* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Directions - Modern World History @ SDA
Intercultural competence wikipedia , lookup
Development theory wikipedia , lookup
Legal anthropology wikipedia , lookup
The Dispossessed wikipedia , lookup
Postdevelopment theory wikipedia , lookup
World Values Survey wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ethnoscience wikipedia , lookup
Political economy in anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Nutritional anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Economic anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Societal collapse wikipedia , lookup
State (polity) wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural differences in decision-making wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Guns, Germs, and Steel wikipedia , lookup
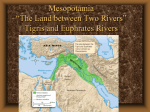
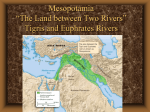
Ch. 2 -- Early Societies in Southwest Asia and the Indo-European Migrations Directions. Printout and review the Chapter outline & Study Guide prior to reading the Chapter. Not all the terms or people are to be found in the Chapter. For these, you are expected to research their relevance and include them. Publisher’s Website for Outlines, etc. -- http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072424354/student_view0/ Introduction. Because of the agricultural transition, societies could sustain larger populations and could become increasingly complex. Thus urban societies emerged in the fourth millennium B.C.E., particularly in the region known as Mesopotamia (“the land between the rivers”) along the fertile river valleys of the Tigris and the Euphrates. Some of the world’s earliest cities developed and prospered in that region. Mesopotamian prosperity and sophisticated culture attracted many migrants and influenced many neighbors, including the Hebrews, the Phoenicians, and the Indo-Europeans. Some of the characteristics of Mesopotamian societies were The establishment of governmental institutions to provide order and stability and to resolve disputes. These institutions evolved into hereditary kingships and., at times, into empires when states sought to expand their dominion to neighboring lands. The emergence of social classes as the result of specialization of labor and accumulation of wealth. The agricultural surplus and the accompanying specialization allowed individuals and groups to produce goods of high quality. The desire for these goods, in turn, helped to stimulate trade with other societies, greatly expanding intercultural contact. Distinctive cultural traditions that developed including a system of writing that would endure for thousands of years and more elaborate religious institutions than had previously existed. The following section, including “People & Terms” is to be highlighted on the Chapter Outline. Words not appearing in the outline must be added to the outline. Incorporate the information for the Study questions into the notes you add to the outline. People & Terms Response should include answers to who, what, where, when, how & why is this person important. Sargon Hammurabi Indo-Europeans Aryans Hittites Hebrews Phoenicians Akkad Sumeria Babylon Assyria Measopotamia State in your own words what each of the following terms means and why it is significant to a study of world history. Ziggurat Cuneiform Lex Talionis Epic of Gilgamesh Monotheism polytheism Centralized bureaucracy patriarchy Study Questions What role did technological innovations and trade play in the rise of city-states in Mesopotamia? What innovations led to turning points in the histories of these societies? How widely did they trade? Compare and contrast the lasting contributions of the Sumerians, Jews, Phoenicians, and Indo-Europeans. Which culture do you believe made the most significant contribution? Explain your answer. Warfare was a significant factor in the development of all cultures discussed in Ch2. Analyse how political institutions, economic factors, social factors, and technology interplayed to create conflict and war throughout the region. Explain the relationship between each of the following pairs. How does one lead to or foster the other? Be specific in your response. Cuneiform & Gilgamesh Hammurabi & Hebrews Phoenicians & bronze Chariots & empire Indo-Europeans & iron