* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download college physics
Survey
Document related concepts
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
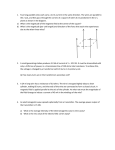
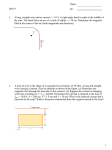
GENERAL PHYSICS II PRACTICE PROBLEMS ELECTRIC FORCES AD THE ELECTRIC FIELD 1. A small dust practical carries a net charge of 2.3 pC. How many electrons were removed to create this net charge? 2. (A) Calculate the distance between the two points whose coordinates are (0.01cm, 0.02cm) and (-0.21cm, 0.31cm). (B) In what direction (angle) is the first point from the second point?\ 3. What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force between a Helium nucleus and an Oxygen nucleus if they are 1mm apart? Is the force attractive or repulsive? 4. (A) A charge of +2 µC is located on the y axis at +5 cm and a charge of -2 µC is located on the y axis at -4 cm. What is the net electric field at +3 cm on the x-axis? (B) If a charged particle of mass 3.5 mg and electric charge of -2.1 µC is placed at +3 cm on the x-axis what initial force and acceleration will it experience ? 5. A pendulum is comprised of a 2.1 m long massless string with a 1.0 g mass at its free end. This mass carries a net charge of +2.3 nC. The pendulum hangs in a uniform electric field of strength 1500 N/C oriented horizontally. (A) what is the net force on the charged pendulum mass? (B) When in equilibrium, what angle does the pendulum string make with the vertical? 6. A proton is released from rest in a uniform electric field of strength 5× 104 N/C. (A) What is the magnitude of the force on the proton? (B) What is the proton’s acceleration? (C) What is the proton's speed after it has moved 0.5 cm? 7. Calculate the net vector force acting on charge 2, q2, shown in the diagram. Show all work, including the appropriate (and complete) vector diagram of the forces on q2. 8. A ball of radius R = 5.0 cm is filled with an electric charge of uniform charge density ρ = -3.2 pC/m3? A. What is the net enclosed charge within a radius of 3.0 cm from the center of this ball? B. What is the net electric flux through a sphere of radius 3.0 cm from the center of this ball? C. What is the electric field at a distance of 3.0 cm from the center of this ball? 3 [The surface area of a sphere of radius r is A = 4π r 2 and its volume is Vol = 43 π r .] 9. Complete the following statements with the best word or phrase. . A. Electric field lines do not B. Electric field lines are perpendicular to C. The net electric charge on a conductor lies D. The electric field is defined as E. The electric field inside a conductor in electrostatic equilibrium is F. The force between two positively charged spheres is G. Only together. H. The direction of force on an electron in an electric field is the direction of the electric field. I. The electric field at a point in space is a J. The principle that the electric fields from multiple sources may be added together is known as the principle of . . . . . . type charge is transferred when rubbing two different materials quantity. 10. Calculate the magnitude of the force between an electron and a proton separated by a distance of 5×10-11m. Specify whether this force is attractive or repulsive. 11. If a conducting plate 2.2 m by 2.2 m is given a net electric charge of +6nC, what is the magnitude of the electric field 1.5 cm from the surface of the plate near its center? 12. A 4 µC and a -3 µC charge are located within a sphere of radius 10 cm. An additional charge of -3 µC is located near but outside the sphere. What is the net electric flux through the sphere? 13. An alpha particle, charge +2e and mass 4mp, is suspended in mid-air at rest in a uniform electric field directed vertically upward. What is the strength , E, of this electric field? ( mp = 1.67 × 10-27 kg ) ELECTRICAL EERGY AD CAPACITACE 1. What is the potential energy of a 5 µC charge placed at an electric potential of 1000 V? 2. Calculate the electric potential 15 cm from a metal sphere whose radius is 5 cm and has a net charge of -2.5 µC. 3. A 10 µC charge is placed at x = 0 and a 5 µC charge is placed at x = 3cm. These two charges are fixed in place. If a charged particle with charge 2 µC and mass 3 mg is placed at x = 6 cm, what will its speed be after it has moved 2 cm? Redo this problem for a similar particle with a charge of -2 µC. 4. (A) Calculate the capacitance of two circular conducting plates each of radius 10 cm held parallel to each other and 3 mm apart. (B) What would the capacitance be if the area between the plates is filled with a material of dielectric constant 3.4? 5. A 2.5 µf capacitor is connected to a 150 V power supply. What charge is stored in this capacitor? 6. A 5cm radius conducting sphere with a net charge of 10 mC is next to a 10 cm radius conducting sphere of net charge 5 mC. The centers of the spheres are 20 cm apart. If the two spheres are momentarily connected by a conducting wire, what force will exist between them after the wire is removed? [Hint: How many conducting surfaces are there while the spheres are connected?] 7. Refer to the diagram below to answer the following questions. A. Calculate the net electric potential at point P, Vp, due to the point charges q1 and q2. B. When a charged particle of charge q = -6.2 µC amd mass m = .01g is placed at point P, what net potential energy will it have? 8. Two square pieces of aluminum, 6.0 cm on a side, are placed parallel to each other and separated by 8.0 mm. These two plates are then connected to the terminals of a 1500V power supply. A. Calculate the capacitance of the two plates. B. How much charge is on the positive plate? C. What is the strength of the electric field between the plates? Use the diagram on the right to draw an approximate sketch of the electric field. D. How much energy do the plates store when fully charged? E. If a 2.0×10-4 kg particle of charge +0.25 pC is released from rest at the positive plate, what speed will it have when arriving at the negative plate? 9. Given the following circuit, determine the equivalent capacitor and the charge stored, voltage, and stored energy in each of the original circuit’s capacitors. Place your answers in the table provided. Show all work. CAPACITOR C1 C2 C3 STORED CHARGE VOLTAGE STORED EERGY 10. Charge q1 = -4.5 nC is located and fixed on the x-axis at x = -5cm. Charge q2 = +3.7 nC is located and fixed on the x-axis at +2 cm. Points A and B are also on the x-axis at 8 cm and 12 cm respectively. See diagram. A. B. C. D. What is the net electric field at point A due to electric charges q1 and q2? If a particle of mass m = 5.2 grams and electric charge q0 = +2.6 nC is placed at point A, what will its initial acceleration be when released from rest? As the particle described in part B moves to point B, what electric potential difference, ∆V = VB - VA, does it experience? What is the particle’s velocity at point B? Assume it was released from rest at point A and has the mass and charge stated in part B. CURRET AD RESISTACE DIRECT-CURRET CIRCUITS 1. A 12 gauge aluminum wire has a diameter of 2.0 mm. If the wire carries a 15 A current, find the drift velocity of the electrons in copper. The electron density of aluminum is 6.0 × 1028 electrons per m3. 2. A certain copper wire is 1.0 m long, 0.5mm in radius. What is the resistance of the wire? 3. If the gold wire has a resistance of 1.52Ω is connected to a 24 V power supply, what current will flow through the wire and what power will be supplied? 4. A certain wire of cross-sectional area A = 7.85 × 10-7 m2 and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2.25 A. The mobile electron density of the wire material is 5.95 × 1028 electrons/m3 and the voltage drop along the length of the wire is 0.001 V. (A) What is the electron drift velocity, vd? (B) Calculate the current density, J. (C) What is the electric field strength, E, inside the wire? (D) Calculate the conductivity, σ, of the wire. 5. A certain portable television was found to have been left on. It was powered by six brand new DCells in series making a 9 volt battery. Each D-Cell has a rating of 1 amp-hour and the initial power supply is 4.5 W. (A) What current did the battery supply? (B) How long was the television on? (C) What total charge moved through this circuit? (D) What total energy did the battery supply? 6. A gold wire 2mm in diameter and 100 m long is heated to 300 oC. What is its resistance at this temperature? 7. If the gold wire in problem 3 is connected to a 24 V power supply, what current will flow through the wire and what power will be supplied? 8. A battery with an emf of 12 V is connected to an external resistor whose resistance is 100 Ohms. If the current through the external resistor is 0.11 A, what is the internal resistance of the battery? 9. If a 3.0 V battery has a 0.5 Ah rating. (a) What is the average current it can maintain for 2 hours? (b) What is the total energy the battery can supply? 10. Three resistors are connected in series. Their values are 2 Ohms, 4 Ohms, and 5 Ohms. What is the potential drop across the 4 Ohms resistor when the group is connected to a 12 V battery? 11. Three resistors are connected in parallel. Their values are 2 Ohms, 4 Ohms, and 5 Ohms. What is the potential drop across the 4 Ohms resistor when the group is connected to a 12 V battery? 12. A capacitor of 5 µf is connected in parallel with a 1.25 MΩ resistor and an 18 V battery. After charging the capacitor a switch is opened disconnecting the battery. (b) How long does it take for the capacitor to loose 80% of its initial charge? (c) What is the power loss through the resistor at this time? (d) How much energy remains in the capacitor at this time? MAGETISM 1. Calculate the net force on a dust particle moving in Earth’s magnetic field. The magnetic field is horizontal and directed southward with a magnitude of 0.5 G. The dust particle has a mass of 0.05 grams, a charge of -4e and is traveling horizontally eastward at 15 m/s. 2. What is the force on a 50m length of wire carrying 15 A in a vertically upward magnetic field of 2 T? 3. A coil is made of 15 loops of wire with a radius of 30 cm. If it carries a current of 5 A, what is its magnetic dipole moment? Add the magnetic dipole moment to the diagram. 4. Wire 1 lies along the y-axis with 2.5 A of current flowing in the +y direction. Wire 2 lies along the x-axis with 3.75 A of current flowing in the -x direction. What is the net magnetic field due to these currents at the point P located at coordinates (5 cm, 6 cm)? 5. Calculate the magnetic field inside a 40 cm long solenoid if the solenoid current is 3.0 A and the there are 300 turns of wire per cm. Indicate the direction of the magnetic field also. 6. In some region of space a uniform magnetic field of 3.5 T points to the right. A microsphere of charge -4nC and mass 1.0 mg moves in this field with a speed of 1.5 × 106 m/s initially directed upward and perpendicular to the field. Draw this magnetic field and the path the microsphere will follow. What is the radius of this path? 7. Suppose the coil (loop) of problem 3 is placed in the magnetic field of problem 5. The plane of the coil makes a 35 degree angle with the magnetic field. Calculate the magnitude of the torque acting on the loop and specify how the loop will respond to this torque. 8. A long wire carrying 7.0 A in the +y direction lies along the y-axis. Next to the wire, in the x-y plane is a square loop whose sides are 5 cm long and is made with 15 turns of wire. The left edge of the loop is 7 cm from the long wire. Current in the loop is 1A going around the loop clockwise. Compute the net force on the loop. I 1= 7A I 2= A 1 9. Shown below is a diagram of a device called a velocity selector, in which particles of a specific velocity pass through undeflected while those with greater or lesser velocities are deflected/accelerated either upwards or downwards. An electric field of 5000 V/m is directed perpendicular to a magnetic field of 0.75 T. Particles of what speed will pass through this velocity selector undeflected? IDUCED VOLTAGES AD IDUCTACE 1. A uniform magnetic field of 15 G is oriented so that it makes a 20o angle with the plane of a square loop of wire of area 5.00 cm2. What is the magnetic flux through this loop? 2. A rectangular loop is initially held with one edge parallel to a long conducting wire carrying a 12 A current. The loop has an area of 4.00 cm2 with one edge 3 cm from the wire. What is the induced emf in the loop when it is pulled at .05 m/s parallel to the wire as shown? 3. The bar magnet in the diagram is suddenly pulled upward away from the loop. Draw an arrow along the front edge of the loop to indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop. 4. The solenoid has a length of 15 cm and is comprised of 7500 turns of wire. The current to the solenoid is changing steadily from 0 A to 12 A in 15 seconds. The coil inside the solenoid has a radius of 4 cm and is comprised of 250 turns of wire with a net resistance of 3 Ω. The axis of the coil is offset 25o to the axis of the solenoid. A. What is the induced emf in the coil? B. What is the induced current in the coil? C. What is the torque on the coil when the solenoid current is 6A? 5. An inductor is 2 cm long, has a radius of .5 cm and is comprised of 75 turns of wire. What is its inductance? 6. The inductor in problem 5 is connected in series to a 0.5 Ω and a battery whose emf is 24 V. What current flows in this circuit 0.1 seconds after the switch is closed? 7. There are two conducting, parallel rods spaced 10 cm apart. The bottom ends of the rods are connected by a wire with a 2 Ω resistor. A uniform and horizontal magnetic field of 2.25 T is oriented perpendicularly to the plane of the two rods. A small conducting bar of mass 15g is placed across the two vertical rods. This bar is horizontal and slides against the vertical rods without friction. When released the bar falls and reaches a constant speed. What is that speed? 8. A conducting loop is pulled away from a current, carrying wire. Show in which direction the induced current will flow around the loop.