* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Positioning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
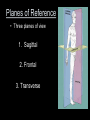
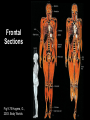
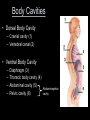
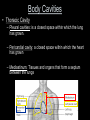
Anatomy and Physiology 120 Body Organization & Terminology Lab Michelle Giffin What you need to Know! 1. Levels of organization 2. 11 organ systems 3. General functions of each system 4. Which system each organ belongs to 5. Which cavity each organ is found in Anatomical Positioning Terms of Direction ►Superior: structure higher than another ►Inferior: _______________________ Anterior: _______________________ Posterior: Pertaining to the back Medial: _______________________ Lateral: Pertaining to the side o Proximal: Closer to the midline or origin o Distal:__________________________ • Superficial: Near the surface • Deep: __________________ 3 3 3) Proximal 2 1 1 1) Distal Planes of Reference • Three planes of view 1. Sagittal 2. Frontal 3. Transverse Sagittal Sections Fig 9.76 Hagens, G., 2003. Body Worlds Frontal Sections Fig 9.75 Hagens, G., 2003. Body Worlds Transverse Sections Fig 9.74 Hagens, G., 2003. Body Worlds Body Cavities • Dorsal Body Cavity – Cranial cavity (1) – Vertebral canal (2) • Ventral Body Cavity – – – – Diaphragm (3) Thoracic body cavity (4) Abdominal cavity (5) Pelvic cavity (6) Abdominopelvic cavity Body Cavities • Thoracic Cavity – Pleural cavities: is a closed space within which the lung has grown. – Pericardial cavity: a closed space within which the heart has grown – Mediastinum: Tissues and organs that form a septum between the lungs Body Membranes Serous membranes • Visceral & Parietal Pleura (lung) • Visceral & Parietal Pericardium (heart) • Visceral & Parietal Peritoneum (abdominal cavity) Note: Visceral – inner layer Parietal – outer layer Heart or Lung Minor Cavities • Oral – Mouth • Orbital – Eye • Nasal – Nose • Middle Ear – Middle Ear Levels of Organization Atom Molecule Macromolecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism 11 Organ Systems 1) Integumentary System *Protects body from damage & body's 1st line of defense *Skin, hair, nails, & sweat glands 2) Skeletal System *Supports the body of an animal & protection *Bones 3) Muscular System *Movement *Skeletal muscles Diaphragm 4) Nervous System * To communicate information *Brain, spinal cord, & nerves 5) Endocrine System *hormone releasing *Thyroid, pituitary, & ovaries / testis 6) Cardiovascular System *Move nutrients, gases & waist *Heart, Aorta, arteries, & veins 7) Lymphatic System * Carries lymph throughout the body & immunity *Lymph nodes, thymus, spleen 8) Digestive System * Breakdown of chemicals in the body so it can be absorbed * Mouth, tongue teeth, salivary gland, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small & large intestine, appendix, rectum 9) Respiratory System * Allow gas exchange *Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs 10) Urinary system * Removal of nitrogenous waist *Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra 11) Reproductive System *Male – scrotum, testes, penis, urethra *Female – Ovaries, uterus, vagina, uterine tubes I Should Not Marry Every Looser Under Dark Cold Rail Roads