* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the handout - Woodbridge High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Test anxiety wikipedia , lookup
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Depression in childhood and adolescence wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
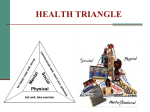
Promoting your Student’s Wellness Lauren Stallings Wellness Coordinator Why is mental health important? Research shows that adding a mental health component to education programs could enhance health behavior, reduce mental health symptoms, and improve grades. Childhood is a critical period for mental, social, and emotional wellbeing and development. 1 in 5 children aged 5 - 16 suffer from a diagnosable mental health disorder that is around 4-5 children in every class In the course of the school year, children with mental health problems may miss as many as 18 to 22 days What is really going on? Approximately 20% of students develop a diagnosable mental health disorder before they reach 18 years of age. 1 in 5 students Approx. 6,400 students in IUSD The Adolescent Brain The Developing Adolescent Brain - Under Construction Physical change ● ● Emotional/Intellectual change Social Change Increased awareness of body image as you grow from a child into an adult Expected healthy weight and height gain ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Brain development o The parts of the brain responsible for more "topdown" control, controlling impulses, and planning ahead—the hallmarks of adult behavior—are among the last to mature. Increased impulsivity Difficulty making decisions with consequences in mind High risk behaviors Hormonal Changes More intense experiencing of emotions New feelings you have never felt before Confusion over what to do with the new feelings ● ● ● ● Increased response to social events Competing social influences between parents and peers Change in social values Increased societal expectations ● Stress and Anxiety Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress. In general, it can help us cope. But when anxiety becomes an excessive, irrational dread of everyday situations, it has become a disabling condition. OCD, PTSD, GAD, Social/ specific phobia About 3 percent of children ages 3-12 have an anxiety disorder. Increases up to 8% in adolescence Am I stressed or having anxiety? Stress Comes from the pressures we feel in life, as we are pushed by school or any other task that puts undue pressure on our minds and body. The way our bodies and minds react to something which upsets our normal balance in life Can come from any situation or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, nervous, or even anxious. What is stressful to one person is not necessarily stressful to another. Some level of stress is good Am I stressed or having anxiety? Anxiety Stress that continues after that stressor is gone. A feeling of apprehension or fear and is almost always accompanied by feelings of impending doom. The source of this uneasiness is not always known or recognized, which can add to the distress you feel and trigger more distress. The physical symptoms of anxiety are caused by the brain sending messages to parts of the body to prepare for the "fight or flight" response. The heart, lungs and other parts of the body work faster. The brain also releases stress hormones, including adrenaline. Disrupts normal functioning What Can I Do? Stress • Time Management • Taking breaks • Setting boundaries (saying no to self and others) • Self-care • Relaxation • Positive self-talk & affirmations • Physical activity • Mindfulness & meditation Anxiety • When Anxiety impacts your functioning in multiple areas of your life it may be important for you to seek professional help. • Academics, Socially, Work • Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) • Short-term, solution focused • Mindfulness/ relaxation training It isn’t just Sadness….. • Depression isn’t just being sad or moody—it’s a serious problem that impacts every aspect of a teen’s life. • 2.3% of children suffer from Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) • Only 30% of individuals suffering seek help • Childhood depression can lead to drug and alcohol abuse, self-loathing and self-mutilation, high risk behaviors, poor relationships and even suicide. Am I sad or depressed? Sadness Depression • Something we all experience; it’s a normal, human emotion. • Depression can propel someone into suicidal ideation. • Sadness is not an every - moment of - every - day thing like depression is. • Remains constant for weeks and months at a time. • Can impact sleep, appetite, energy, thoughts, physical health, relationships, etc. • Doesn't seem to go away no matter what you try, often leads to isolation, feeling misunderstood. • Often requires professional help to find relief • Subsides after a period of time with use of supports and coping skills, not constant. What Can I Do? Sadness • • • • • Talk to a trusted support person Express emotion in healthy/ constructive way • art, music, crying, dancing, journaling, writing, coloring, exercise, be silly • Allow yourself to feel so the emotion can pass Engage in positive, self-care activities Remind yourself of your strength and other times you have come through difficult situations. Use affirmations that you can believe. Depression • Tell someone • Seek professional help including therapy and medication management • Create a schedule and make reasonable attempts to follow it • There is hope and treatment for depression The Truth About Suicide Suicide is the SECOND leading cause of death for ages 10-24. Almost 40% of kids attempting suicide make their first try in middle or even elementary school About 1 in 9 children have attempted suicide before their high school graduation, but learning that they’re making plans as early as elementary school Suicide affects young people from all ages, races, genders, and socioeconomic groups (CDC 2013; Family Matters, 2013) Red Flags to Watch for: • Four out of Five (80%) students who attempt suicide have given clear warning signs • Warning signs: • • Talking about wanting to die • Withdrawal/ decrease participation from social activities • Giving away favorite belongings • Verbal hints about “if something happens to me…..” Always err on the side of caution, take all warning signs seriously There is Hope At some point in all of our lives, we may meet criteria for Anxiety or a Major Depressive Episode Anxiety and Depression are not necessarily life long disorders With treatment and intervention, an individual can lead a productive life without reoccurring symptoms Some individuals need support to get better. Let your student know they are not alone Impact of mental health stigma… 40% of individuals suffering from mental health issues don’t seek support services and the #1 reason sited is fear of judgment. Stigma leads to Reluctance to recognize a problem Reluctance to seek treatment Reluctance to ask about services available Ways to Reduce Stigma Create positive school climate A collaborative commitment between school staff, students, parents, and the community to create a culture of acceptance, support, and knowledge. Implementing a holistic approach to each student Educational Social Emotional All research finds a positive correlation between better school climate and increased student learning and achievement (Jones et al., 2008) Domains of Wellness What is Wellness? Wellness is an active process of becoming aware of and making choices toward a healthy and fulfilling life. Wellness is more than being free from illness, it is a dynamic process of change and growth. Wellness is the compete integration of body, mind, and spirit - the realization that everything we do, think, feel, and believe has an effect on our state of well-being- Greg Anderson Intellectual Wellness Encourages us to engage in creative and mentally-stimulating activities. Activities should expand your knowledge and skills while allowing you to share your knowledge and skills with others. Can be developed through academics, cultural involvement, community involvement and personal hobbies Encourages learning. It is important to explore new ideas and understandings in order to become more mindful and better-rounded. Stimulates curiosity. Curiosity motivates you to try new things and develop an understanding of how you see the relationship between yourself, others and the environment. Social Wellness Refers to the relationships we have and how we interact with others. Our relationships can offer support during difficult times and help build self-esteem. Involves building healthy, nurturing and supportive relationships as well as fostering a genuine connection with those around you. Conscious actions are important in learning how to balance your social life with your academic lives. Includes balancing the unique needs of romantic relationships with other parts of your life. Enables you to create boundaries that encourage communication, trust and conflict management. Having good social wellness is critical to building emotional resilience. Physical Wellness Promotes proper care of our bodies for optimal health and functioning. Encourages the balance of physical activity, nutrition and mental wellbeing to keep your body in top condition. Obtaining an optimal level of physical wellness allows you to nurture personal responsibility for your own health. As you become conscious of your physical health, you are able to identify elements you are successful in as well as elements you would like to improve. Emotional Wellness Emotional wellness inspires self-care, relaxation, stress reduction and the development of inner strength. It is important to be attentive to both positive and negative feelings and be able to understand how to handle these emotions. Emotional wellness also includes the ability to learn and grow from experiences. Emotional well-being encourages autonomy and proper decision making skills. It is an important part of overall wellness. Finding balance is key Try not to over schedule Help your child see the bigger picture Acknowledge limitations Everyone’s “wellness” will look different Campus Supports References