* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Body Systems Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
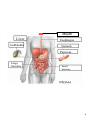
Human Body Systems Review 1.The purpose of the 11 organ systems is for the human body to maintain Homeostasis. What is homeostasis? The bodies maintenance of a stable internal environment 1 E. Sends and receives electrical signals 1. Nervous system* A. Absorbs oxygen 2. Respiratory system* 3. Excretory system G. Gets rid of waste 4. Muscular system* B. Moves bones 5. Endocrine system F. Regulates body function 6. Immune system H. Body's defense against illness 7. Reproductive system I. Produces reproductive cells 8. Cardiovascular system* D. Pumps blood 9. Digestive system* C. Breaks down food 10. Skeletal system* J. Provides a frame and support 11. Integumentary system K. Protects underlying tissues 2 Name the 8 organs that make up the digestive system and describe their function. Mouth To chew and grind up food. It produces saliva Esophagus Pipe connecting the mouth to the stomach Stomach Secretes a strong acid to break down food. Pancreas Produces the hormone insulin to regulate blood sugar levels Liver Produces bile, which breaks down fats in food. Gallbladder Pouchlike organ that stores bile for future use. Small Intestine Absorbs nutrients from food into the bloodstream Large Intestine Removes water from food and gets waste ready for excretion 3 3.What are the digestive organs that make up the digestive track? (in order) Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine 4 Mouth Liver Gallbladder Esophagus Stomach Pancreas Large Intestine Small Intestine 5 4. The nervous system controls the 5 senses which are: Sight, Touch, Taste, Smell, Hearing 5. The nervous system is made up of two systems. Central Nervous System ______________________________ (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System ________________________________ (PNS) 6 6. What 2 organs make up the CNS? Brain Spinal Cord 7. What is the overall function of the CNS? Control Center 8. What makes up the PNS? Nerves 9. What is the overall function of the PNS? Carries Information 7 10. What are the three parts of the human brain and what do they control? Cerebrum Memory, Problem solving, Thinking & Feeling. It also controls movement. Brain Stem Automatic functions such as Breathing, Digestion, Heart rate and Blood pressure. Cerebellum Coordination and Balance. 8 11. What are the eight organs (in order) that make up the respiratory system and what are their functions? Nose Entry and exit point for air PharynxPassage way for both air and food (back of throat) Epiglottis Skin flap that covers the trachea when we swallow Larynx "Voicebox" Helps you speak using vocal chords Trachea"Windpipe" Connects your pharynx to your lungs Bronchial TubesGive oxygen to the blood Lungs 2 large organs in the chest that hold oxygen Diaphragm Muscles that cause you to breath 9 Epiglotis Bronchial Tubes 10 12. What is the major muscle of the circulatory system? Heart 13. How many chambers does the human heart have? Four 14. Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle 11 15. What are the three types of blood vessels and what are their functions? Arteries • ___________ Carry blood ______________ the heart Away and to the major organs of the body. Veins • __________ Carry blood _____________ Towards the heart, away from the major organs of the body. Capillaries Small blood vessels where • _______________ Gas exchange ____________________ occurs. 12 16. What are the three types of blood cells and what are their functions? __________________ cells contain hemoglobin, Red Blood Cells an ironrich protein that carries oxygen. White Blood Cells ___________________ cells function in the immune system Platelets ___________________help in blood clotting 13 17.) Pretend you are a red blood cell. Describe the journey you would go on during your lifetime • I am made in the bone marrow of an animals body. • I am then sent to the right atrium and then flow down to the right ventricle. • I then travel to the lungs to pick up oxygen before I make my long trip around the body. • The lungs send me back to the heart I then enter the left atrium which sends me down to the left ventricle so it can pump me down through the arteries to the organs and cells that need oxygen. • Once I reach the cappilaries I perform gas exchange by giving up the oxygen I have been carrying. • Now that I don't have any more oxygen I hitch a ride up the veins, back to the lungs so I can grab some more. • I then repeat my journey until it is my time to die. 14 19. What are 7 reasons why bones are so important? 1. Structure 2. Support 3. Protection 4. Make Red Blood Cells 5. Make White Blood Cells 6. Make Platelets 7. Store Minerals 20. How many bones do we have in our adult bodies? 206 21. How many bones doe we have when we are born? 300 15 Cranium Maxilla Vertebrate Mandible Clavicle Scapula Sternum Humerus Ribs Pelvis Coccyx Ulna Radius Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Patella Fibula Tibia Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges 16 Attachments Jeopardy bubbled.ppt