* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
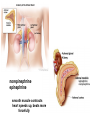
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
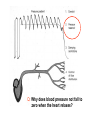
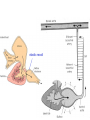
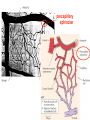
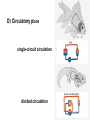
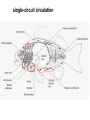
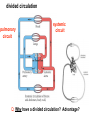
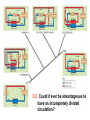
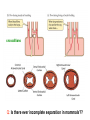
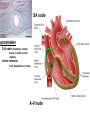
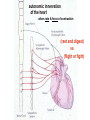
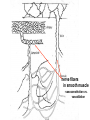
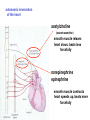
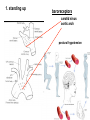
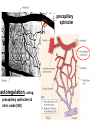
Circulation Circulatory Plans Regulation of heart & cardiac output (CO) Circulatory adjustments to stress, including Exam II -week from today -format as on Exam 1 Review Session – Thursday Oct 27, 5:00-6:00, Cushing 001 Q: Why does blood pressure not fall to zero when the heart relaxes? elastic recoil capillaries precapillary sphincter D) Circulatory plans single-circuit circulation divided circulation single-circuit circulation divided circulation pulmonary circuit systemic circuit Q: Why have a divided circulation? Advantage? QQ: Could it ever be advantageous to have an incompletely divided circulation? crocodilians Q: Is there ever incomplete separation in mammals?? E) Regulation of Heartbeat and Cardiac Output myogenic …not neurogenic SA node pacemaker S-A node (mammals; similar tissue in birds & most reptiles) sinus venosus (fish, amphibians, turtles) A-V node Myogenic! autonomic innervation of the heart -alters rate & force of contraction (rest and digest) vs (flight or fight) nerve fibers in smooth muscle -vasoconstriction vs. vasodilation autonomic innervation of the heart acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) smooth muscle relaxes heart slows, beats less forcefully norepinephrine epinephrine smooth muscle contracts heart speeds up, beats more forcefully norepinephrine epinephrine smooth muscle contracts heart speeds up, beats more forcefully autonomic nervous system allows adjustments in: 1) distribution of blood flow 2) cardiac output (CO) Q: what parameters determine CO? CO (ml/min) = HR (beats/min) X SV (ml/beat) heart rate stroke volume parasympathetic activation HR SV sympathetic activation HR SV Circulatory Adjustments to Stress homeostasis -an integrated compensatory response to a ‘challenge’, that in turn helps to maintain a balance In some physiological parameter exercise… sensory receptors à brain à effectors (neural/endocrine) 1. standing up baroreceptors carotid sinus aortic arch postural hypotension vasomotor center increase HR vasoconstriction in large arteries peripheral venoconstriction below heart 2. exercise Q: Could the concentration of O2 in the blood be increased? HR during exercise capillaries in skeletal muscle vasodilation of arterioles supplying muscle precapillary sphincter precapillary sphincter autoregulation, using precapillary sphincters & nitric oxide (NO)