagram below shows proton P located at point A near a positively charged sphere. What does the slope of this graph represent? B) potential difference D) electric field intensity A) power C) force If 6.4 ×10–19 joule of work is required to move the proton from point A to point B, the potential difference between A and B is 6.4 × 10–19 V A) C) 6.4 V 4.0 × 10–19 V B) D) 4.0 V 34. The work required to move 2 coulombs of charge through a potential difference of 5 volts is A) 10 J B) 2 J C) 25 J D) 50 J Answer Key Electrostatics Review 1. A 2. C 3. C 4. C 5. C 6. A 7. D 8. D 9. B 10. C 11. D 12. C 13. B 14. A 15. D 16. C 17. D 18. C 19. B 20. B 21. C 22. C 23. B 24. A 25. D 26. B 27. B 28. B 29. C 30. B 31. A 32. D 33. B 34. A