* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Radiation Safety - 7
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
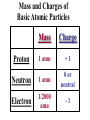
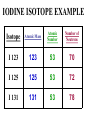
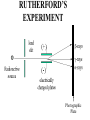
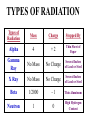
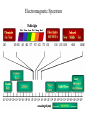
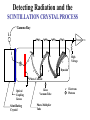
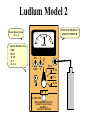
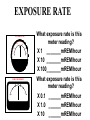
Radiation Safety Capt. David Ayre CAP, SWR-TX-176 RADIATION The definition of radiation is the emission (sending out) of waves and/or particles thru space. TYPES OF RADIATION TYPES OF RADIATION IONIZING OR NON IONIZING • • • • • • • • • • heat light radio waves x-rays nuclear non -ionizing non - ionizing non - ionizing ionizing ionizing Nuclear Radiation One source of radiation is the nuclei of an unstable atom. These radioactive atoms become more stable when the nuclei ejects or emits subatomic particles and/or high-energy photons (gamma rays). This Is the Way the Atom Probably Looks Atomic Structure Electron Nucleus Proton Neutron Atomic Number Atomic number (Z number) is the number of PROTONS in the nucleus of an atom. Atomic Mass Atomic Mass (A number), is the number of PROTONS plus the number of NEUTRONS in the nucleus of an atom. Mass and Charges of Basic Atomic Particles Mass Charge 1 amu +1 Neutron 1 amu 0 or neutral Electron 1/2000 amu -1 Proton ISOTOPE Atoms with the same atomic number, . but different atomic mass Carbon-12 (6P + 6N) Atomic Mass = 12 Carbon-13 (6P + 7N) Atomic Mass = 13 Carbon-14 (6P + 8N) Atomic Mass = 14 6 Protons 6 Protons 6 Protons 6 Neutrons 7 Neutrons 8 Neutrons IODINE ISOTOPE EXAMPLE Isotope Atomic Mass Atomic Number Number of Neutrons I 123 123 53 70 I 125 125 53 72 I 131 131 53 78 Discovery of Radiation Henri Becquerel 1896 Ernest Rutherford Wilhelm Roentgen 1895 Marie Curie-To describe the behavior of uranium and thorium she invented the word “radioactivity” --based on the Latin word for ray. RUTHERFORD’S EXPERIMENT Photographic Plate TYPES OF RADIATION Types of Radiation Mass Charge Stopped By Alpha 4 +2 Thin Sheet of Paper Gamma Ray No Mass No Charge Several Inches of Lead or Steel X Ray No Mass No Charge Several Inches of Lead or Steel Beta 1/2000 -1 Thin Aluminum 0 High Hydrogen Content Neutron 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum INDUSTRIAL USES OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS Power Plants Medical Farming Ranching Textile Auto Soda Can CASES OF HIGH OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO RADIATION Early Scientists Watch Dial Painters Nuclear Weapons Research Military Personnel Emergency/Medical Personnel COMMON PREFIXES Giga (G) = 1 billion Mega (M) = 1 million kilo (k) = 1 thousand milli (m) = 1 thousandth micro (u) = 1 millionth UNITS OF MEASUREMENT Curie A UNIT used to measure the activity of a radioactive source and equals 37,000,000,000 disintegration's per second. The SI UNIT is the _____Becquerel____ which is one nuclear transformation or one disintegration per second. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT Roentgen A measure of the ionization effect Gamma and X radiation have in AIR. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT REM A measure of the biological effect radiation has on man. REM stands for Roentgen Equivalent Man Half-Life The time required for the amount of radioactive material to decrease by one half. Original Material Material after one Half-Life Material after two Half-Lives HALF-LIVES OF VARIOUS ISOTOPES HalfIsotope Life Am 241 454 Years Cs 137 30 Years Ra 226 1602 Years I 131 8 Days Co 60 5.2 Years Detecting Radiation and the PHOTOGRAPHIC PROCESS FILM BADGES Radiation will expose film just as light will. The greater the dose of radiation the darker the film will become. THERMOLUMINESCENT DOSIMETER TLD’s use three chips that when exposed to radiation store the energy. When the chip is heated it gives off light proportional to the radiation absorbed. LANDAUER John Doe JAN 01, 1997 Z1 N 030000 T29 07469 0561420 T OPTICALLY STIMULATED LUMINESCENCE (OSL) DOSIMETER OSL’s use two thin Al2O3 strips which when exposed to radiation record Photons (X & d Rays) in the 5 keV / 40 MeV range & Beta Particles in the 150 keV / 10 MeV range. During analysis, the Al2O3 is stimulated with selected frequencies of laser light, which cause it to become luminescent in proportion to the amount of radiation exposure received. A third component, for the measurement of Neutrons, is also enclosed. This is a Neutrak 144 Allyl Diglycol carbonate solid state track detector. In this case measurement is made by chemical etching followed by track counting. Energies measured are between 100 keV / 30 MeV. JOHN DOE TRAINING luxel LANDAUER FRONT ® OPTICALLY STIMULATED LUMINESCENCE (OSL) DOSIMETER Dose Measurement Range Photon Beta Particle Neutron 1 mREM to 1000 REM 10 mREM to 1000 REM 20 mREM to 25 REM 01 - 01 - 99 0030000 T29 04839 Whole Body (chest) Accuracy 0554677A2 Shallow Dose = ±15% at the 95% confidence interval for photons above 20 keV and beta particles above 200 keV 3073719 Deep Dose = ±15% at the 95% confidence interval for photons above 20 keV BACK OPTICALLY STIMULATED LUMINESCENCE (OSL) DOSIMETER The OSL is the principle device used to measure radiation exposure personnel. John Doe The OSL will only measure what your body will receive and does not TRAINING “protect” from luxel LANDAUER ® radiation. A OSL will simply measure what you have been exposed to and will allow us to determine if you have received to much radiation. RADIATION MONITORING Radiation Quality is an indication of the type of radiation received Radiation Quality Type of Radiation Received P Gamma Only CPN Combination Gamma and Neutron NF Fast Neutron M Minimal (Less than 1.0 mR) MAXIMUM PERMISSIBLE EXPOSURES 5 REM per Year Lifetime Dose – ( Age - 18 ) * 5 REM Recommended exposure while pregnant 500 mREM Average exposure for Wireline Logging & Perforating Personnel 150 - 250 mREM per Quarter Detecting Radiation and the ENCLOSED GAS VOLUME PROCESS Voltage Source + - Incident Ionizing Radiation Anode + Inert Gas Electrical Current Measuring Device Cathode - Geiger-Mueller Counters An enclosed tube has an anode and a cathode and usually an inert gas inside the tube. The radiation enters the tube ionizing the gas thus creating a current flow. The amount of radiation is proportional to the current flow. Detecting Radiation and the SCINTILLATION CRYSTAL PROCESS Gamma Ray Preamp e- P e- High Voltage ee- e- e- Dynodes Photo-Cathode Optical Coupling Grease Scintillating Crystal Glass Vacuum Tube Photo-Multiplier Tube e- Electrons P Photons Detecting Radiation and the Direct-Read Pocket Dosimeter A + + DIRECT - READING POCKET DOSIMETER A. Charging Rod B. Metal Support for Fibers C. Movable Fine Metal Coated Quartz Fiber D. Transparent Scale + - B + C - LENS D Milliroentgens 0 50 100 150 200 LENS EYE PIECE VICTOREEN MODEL 493 Scale reads from 0 to 0.5 Switch positions are: • Off mR/h 0.2 • bat. • x100 • x10 • x1 0.1 0.3 B AT . 0.4 c/m 0 PHONE VICTOREEN 0.5 493 VICTOREEN Ludlum Model 2 LUDLUM MODEL 2 SURVEY METER Scale Reads from: 0 to 5 0 Switch Position Are: • OFF • BAT • X 10 •X 1 • X 0.1 1 2 3 mR/h ON F OFF S A U D O F F 4 5 BAT X 10 X1 HV X 0.1 LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS, INC. SWEETWATER,TEXAS MODEL 2 SURVEY METER EXPOSURE RATE VICTOREEN 493 mR/h 0.2 0.3 0.1 0.4 0 0.5 LUDLUM MODEL 2 2 1 0 3 4 5 What exposure rate is this meter reading? X 1 _______mREM/hour X 10 _______mREM/hour X 100_______mREM/hour What exposure rate is this meter reading? X 0.1 ______mREM/hour X 1.0 ______mREM/hour X 10 ______mREM/hour OCCUPATIONAL DOSE RATES _____ mREM/hour 100 mREM/year (General Public) 500 mREM/year (If Attended Awareness Training) 5 REM/year BACKGROUND RADIATION DOSE Source Radiation Received Radon Gas 200 mREM/year Daughter Products 28 mREM/year Food & Water 40 mREM/year Cosmic Rays 28 mREM/year Medical Radiation 53 mREM/year T.V. Consumer Products 7 mREM/year TOTAL 356 mREM/year RADIATION DOSES FROM OTHER SOURCES SOURCE EXPOSURE • • • • • • One Hour of Jet Flight at 37,000 Feet Chest X-Ray or Dental Exam Dose to Unborn Child Due to Background Pelvic Exam Lower GI Series Areas of High Background 2 mREM/hour 10 mREM/hour 200 mREM/hour 600 mREM/hour 700 mREM/hour Up to 5000 mREM/year Biological Effects Due to Exposure Can Be Divided Into Two Groups EARLY EFFECTS (ACUTE) Blood Count Changes Damage Vomiting Cancer Risk Nausea Life Span Death LATE EFFECTS (DELAYED) Genetic Increased Shortened Some Acute Effects of High Exposure Over a Short Period Are DOSE (1 week) EFFECT (30 days) • 30-150 REM Detectable changes in blood counts • 150-250 REM Nausea and vomiting within 24 hours • 250-350 REM Death may occur • 350 REM 50% will Die within 30 days • 350-600 REM Death will probably occur • over 600 REM 100% will die within 30 days Estimated Loss of Life Expectancy From Health Risks HEALTH RISK ESTIMATES OF DAYS OF LIFE EXPECTANCY LOST, AVERAGE Smoking 20 Cigarettes/Day 2370 (6.5 years) OVERWEIGHT (by 20 %) 435 (1.2 years) RISK CHART CONTINUED AUTO ACCIDENTS 200 DAYS ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION 130 DAYS RISK CHART CONTINUED HOME ACCIDENTS 95 DAYS DROWNINGS’ 41 DAYS RISK CHART CONTINUED SAFEST JOBS (SUCH AS ………………..) 30 DAYS NATURAL BACKGROUND RADIATION (Calculated) 8 DAYS RISK CHART CONTINUED 1 REM Occupational Radiation Dose Calculated (Industry Average Is 0.34 REM/year) 1 DAY 1 REM/year for 30 Years, Calculated 30 DAYS 5 REM/year for 30 years, Calculated 150 DAYS Everyday Items Containing Radioactive Materials Scale Found on Oil Field Pipe Brazil Nuts Smoke Detectors Lantern Mantles Some Ceramics Salt Substitutes ALARA PRINCIPLE ALARA stands for AS LOW AS REASONABLY ACHIEVABLE REDUCING YOUR EXPOSURE The three most important safety rules to remember while working with radiation are Time Distance Shielding The Effect of Time on Radiation Exposure EXPOSURE = DOSE RATE X TIME For Example: 495 mREM per hour 1 HOUR = 495 mREM 2 HOURS = 990 mREM 3 HOURS = 1485 mREM The Effect of Distance on Radiation Exposure The Equation for Calculating Radiation Exposure as a Function of Distance: I 1 x ( D1 ) 2 = I 2 x ( D 2 ) 2 OR I 2 = I 1x ( D 1 ) 2 (D2)2 SHIELDING GAMMA RAYS DEFINITION OF SHIELDING Using some material as a shield to reduce the radiation exposure. SHIELD SHIELDING MATERIALS ALPHA PAPER GAMMA BETA LEAD TIN NEUTRONS WATER SKIN STEEL THIN ALUMINUM WAX SEVERAL INCHES OF AIR GOLD DEPLETED URANIUM PARAFFIN