* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Components of the Spheres
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
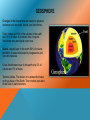
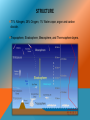
GEOSPHERE Geo means “Ground” so basically the ground is the location Includes the Earth's interior, rocks and minerals, landforms and the processes that shape the Earth's surface. Interactions of the spheres : GEOSPHERE Changes in the Geosphere are based on physical evidence such as rocks, fossils, and land forms Core- makes up 16% of the volume of the earth and 31% of mass. It is divided into 2 regions : Solid inner core and liquid outer core. Mantle- largest layer in the earth 82% of volume and 68% of mass dominated by magnesium and iron-rich minerals Crust- the thinnest layer in the earth only 2% of volume and 1% of mass. Tectonic plates- The dozen or so plates that make up the surface of the Earth. Their motion is studied in the field of plate tectonics. HYDROSPHERE Liquid water component of the Earth Covers about 70% of Earth 3 % of total water is fresh water, and only 1% of this is attainable The hydrosphere is always in motion http://earth.rice.edu/mtpe/hydro/hydrosphere/hydrosphere_what.html HYDROSPHERE Salinity and temperature of the water affect motion Warm/fresh water = less dense, rises to top Cold/salt water = more dense, sinks down Acts as reservoir for chemicals and gases Limits how fast climates can change Distributes heat to entire globe CRYOSPHERE The Solid Water or Ice part of the earth Antarctica The Arctic Circle The composition of the cryosphere is water. Just. Water. Glaciers form sedimentary rock style, except, you know, ice. Glaciers are melting due to global warming and this causes flooding, icebergs, and loss of habitat. Permafrost is a permanently frozen layer below the topsoil Global Warming causes permafrost to melt which causes the freshwater permafrost supports to sink below the surface MID-PRESENTATION QUESTIONS 1. What is the difference between tectonic plates and plate tectonics? 2. How does the Hydrosphere affect climate? 3. How are Glaciers formed? INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERE Gaseous layer of the Earth, formed 4 billion years ago. Started off with water vapor, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrochloric acid, methane, ammonia, nitrogen, and sulfur gases. The lack of free oxygen caused the atmosphere to reduce. Water vapor eventually rained down forming bodies of water. The bodies of water became home to the first organisms which began releasing oxygen, thus oxidizing the atmosphere. STRUCTURE 71% Nitrogen, 28% Oxygen, 1% Water vapor, argon and carbon dioxide. Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, and Thermosphere layers. THE LAYERS Troposphere- the lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere and site of all weather on Earth. Stratosphere- the layer of the earth's atmosphere above the troposphere, extending to about 32 miles (50 km) above the earth's surface (the lower boundary of the mesosphere). Mesosphere- the region of the earth's atmosphere above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere, between about 30 and 50 miles (50 and 80 km) in altitude Thermosphere- the region of the atmosphere above the mesosphere and below the height at which the atmosphere ceases to have the properties of a continuous medium. The thermosphere is characterized throughout by an increase in temperature with height. BIOSPHERE Everything that contains life Includes atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, etc. Erosion and deforestation impact everything within the biosphere greatly. Basically, people are messing up the part of the world that has life BIOMES The biosphere consists of several biomes, each with different climates and abiotic/biotic factors Desert Deciduous Forest Rainforest Grassland Tundra Taiga Savanna Salt Water Fresh Water POST-PRESENTATION QUESTIONS 1. What are the layers of the atmosphere? 2. What two issues affect the biosphere greatly? 3. Name at least four biomes.