* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy ATP: the Cell`s Rechargeable Battery
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
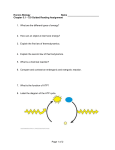
Energy Energy •The capacity to do work KEY WORDS: Energy Enzyme Substrate Product Active Site Activation energy Catalyst ATP/ ADP Energy •The capacity to do work •Move matter ATP: the Cell’s Rechargeable Battery • ATP energy ADP charged battery dead battery • This provides energy for cells Figure 6.8 The structure and hydrolysis of ATP Figure 6.10 The ATP cycle 1 Activation Energy ATP stores energy in the form of 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Activation Energy mechanical energy heat complex carbohydrates chemical bond energy amino acids Net Energy Released Enzymes Enzymes •Proteins that speed up chemical reactions (catalysts) •Lower activation energy for a reaction Key Points: •Catalyze reactions •Don’t change reactions •Enzymes are not changed by reaction •Each enzyme catalyzes a specific chemical reaction Enzyme reactions can be simplified as: E+S ES Enzymes and Shape E +P • S = Substrates (reactants) enter reaction. • P = Product (what you get at the end) • E = Enzymes catalyze reaction Active Site sucrase sucrose + H2O glucose + fructose 2 Figure 6.15 The catalytic cycle of an enzyme 4 Things that Affect Enzyme Activity 1. Substrate concentration 2. Enzyme concentration 3. pH 4. Temperature Which of the following will lower the activation energy of a reaction in a cell? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. lowering the temperature lowering the pressure using an enzyme changing the amount of the reactants supplying ATP Change shape of enzyme (Protein denatured) An enzyme accelerates a metabolic reaction by a) Altering the overall free energy change for the reaction b) Making an endergonic reaction occur spontaneously c) Lowering the activation energy d) Pushing the reaction away from equilibrium e) Making the substrate molecule more stable Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because a) They are able to maintain a cooler internal temperature b) High temperature facilitates active metabolism w/o need of catalysis c) Enzymes have high optimal temperatures d) Enzymes are insensitive to temperature 3