* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of a Neuron
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
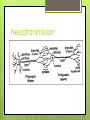
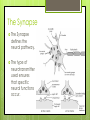
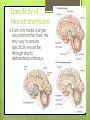
Structure of a Neuron Types of Neurons and their basic structures. The Neuron A Neuron is a specialized type of cell that carries messages throughout the nervous system. Message are transmitted through an electrochemical process called neurotransmission. Neurons have structures similar to other cells. They have a cell membrane They have a nucleus containing DNA And organelles such as Ribosomes and Mitochondria. Three basic types of Neurons Sensory Neurons carry signals from the sensory organs to the central nervous system along afferent nerve fibers. Inter Neurons carry signals from one neuron to another either within the central nervous system or from sensory to motor neurons. Motor Neurons carry signals from the Central Nervous System to the motor cells or muscles along efferent nerve fibers. Basic Structure of a Neuron Dendrites Axon Soma (cell body) Terminal Buttons Myelin Sheath (Schwann Cells) Image: Biological Neuron Schema. Wikimedia Commons. Nicolas.Rougier Parts of a Neuron Soma or Cell body - contains cytoplasm and the nucleus, which includes the chromosomes. Mitochondria in the cell body perform metabolism. Ribosomes synthesize proteins. Dendrites – receive input from previous neurons. Axon – Carries the electrical impulse (action potential) to the terminal buttons. Terminal Buttons – Contains vesicles that release chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) across the synaptic gap to other neurons. Image of real neurons Neurotransmission The Synapse The Synapse defines the neural pathway. The type of neurotransmitter used ensures that specific neural functions occur. Neurotransmitters Specificity of Neurotransmission If we only hade a single neurotransmitter then the only way to ensure specificity would be through strictly delineated pathways. Stimulus - Response A specific stimulus: Light Sound Pressure Chemical Yields a specific response: Color Pitch Texture Odor Neurotransmission The complexity of our nervous system allows us to not only experience the world around us, but contemplate it’s meaning even it’s very existence. “If our brains were simple enough for us to understand them, we'd be so simple that we couldn't.” Ian Stewart