* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Biomedical Therapies
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Dyadic developmental psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adventure therapy wikipedia , lookup
Emotionally focused therapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Equine-assisted therapy wikipedia , lookup
Relationship counseling wikipedia , lookup
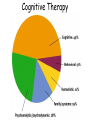
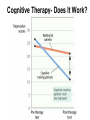
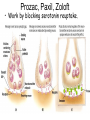
Psychological Therapies Psychotherapy • An emotionally charged, confiding interaction between a trained therapist and someone suffering from psychological difficulties. Eclectic Approach • The most popular form of therapyit is basically a smorgasbord where the therapist combines techniques from different schools of psychology. Psychoanalysis • Sigmund Freud's therapeutic technique • The use of free association, hypnosis, and dream interpretation to gain insight into the client’s unconscious. Psychoanalytic Methods • Psychotherapists use their techniques to overcome resistance (blocking from consciousness of anxiety-laden emotions) by the client. • The psychoanalyst wants you to become aware of the resistance and together interpret its underlying meaning (latent content). Transference • In psychoanalysis, the patient’s transfer to the analyst of emotions linked with other relationships Humanistic Therapy The aim is to help people reach their potential for self-fulfillment (self-actualization) • Focuses on the present and future (not the past) • Focuses on conscious thoughts (not unconscious ones) • Believes in taking responsibility for your actions instead of blaming childhood anxieties • Promotes growth instead of curing illness (those in therapy are “clients” rather than “patients”) Most widely used Humanistic technique is: Client (Person) Centered Therapy • Developed by Carl Rogers • Therapist should use genuineness, acceptance and empathy to show unconditional positive regard towards their clients Active Listening • Central to Roger’s client-centered therapy • Empathetic listening where the listener echoes, restates and clarifies. Behavior Therapies • Therapy that applies learning principles to the elimination of unwanted behaviors •The behaviors are the problems - so we must change the behaviors Classical Conditioning Techniques Counterconditioning: • A behavioral therapy that conditions new responses to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors. Two Types: Systematic Desensitization Aversive Conditioning Systematic Desensitization • A type of counterconditioning that associates a pleasant relaxed state with gradually increasing anxietytriggering stimuli How would a psychoanalyst use systematic desensitization to reduce the fear of old women? Systematic Desensitization Progressive Relaxation Exposure Therapy Flooding Virtual Technology Exposure Therapy Aversive Conditioning • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state with an unwanted behavior • What are some ways you can change the behaviors of your friends with aversive conditioning? Aversive Conditioning Aversion therapy for alcoholics Operant Conditioning Token Economy: an operant conditioning procedure that rewards a desired behavior. A patient exchanges a token of some sort, earned for exhibiting the desired behavior, for various privileges or treats. Cognitive Therapies • A therapy that teaches people new, more adaptive (more constructive) ways of thinking and acting; based on the assumptions that thoughts intervene between events and our Is .300 a good or emotional reactions. bad batting average? Cognitive Therapy Cognitive Therapy Aaron Beck and his view of Depression • Noticed that depressed people were similar in the way they viewed the world. • Used cognitive therapy get people to take off the “dark sunglasses” in which they view their surroundings Cognitive Therapy- Does It Work? Family & Group Therapies treats the family or group as a system views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as influenced by or directed at other family members attempts to guide family members toward positive relationships and improved communication Evaluating Psychotherapies To whom do people turn for help for psychological difficulties? The Biomedical Therapies Therapies aimed at the altering the body chemistry Psychopharmacology • The study of the effects of drugs on mind and behavior Drugs and Hospitalization Emptying of Mental Hospitals Testing New Drugs • When a new drug is released there is always too much enthusiasm •Must use a double-blind procedure to combat placebo and experimental effects These experiments enable us to classify different types of drugs: Antipsychotic Drugs • Antipsychotic drugs are a class of medicines used to treat psychosis and other mental and emotional conditions These drugs are beginning to help schizophrenics with both positive and negative symptoms These drugs (i.e. Thorazine) often have powerful side effects Antianxiety Drugs • Includes drugs like Xanax, Valium and Librium • Like alcohol, they depress nervous system activity • Most widely abused drugs Do they really solve the problem? Antidepressant Drugs • Lift you up out of depression • Most increase the availability of the neurotransmitters: norepinephrine or serotonin (which elevate arousal and mood) Prozac, Paxil, Zoloft • Work by blocking serotonin reuptake. Biomedical Therapies Antidepressant prescriptions have soared! Biomedical Therapies Lithium Chemical (simple salt) that provides an effective drug therapy for the mood swings of bipolar (manic-depressive) disorders With continued use, emotional highs and lows typically level Suicide risk is one-sixth that of bipolar patients not taking lithium Electroconvulsive Therapy • Biomedical therapy for severely depressed patients in which brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient • Although controversial, it is the preferred treatment for depression that does not respond to drug therapy Psychosurgery • Surgery that removes or destroys brain tissue in an effort to change behavior Egas Moniz developed the lobotomy in the 1930s. Ice pick like instrument through the eye sockets cutting the links between the frontal lobes and the emotional control centers Lobotomy Mind-Body Interaction